A device for removing fluorine in zinc waste electrolyte
A waste electrolyte, hollow technology, applied in the field of zinc hydrometallurgy, can solve the problems of rare earth consumption, limited effect of fluorine removal, high cost, etc., and achieve the effect of maintaining permeability and preventing settlement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
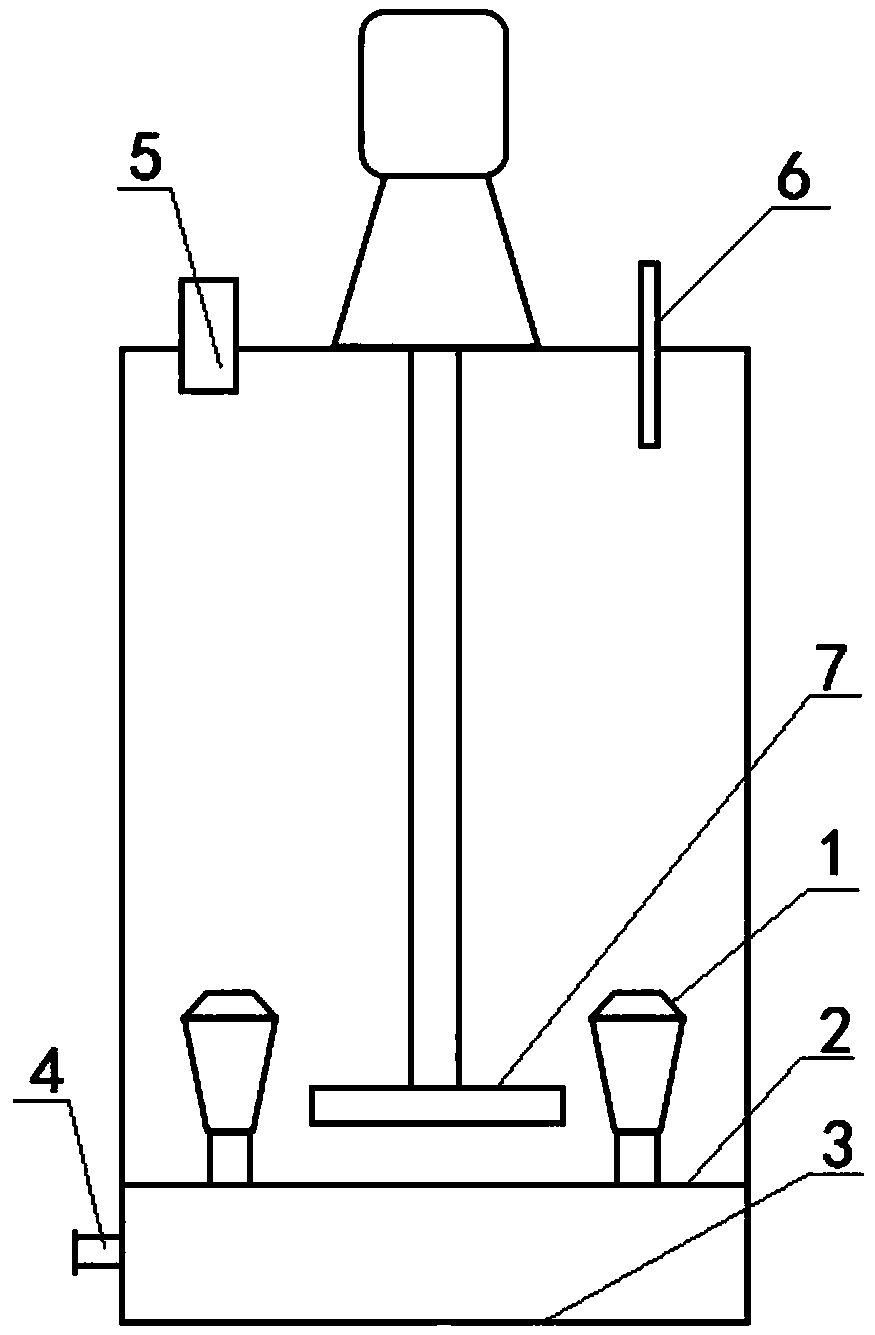
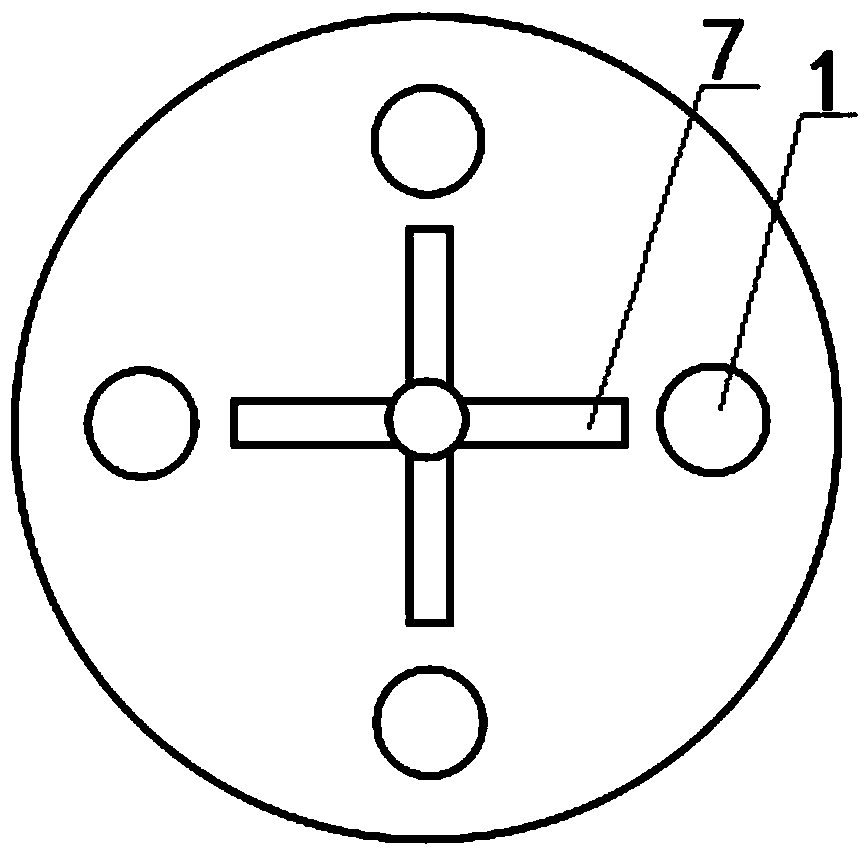
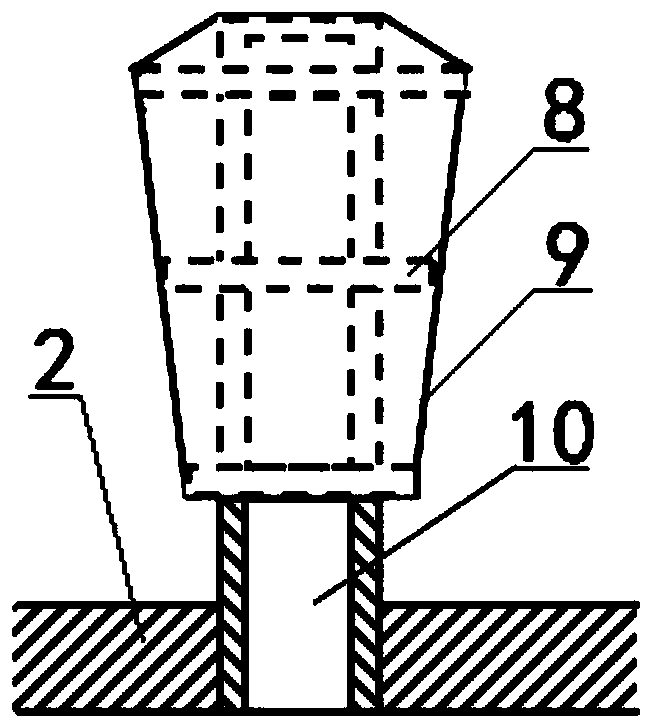
[0024] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, a device for removing fluorine in zinc waste electrolyte, comprising a hollow reaction vessel and its waste electrolyte feed port 5 and drain port 4, the top of the hollow reaction vessel is provided with a stirring structure , the waste electrolyte feed inlet 5 and the heating steam pipe 6 that can be stretched into the waste electrolyte surface; An inverted tapered tower column 1 is connected, and the inverted tapered tower column 1 is composed of a pipe with several holes in the pipe wall and a filter screen 9 with a diameter of 0.1mm on the surface of the pipe. The lower bottom layer 3 and the upper bottom layer 2 A liquid outlet 4 is opened on the container wall between; a support ring 8 is provided between the pipe of the inverted tapered column 1 and the filter screen 9; a container wall between the lower bottom 3 and the upper bottom 2 is opened There is a liquid discharge port 4; the stirring structure includes a motor, a reducer and...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Such as figure 1 , 2, 3, a device for removing fluorine in zinc waste electrolyte, comprising a hollow reaction vessel and its waste electrolyte feed port 5 and drain port 4, the top of the hollow reaction vessel is provided with a stirring structure , the waste electrolyte feed inlet 5 and the heating steam pipe 6 that can be stretched into the waste electrolyte surface; An inverted tapered tower column 1 is connected, and the inverted tapered tower column 1 is composed of a pipe with several holes in the pipe wall and a filter screen 9 with a diameter of 0.05mm on the surface of the pipe. The lower bottom layer 3 and the upper bottom layer 2 A liquid outlet 4 is opened on the container wall between; a support ring 8 is provided between the pipe of the inverted tapered column 1 and the filter screen 9; a container wall between the lower bottom 3 and the upper bottom 2 is opened There is a liquid discharge port 4; the stirring structure includes a motor, a reducer and...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Such as figure 1 , 2 , 3, a device for removing fluorine in zinc waste electrolyte, comprising a hollow reaction vessel and its waste electrolyte feed port 5 and drain port 4, the top of the hollow reaction vessel is provided with a stirring structure , the waste electrolyte feed inlet 5 and the heating steam pipe 6 that can be stretched into the waste electrolyte surface; An inverted tapered tower column 1 is connected, and the inverted tapered tower column 1 is composed of a pipe with several holes in the pipe wall and a filter screen 9 with a diameter of 0.03mm on the surface of the pipe. The lower bottom layer 3 and the upper bottom layer 2 A liquid outlet 4 is opened on the container wall between; a support ring 8 is provided between the pipe of the inverted tapered column 1 and the filter screen 9; a container wall between the lower bottom 3 and the upper bottom 2 is opened There is a liquid discharge port 4; the stirring structure includes a motor, a reducer an...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com