Method and device for extracting and separating phenolic compounds from coal derived oil
A technology of phenolic compounds and extraction equipment, which is applied in the preparation of organic compounds, chemical instruments and methods, organic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution, low efficiency of multi-stage stripping and extraction of phenols, and cumbersome process, so as to avoid A large amount of high-salt wastewater, high efficiency of extraction and extraction of phenols, and the effect of improving environmental benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
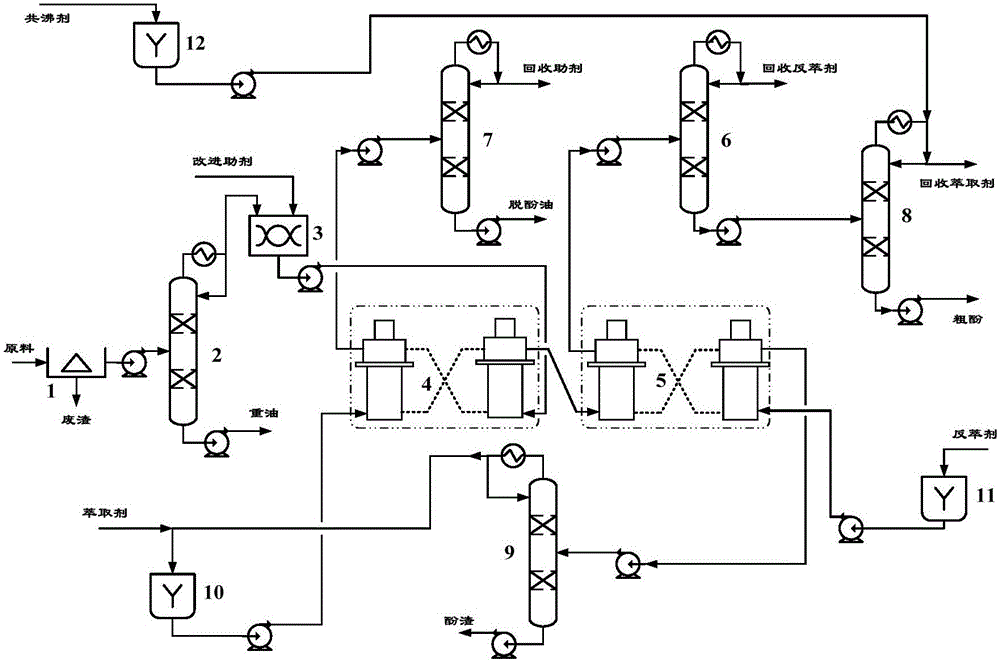
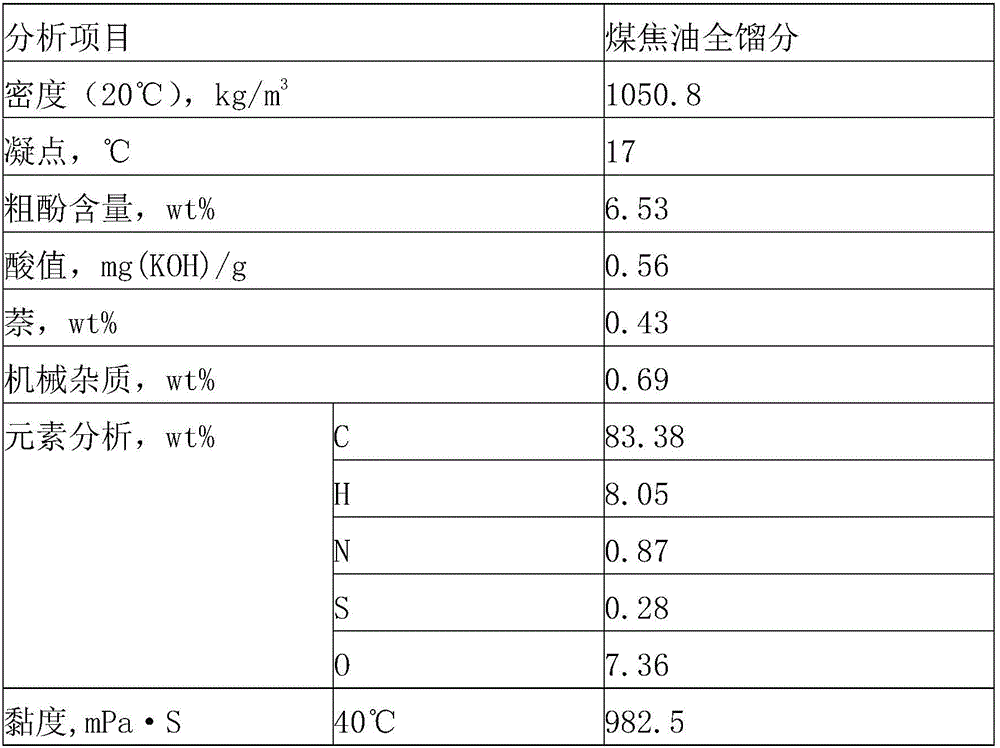
[0082] A typical medium and low temperature coal tar in northern Shaanxi was selected as the raw material of this example. The properties of the raw material are shown in Table 1. After being desolidified and pretreated by a decanter centrifuge, it was input into a phenol-rich fraction distillation tower for distillation and cutting of the phenol-rich fraction. After distillation and cutting, a phenol-rich fraction at 170-230°C was obtained, and its properties are shown in Table 2.
[0083] The properties analysis results of the whole fraction of low temperature coal tar in Table 1
[0084]
[0085]
[0086] Properties of the phenol-rich fraction after pretreatment of low-temperature coal tar in Table 2
[0087]
[0088] The phenol-rich fraction obtained after the desolidification of the desolidification preprocessor 1 and the distillation and cutting of the phenol-rich fraction distillation tower 2 is uniformly mixed with the auxiliary agent through the online contin...
Embodiment 2
[0100] Example 2: Coal Direct Liquefaction Oil Extraction and Separation of Phenolic Compounds
[0101] The low-fraction oil obtained from a typical bituminous coal operated on a 0.1t / d coal direct liquefaction continuous test device, the properties of the low-fraction oil are shown in Table 6, and used as the raw material of this example, it was desolidified and pretreated by a decanter centrifuge. After the treatment, the phenol-rich fraction was input into a distillation tower for distillation and cutting of the phenol-rich fraction. After distillation and cutting, a phenol-rich fraction at 170-275°C was obtained. The properties of the phenol-rich fraction are shown in Table 7.
[0102] Table 6 Analysis results of low oil content in direct coal liquefaction
[0103]
[0104]
[0105] Table 7 Properties of phenol-rich fractions cut from direct coal liquefied oil distillation
[0106]
[0107] Since the phenol content in direct coal liquefaction oil is relatively lo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com