No-waste utilization method of heavy metal-contained sludge
A technology of heavy metal sludge and solution, applied in the direction of process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of sludge reduction, pollution, secondary pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
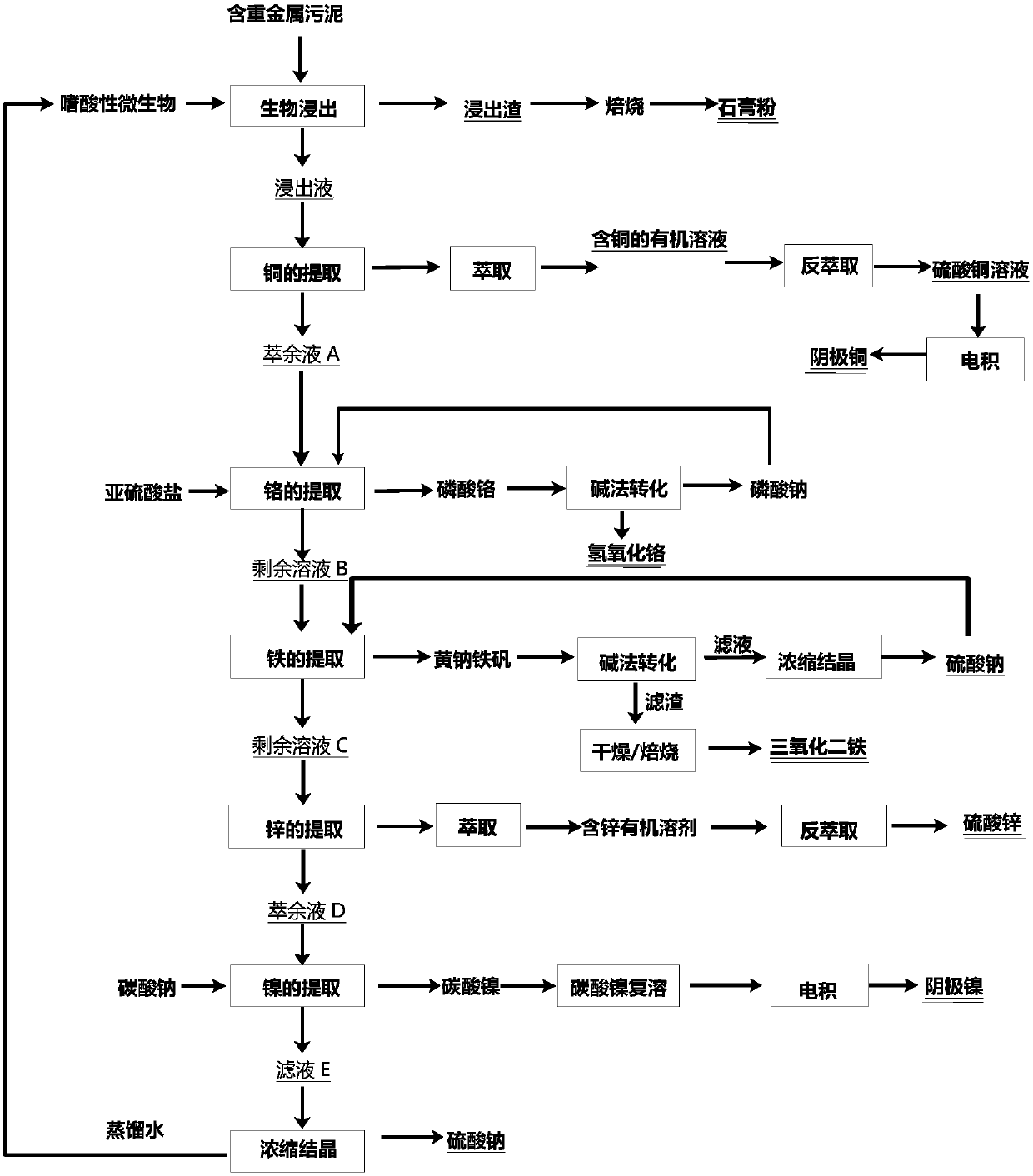
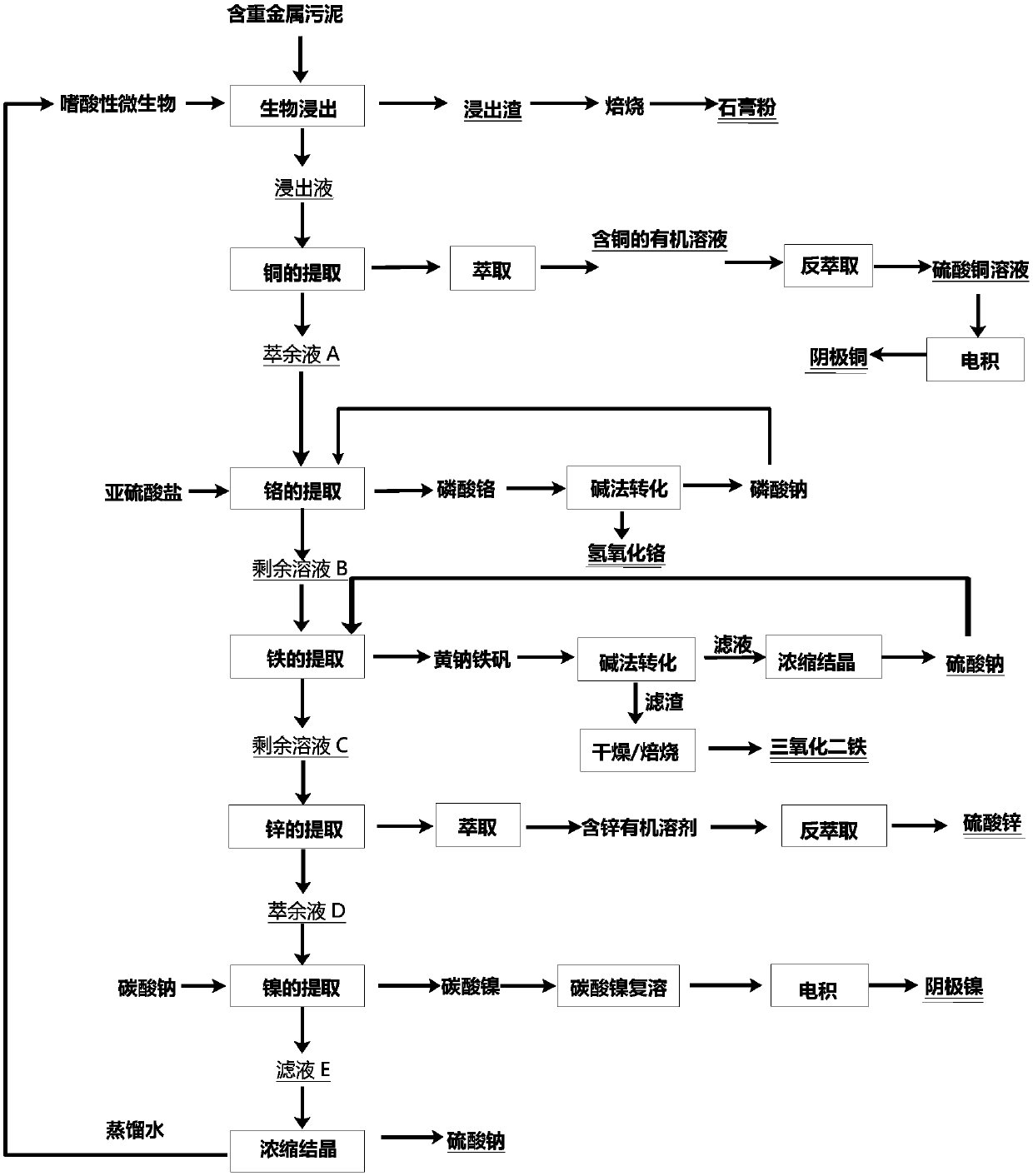
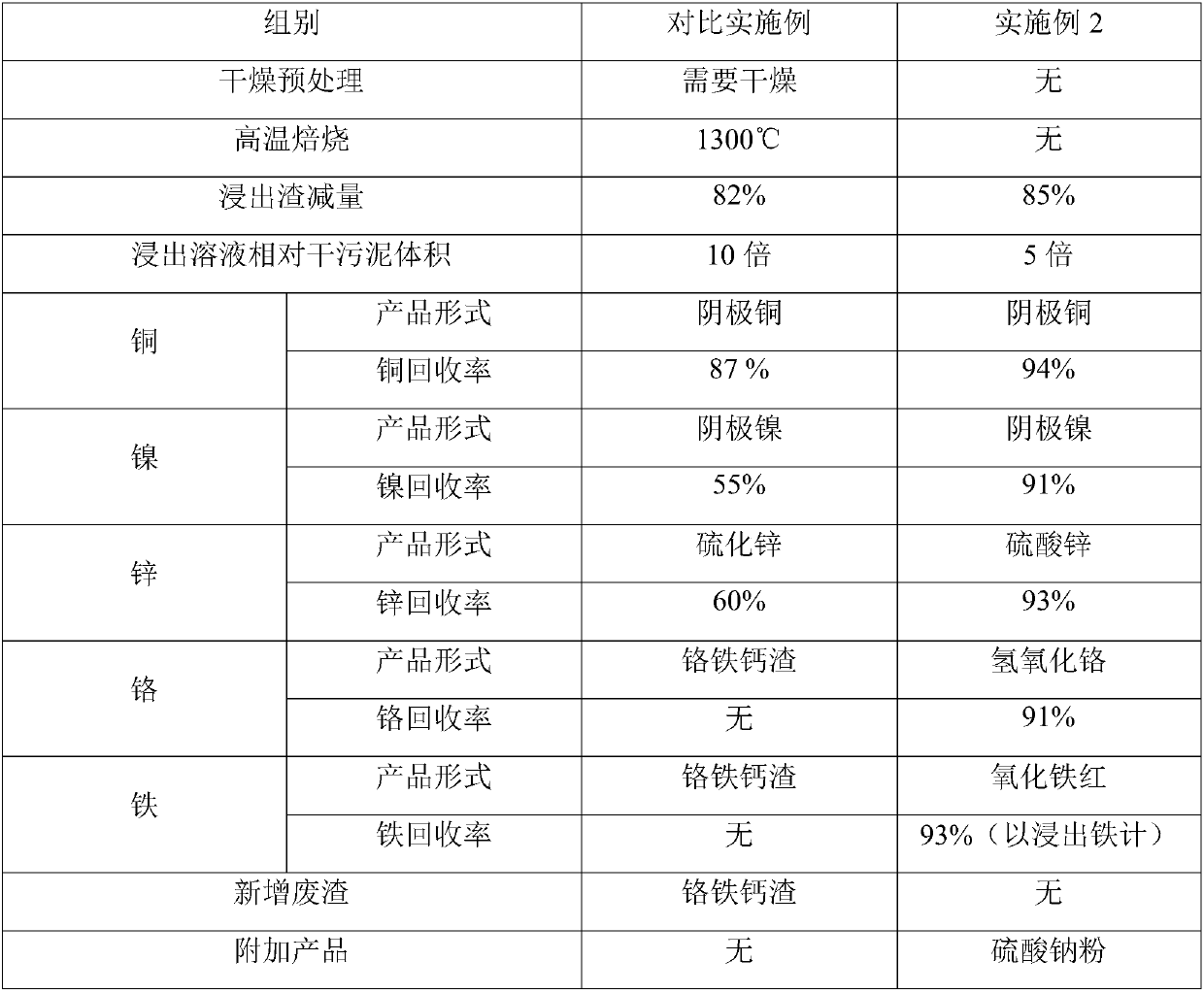
[0046] see figure 1 , is a flow diagram of a preferred embodiment of the method for non-waste utilization of heavy metal-containing sludge provided by the present invention. The heavy metal-containing sludge comes from a wastewater treatment plant in a surface treatment park in Guangdong, with a moisture content of about 65%. The dry sludge contains 5.74% chromium, 7.7% iron, 0.54% copper, 0.54% nickel, 3.87% zinc, and sulfide Heavy metals in physical form account for 0.8% of the total amount of heavy metals. The non-waste utilization method of sludge containing heavy metals includes the following steps:
[0047] Step S1, bioleaching: Weigh 1kg of heavy metal-containing sludge into a 5L polypropylene stirred reactor, add acidophilic microorganisms, control the liquid-solid ratio to 5:1, adjust the pH value to 1.8 with sulfuric acid, stir at 500rpm, and stir for 4 hours Complete bioleaching treatment, solid-liquid separation, and prepare leaching residue and leaching liquid. ...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The heavy metal-containing sludge comes from a wastewater treatment plant in a surface treatment park in Tianjin, with a water content of about 68%. The dry sludge contains 7.11% chromium, 3.28% iron, 7.56% copper, 7.9% nickel, and 5.72% zinc, of which The sulfide-bound heavy metals account for 4% of the corresponding heavy metals respectively, and the non-waste utilization method of heavy metal-containing sludge includes the following steps:
[0061] Step S1, weighing 50kg of wet sludge into a 300L polypropylene stirring reactor, adding acidophilic microorganisms, the acidophilic microorganisms are Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270 (bacteria preservation number: ATCC23270, purchased from American Type Culture Collection, American Type Culture Collection), Ferroplasma acidiphilum CS1 (bacteria collection number: CCTCC M 2015017, China Type Culture Collection Center) and Sulfobacillus acidophilus CS5 (bacteria collection number: CCTCC M 2015006, China Type Culture...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com