Extraction method and purpose of renewable particles of umbilical cord blood
An extraction method and a technology of umbilical cord blood, applied in the fields of biomedicine, histocytology, and regenerative medicine, can solve the problems of immature technology of expanding adult stem cells in vitro and the small number of adult stem cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
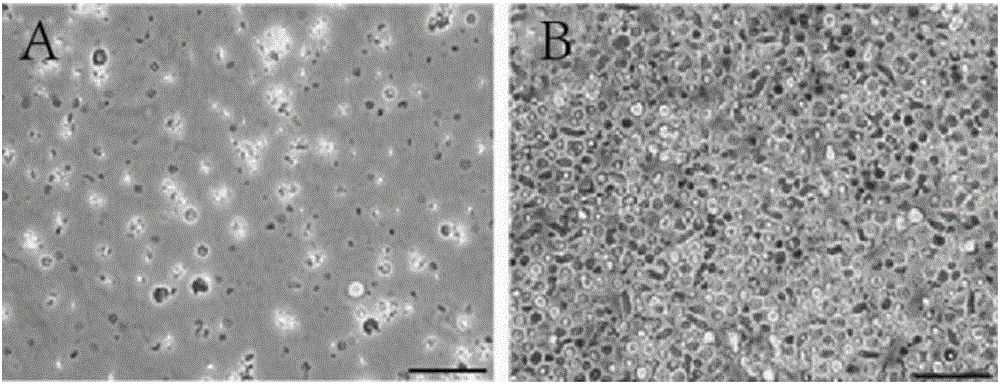
[0069] Example 1. Extraction and cultivation of umbilical cord blood regeneration particles
[0070] In this example, the extraction and cultivation of umbilical cord blood regeneration particles are exemplified.
[0071] Blood source: The umbilical cord blood is collected into a blood bag containing anticoagulant. The anticoagulant is the original sodium citrate in the blood bag, and the umbilical cord blood is transported to company.
[0072] Conditions: The process of obtaining umbilical cord blood regeneration particles requires a complete aseptic operation.
[0073] (1) The umbilical cord blood was taken and centrifuged at 200g for 10 minutes. After centrifugation, it was divided into two parts, the upper layer solution A and the lower layer precipitate A.
[0074] (2) Take the lower layer of precipitate A, add PBS at a volume ratio of 1:2-5 for slight washing, and centrifuge at 200g for 10 minutes. After centrifugation, it is divided into two parts, the upper layer sol...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2. The function of umbilical cord blood regeneration particles to promote the regeneration and repair of myocardial injury
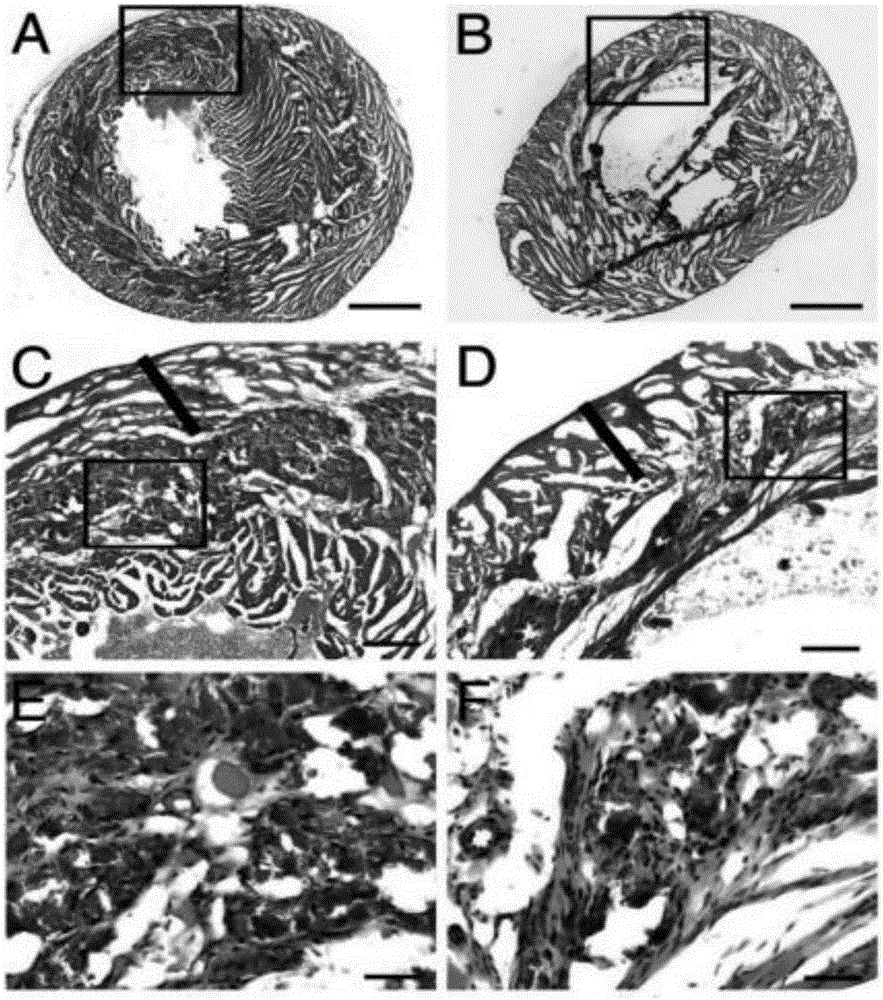
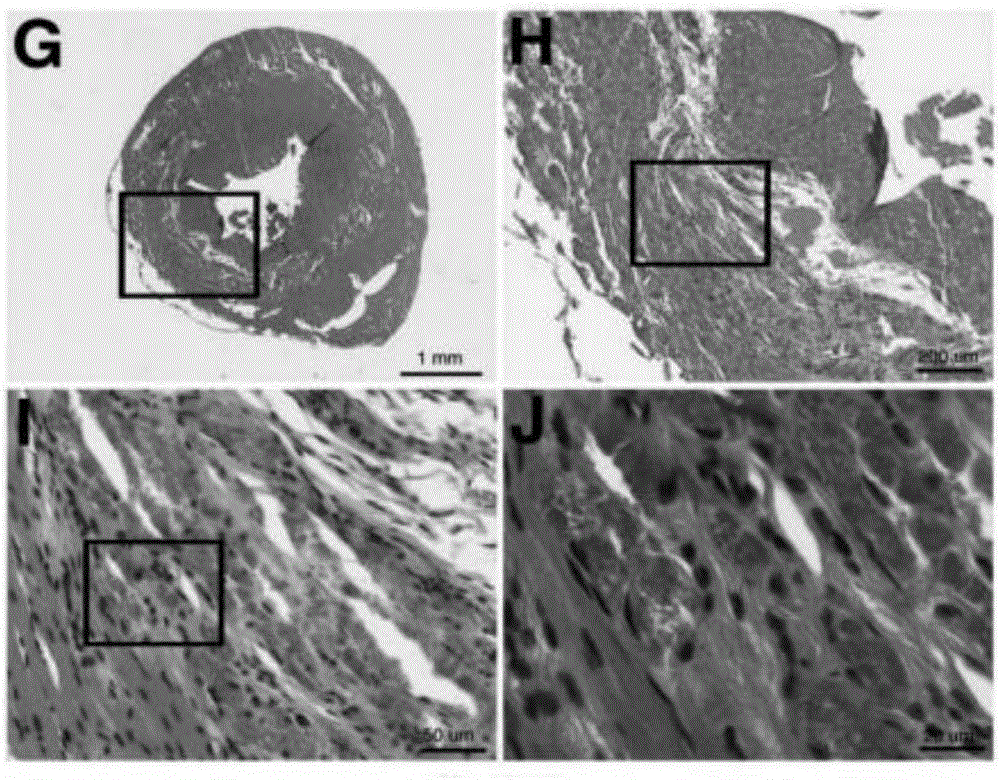
[0081] The experimental group injected the umbilical cord blood regeneration particles (GFP marker) obtained in Example 1 into mice with ischemic myocardial injury through the tail vein, and the control group injected physiological saline. The blood of each mouse was collected every 24 hours after injection for AST detection. After injection, the mouse hearts were collected for 9 consecutive weeks and sectioned to detect the damaged area.
[0082] After transplantation of umbilical cord blood regeneration particles into mice, more cardiospheres accumulated in the myocardial infarction area in the experimental group (see figure 2 , image 3 ), indicating that cord blood regeneration particles formed cardiospheres. Through the detection of Oct4 and CXCR4 in the cardiospheres area of the experimental group (see Figure 4 ), it was foun...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3. The function of umbilical cord blood regeneration particles to promote the regeneration of cerebral blood vessels
[0085] The experimental group injected the regenerative particles (GFP marker) obtained in Example 1 into the mice with ischemic brain injury through the tail vein, and the control group injected normal saline.
[0086] In the 10-week brain examination, it was found that there was no GFP staining in the control group ( Figure 6 A), but there is strong GFP expression in the blood vessel-like structures of the GFP-specific antibody reactive part of the experimental group ( Figure 6 B). Further studies found that GFP and Oct4 co-expressed in blood vessel-like structures ( Figure 7 C-7F) or nestin is also checked ( Figure 7 G-7J).
[0087] The above examples illustrate that the umbilical cord blood regeneration particles of the present invention have the function of promoting the regeneration of brain-injured blood vessels.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com