Monomolecular gene typing method based on DNA paper folding probe specificity marking and application thereof
A genotyping method and specific technology, applied in the field of single-molecule genotyping based on specific markers of DNA origami probes, to achieve precise positioning, high-resolution haplotype maps, and improved accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] According to this preferred embodiment, the design and preparation of 6 kinds of DNA origami probes are provided, and its specific operations are:
[0034] (1) Mix M13mp18 phage circular single-stranded DNA, more than 100 unmodified staple strands, and more than 100 staple strands with end-modified capture strands at a molar ratio of 1:10:10, that is, the added The volumes were 2.5 μL, 5 μL, 5 μL, and then 10 μL of 10×TAE-Mg was added 2+ Buffer (Mg 2+ Concentration 12.5mol / L), supplemented with ultrapure water to a final volume of 100 μL, shake well.
[0035] (2) Place the mixed solution in step (1) in a PCR instrument and anneal at a rate of 0.1°C / 10s from 95°C to 20°C. After the reaction, use a 100kDa ultrafiltration tube to centrifuge to remove excess staple chains, or, Purified by agarose electrophoresis, concentrated and recovered using Freeze'N Squeeze DNA Gel Extraction Spin Columns, and stored at 4°C for use. When streptavidin (streptavidin, STA) is required ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] According to this preferred embodiment, there is provided a PhiX 174-based model constructed using "diblock" primers, the specific operations of which are as follows:
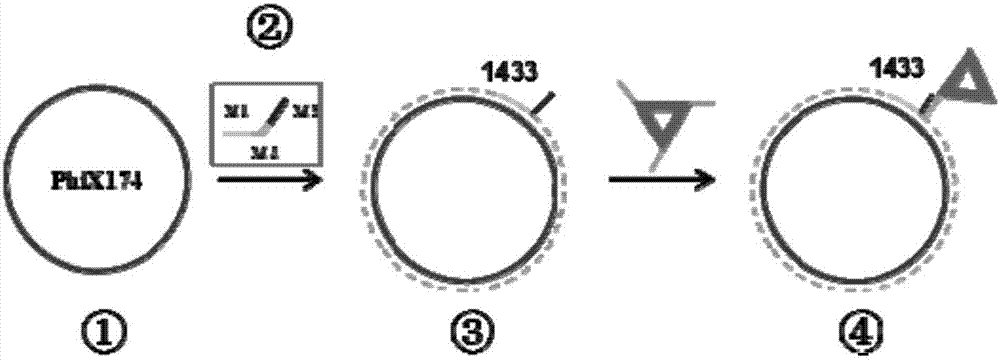
[0039] (1) figure 2 ① in ① is a single-stranded closed circular DNA with a length of 5386 bases (purchased from New England Biolabs Inc.), named PhiX 174. ② is the "double block" primer constructed, the M1 part binds to the specific site of the target DNA and effectively extends, the M3 part hybridizes with the DNA origami probe, and the M1 part and the M3 part are connected by a small spacer chain of the M2 part in the middle stand up. In a 30 μL reaction system, 6 μL of PhiX 174 template strand, Vent(exo - ) enzyme 0.8 μL, 10×ThermoPol buffer 3 μL, “diblock” primer (10 μM) 2 μL, dNT mixture (2.5 mM) 2 μL, ultrapure water 16.2 μL. well mixed.
[0040] (2) Place the mixed solution in step (1) in a PCR instrument and start high-temperature denaturation at 92°C, anneal at 65°C to 80°C for 30 cycles of...
Embodiment 3
[0044] According to this preferred embodiment, the PhiX174 model provided in Example 2 is used for specific labeling of different sites using the DNA origami probe designed according to Example 1, and the specific operations are as follows:
[0045] (1) Mix excess DNA origami probes with target DNA molecules labeled with specific diblock primers, place them in a closed foam box filled with 2L of water at 45°C, and react with natural cooling for more than 12 hours.
[0046] (2) The product obtained in step (1) is diluted to a certain number of times and observed under an atomic force microscope. Drop 3 μL of the sample on the freshly peeled mica sheet, let it stand for about 3 minutes for adsorption, then dry it with nitrogen gas and observe it under the gas phase conditions of multi-mode 8 AFM (NanoScope 5 controller, Bruker Company), the schematic diagram is as follows figure 2 Shown in ④.
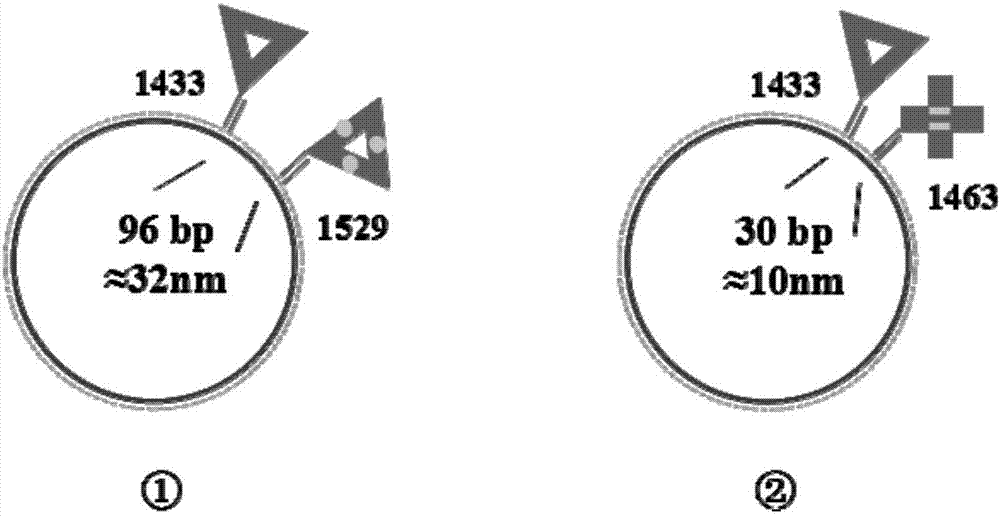
[0047] (3) After statistical analysis of the obtained AFM images, the highest label...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com