Method for extracting potassium chloride and sodium chloride from secondary zinc oxide ash and application
A technology of secondary zinc oxide and potassium chloride, applied in chemical instruments and methods, purification of alkali metal chlorides and alkali metal halides, etc., can solve the problems of scarcity and waste potassium resources, reduce environmental pressure, and simplify the process flow. , the effect of reducing emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
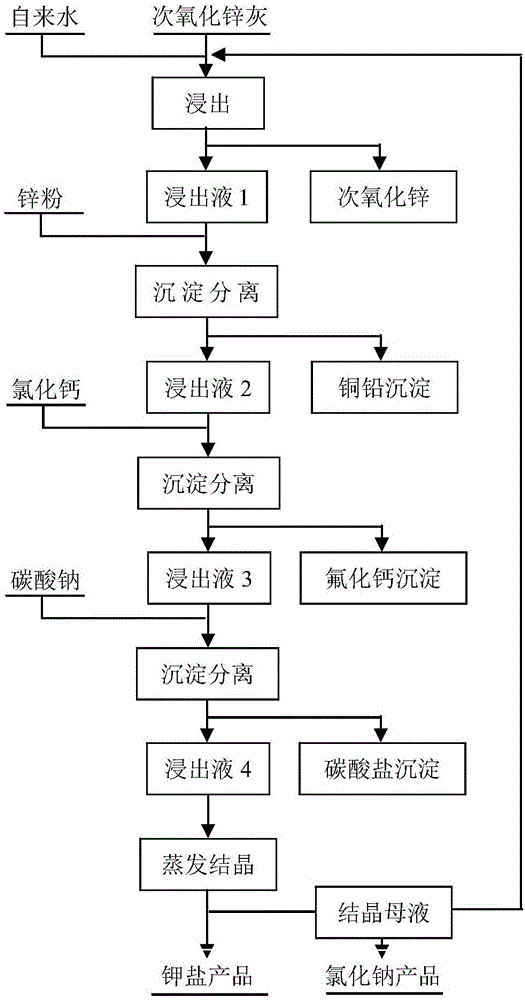
[0032] A method for extracting potassium chloride and sodium chloride from secondary zinc oxide ash, comprising the following steps:
[0033] S1. Raw material leaching and filtration: Mix the raw material sub-zinc oxide ash with 30°C tap water at a mass ratio of 1:2 and stir for 30 minutes, let stand for 1 hour to obtain a mixed slurry with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:2, and filter to obtain a leachate.
[0034] S2, impurity removal and purification: first analyze and detect the concentration of copper and lead heavy metal ions in the leaching liquid in S1, and add zinc powder of 1.1 times the equivalent of copper and lead ions to replace the molar equivalent of chemical reaction equations (3-1) and (3-2), Stir until the reaction is complete, and filter to obtain filtrate A after solid-liquid separation;
[0035] Analyze and detect the fluoride ion concentration in the filtrate A, add calcium chloride of 1.1 times the calculated molar equivalent of the complete reaction with ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] A method for extracting potassium chloride and sodium chloride from secondary zinc oxide ash, comprising the following steps:
[0040] S1. Raw material leaching and filtering: mix the raw material secondary zinc oxide ash with industrial water at a temperature of 30°C according to the mass ratio of 1-4 and stir for 60 minutes, and let it stand for 3 hours to obtain a mixed slurry with a solid-liquid ratio of 1-4, and then filter get leaching solution.
[0041] S2, impurity removal and purification: first analyze and detect the concentration of copper and lead heavy metal ions in the leaching liquid in S1, and add zinc powder of 1.2 times the equivalent of copper and lead ions to replace the molar equivalent of the chemical reaction equations (3-1) and (3-2), Stir until the reaction is complete, and filter to obtain filtrate A after solid-liquid separation;
[0042] Analyze and detect the fluoride ion concentration in the filtrate A, add calcium chloride of 1.2 times th...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A method for extracting potassium chloride and sodium chloride from secondary zinc oxide ash, comprising the following steps:
[0047] S1. Raw material leaching and filtering: mix the raw material secondary zinc oxide ash with industrial water at a temperature of 50°C according to the mass ratio of 1-3 and stir for 45 minutes, and let it stand for 2 hours to obtain a mixed slurry with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:3, and then filter get leaching solution.
[0048] S2, impurity removal and purification: first analyze and detect the concentration of copper and lead heavy metal ions in the leaching liquid in S1, add zinc powder of 1.15 times the equivalent of copper and lead ion molar equivalents replaced by chemical reaction equations (3-1) and (3-2), Stir until the reaction is complete, and filter to obtain filtrate A after solid-liquid separation;
[0049] Analyze and detect the fluoride ion concentration in the filtrate A, add calcium chloride 1.15 times the calculated...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com