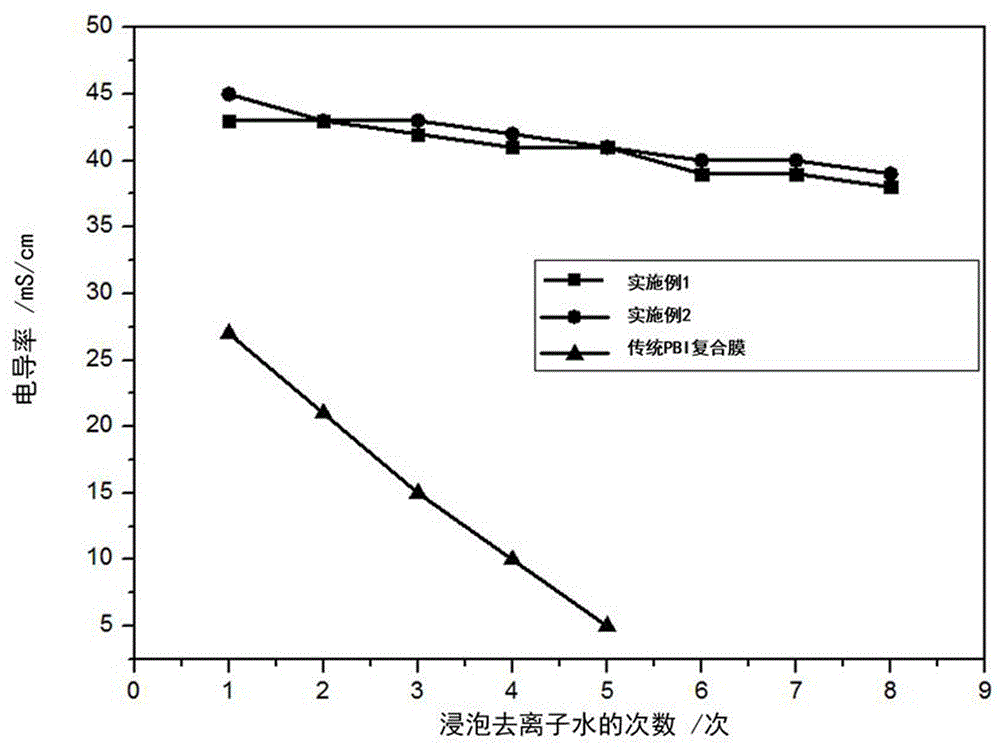
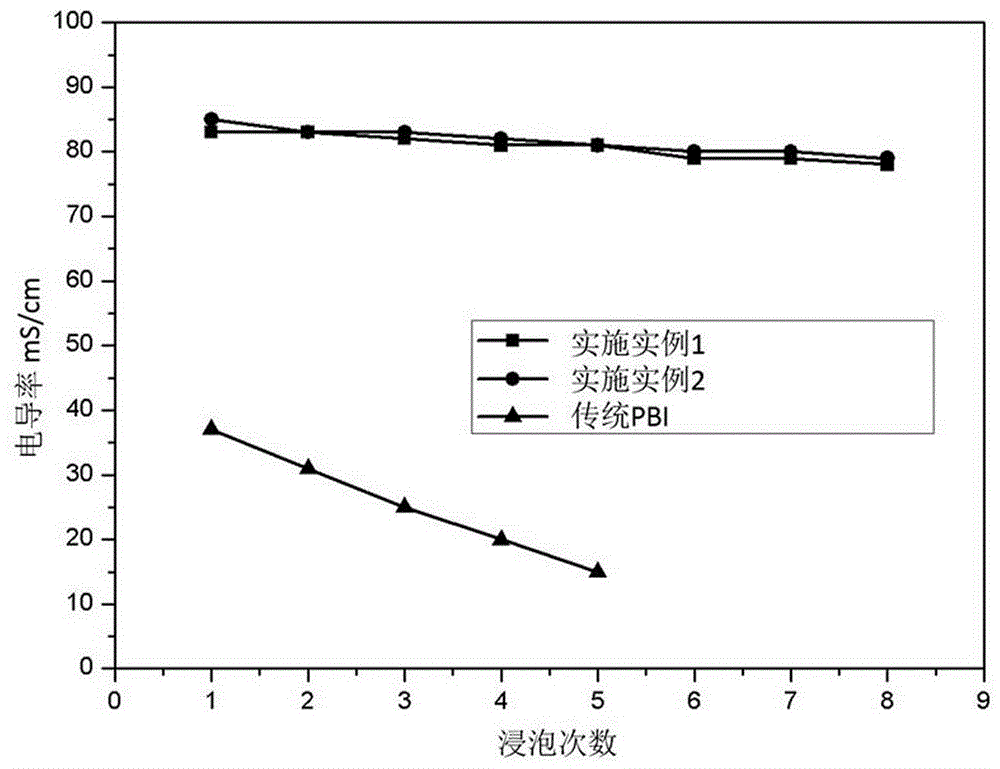
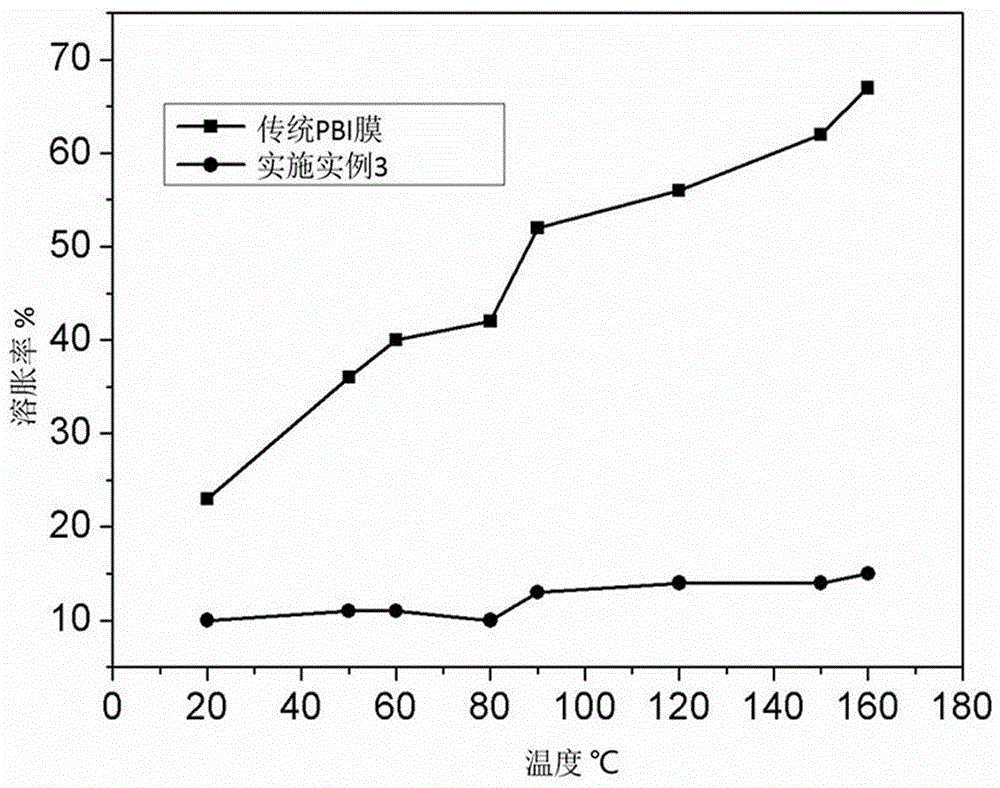
High conductivity cross-linked organic phosphate polybenzoimidazole high temperature proton exchange membrane and preparation method thereof
A proton exchange membrane and organic phosphoric acid technology, which is applied in solid electrolyte fuel cells, circuits, fuel cells, etc., to achieve the effects of improving dimensional stability, improving conductivity stability, and reducing phosphoric acid loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A method for preparing a cross-linked organophosphate polybenzimidazole high-temperature proton exchange membrane with high conductivity, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0029] (1) Dissolve 0.5 g vinylphosphonic acid in 10 mL N-methylpyrrolidone, stir until dissolved, add vinylbenzyl chloride, stir at room temperature for 30 min, the mole of vinylphosphonic acid and vinylbenzyl chloride The ratio is 5:1;
[0030] (2) Add 0.1 g of azobisisobutyronitrile to the solution, transfer the solution to an oil bath at 60-150 °C, stir, and pass through nitrogen protection, the nitrogen flow rate is 100 mL / min, and react for 12 h;
[0031] (3) After the reaction, pour the solution into ethanol to precipitate, and wash with ethanol several times, deionized water several times, and then dry at 60°C;
[0032] (4) Weigh 0.2 g of the product, 0.1 g of polybenzimidazole, dissolve in 20 mL of N-methylpyrrolidone, and stir to dissolve at room temperature;
[0033] (5) Transfe...
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for preparing a cross-linked organophosphate polybenzimidazole high-temperature proton exchange membrane with high conductivity, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0039](1) Dissolve 0.8 g vinylphosphonic acid in 20 mL N-methylpyrrolidone, stir until dissolved, add vinylbenzyl chloride, stir at room temperature for 30 min, the molar ratio of vinylphosphonic acid to vinylbenzyl chloride 2:1;
[0040] (2) Add 0.8 g of azobisisobutyronitrile to the solution, transfer the solution to an oil bath at 60-150 °C, stir, and protect with nitrogen gas flow rate of 100 mL / min; react for 24 h;
[0041] (3) After the reaction, pour the solution into ethanol to precipitate, and wash with ethanol several times, deionized water several times, and then dry at 60°C;
[0042] (4) Weigh 0.5 g of the product, 0.25 g of polybenzimidazole, dissolve in 23 mL of N-methylpyrrolidone, stir and dissolve at room temperature;
[0043] (5) Transfer the casting liquid to an 80°C oil...
Embodiment 3
[0048] A method for preparing a cross-linked organophosphate polybenzimidazole high-temperature proton exchange membrane with high conductivity, which is prepared by the following steps:
[0049] (1) Dissolve 1.5 g vinylphosphonic acid in 30 mL N,N-dimethylacetamide, stir until dissolved, then add vinylbenzyl chloride; stir at room temperature for 60 min, vinylphosphonic acid and vinylbenzyl The molar ratio of base chloride is 5:1;
[0050] (2) Add 1.5 g of azobisisobutyronitrile to the solution, transfer the solution to an oil bath at 60-150 °C, stir, and pass through nitrogen protection, the nitrogen flow rate is 100 mL / min, and react for 24 h;
[0051] (3) After the reaction, pour the solution into ethanol to precipitate, and wash with ethanol several times, deionized water several times, and then dry at 60°C;
[0052] (4) Weigh 0.5 g of the product, 0.5 g of polybenzimidazole, dissolve in 30 mL of N,N-dimethylacetamide, stir and dissolve at room temperature;
[0053] (5)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com