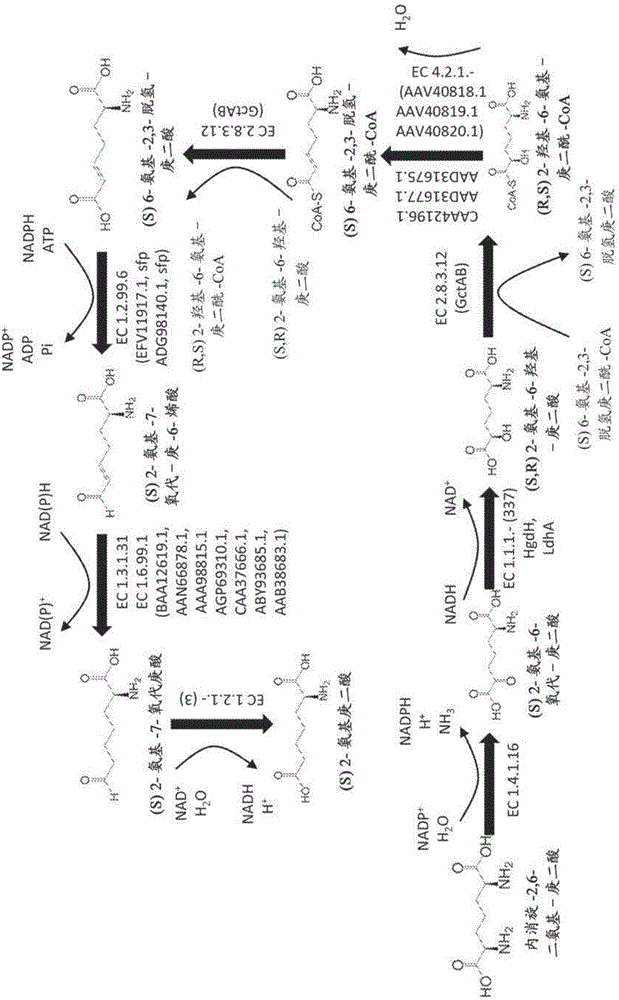
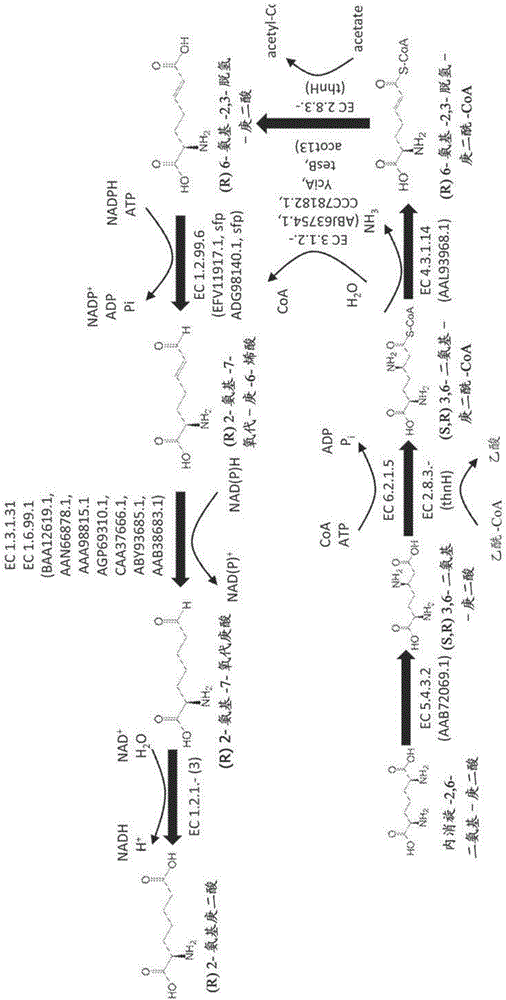
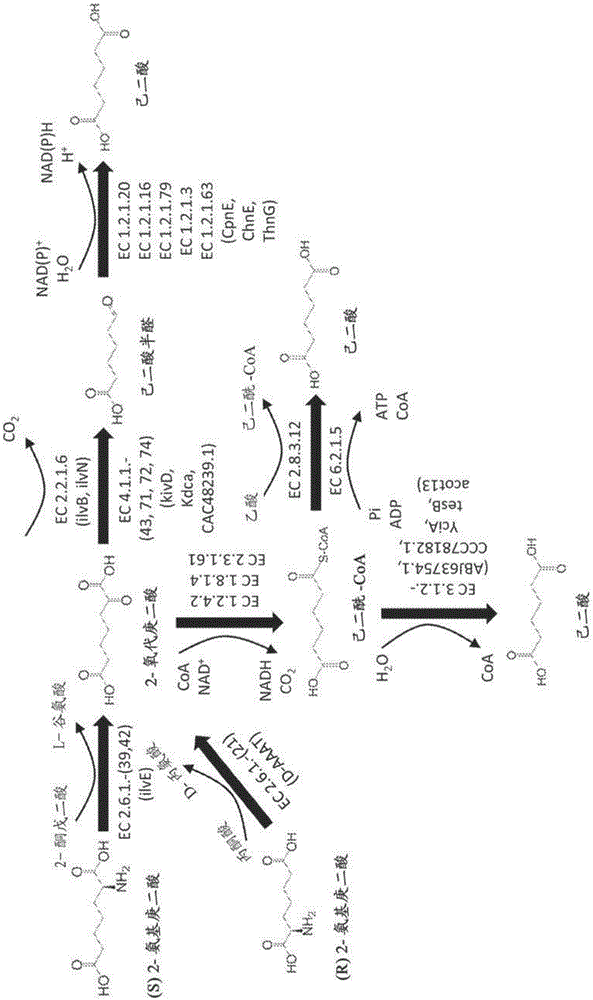
Methods of producing 6-carbon chemicals using 2,6-diaminopimelate as precursor to 2-aminopimelate
A technology of diaminopimelic acid and aminopimelic acid, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, carbon-nitrogen lyase, carbon-oxygen lyase, etc., can solve the problem of no report
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0275] Enzymatic activity of ω-transaminase using adipate semialdehyde as substrate and forming 6-aminocaproic acid
[0276] The nucleotide sequence encoding the His-tag was added to the omega-transaminases from Chromobacterium violaceum, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas syringae, spheroid Rhodobacter and Vibrio genes (see Figure 20 ), allowing the generation of N-terminally HIS-tagged ω-transaminases. Each of the resulting modified genes was cloned into the pET21a expression vector under the control of the T7 promoter, and each expression vector was transformed into a BL21[DE3] E. coli host. The resulting recombinant E. coli strains were grown in 250 mL shake flask cultures containing 50 mL LB medium and antibiotic selection pressure at 37° C. with shaking at 230 rpm. Each culture was induced overnight at 16°C with 1 mM IPTG.
[0277] The pellet from each induced shake flask culture was harvested by centrifugation. Each pellet was resuspended and lysed by sonication. ...
Embodiment 2
[0283] Enzyme activity of carboxylic acid reductase using 6-hydroxyhexanoic acid as substrate and forming 6-hydroxyhexanal
[0284] The nucleotide sequence encoding the His-tag was added to the carboxylic acid reductases from Mycobacterium marinum, Mycobacterium smegmatis, Mycobacterium smegmatis, Segniliparus rugosus, Marseilles respectively encoding the carboxylic acid reductase of SEQ ID NO:3-7. Mycobacterium, and Segniliparus rotundus genes (see Figure 20 ), allowing the generation of an N-terminally HIS-tagged carboxylic acid reductase. Each modified gene was cloned into the pET Duet expression vector together with the sfp gene encoding the His-tagged phosphopantetheinyl transferase from Bacillus subtilis, all under the control of the T7 promoter. Each expression vector was transformed into a BL21[DE3] E. coli host. Each resulting recombinant E. coli strain was grown in a 250 mL shake flask culture containing 50 mL LB medium and antibiotic selection pressure at 37°C wi...
Embodiment 3
[0289] For 6-aminohexanol, omega-transaminase activity to form 6-oxohexanol
[0290] The nucleotide sequence encoding the N-terminal His-tag was added to Chromobacterium violaceum, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Pseudomonas syringae, Rhodobacter sphaericus, Escherichia coli Bacillus and Vibrio genes (see Figure 20 ), allowing the generation of N-terminally HIS-tagged ω-transaminases. The modified gene was cloned into the pET21a expression vector under the T7 promoter. Each expression vector was transformed into a BL21[DE3] E. coli host. Each of the resulting recombinant E. coli strains was cultured in a 250 mL shake flask containing 50 mL of LB medium and antibiotic selection pressure at 37° C. with shaking at 230 rpm. Each culture was induced overnight at 16°C with 1 mM IPTG.
[0291] The pellet from each induced shake flask culture was harvested by centrifugation. Each pellet was resuspended and lysed by sonication. Cell debris was separated from the supernatant by centrifug...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com