A method of manufacturing vertical LED chips to realize the reuse of sapphire substrates
A sapphire substrate and LED chip technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as waste, GaN film damage, sapphire substrate surface damage, etc., to improve luminous efficiency and reduce costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] The method for preparing a vertical LED chip of this embodiment includes the following steps:
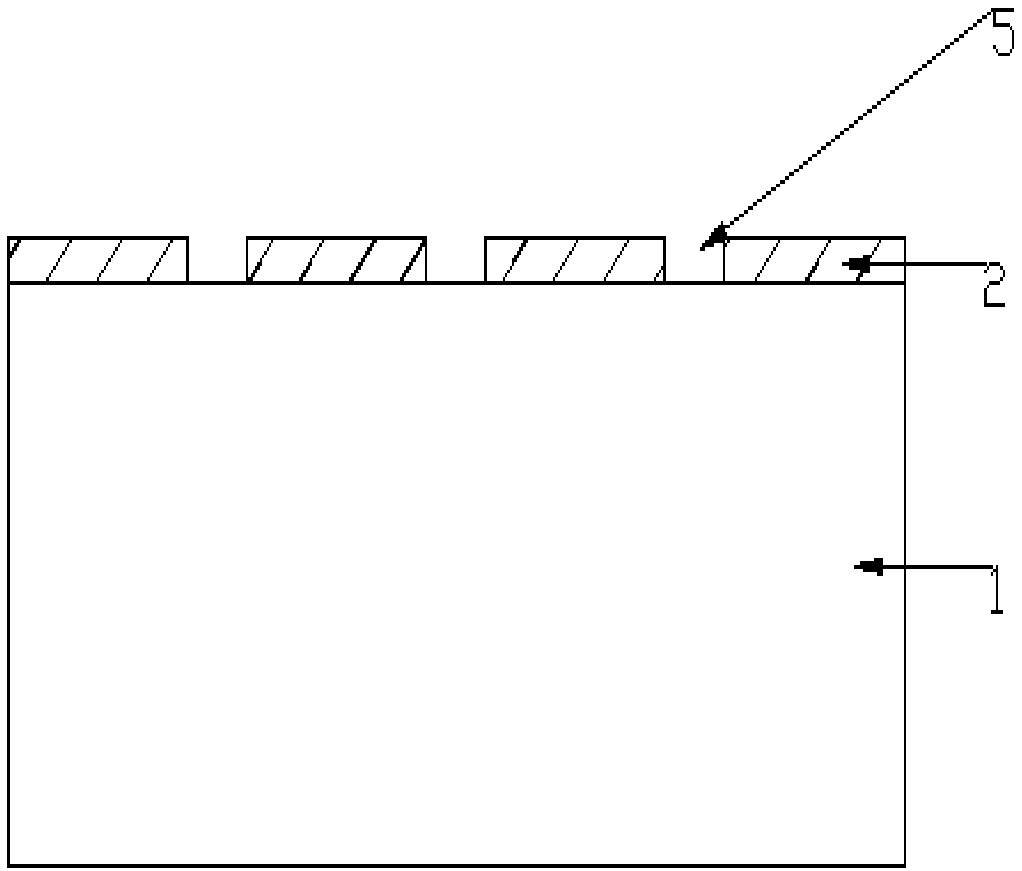
[0051] The first step is to deposit Si on the sapphire substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD, Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) 3 N 4 Sacrificial layer (among them, PECVD radio frequency power 60W, substrate temperature 300℃, cavity pressure 500mTorr, SiH 4 Flow 30sccm, NH 3 Flow rate 120sccm, deposition time 160s), sacrificial layer thickness 100nm;
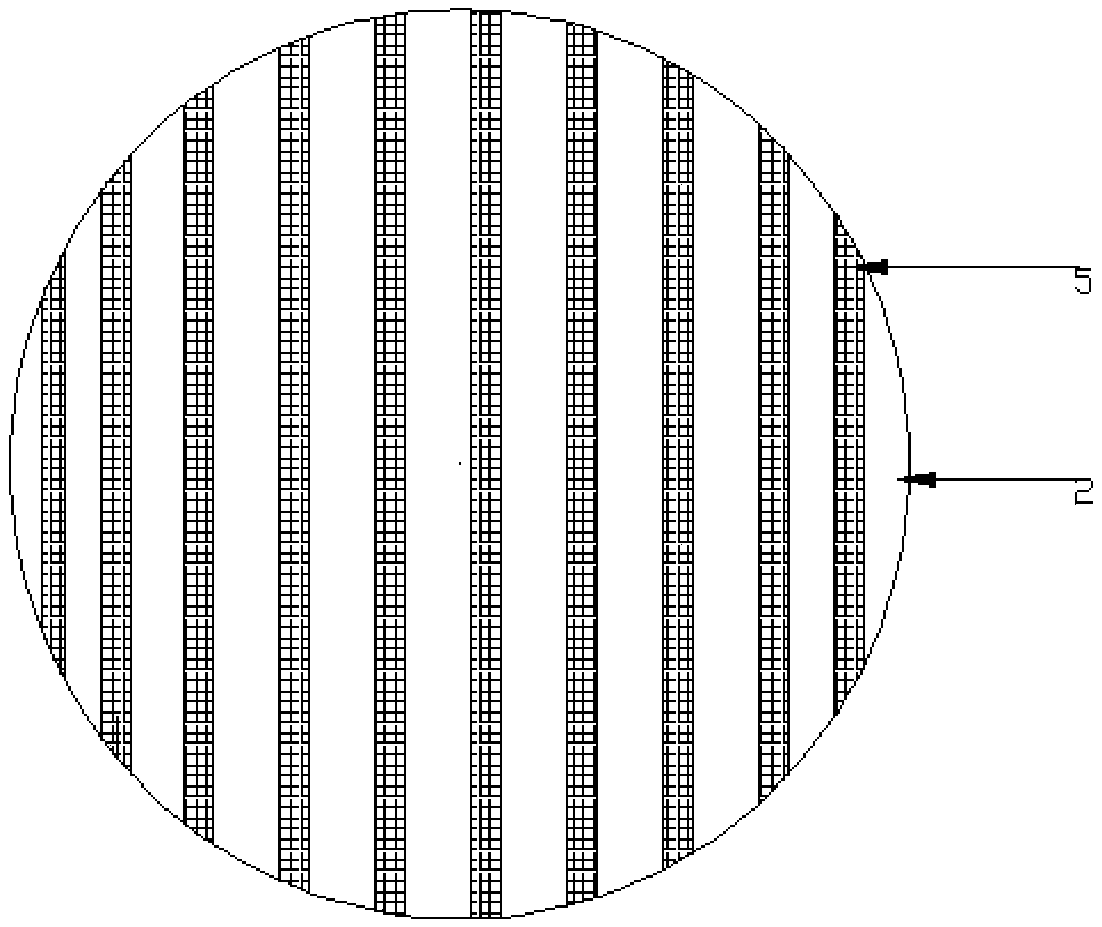
[0052] In the second step, the sacrificial layer is coated, exposed, and developed to prepare a groove pattern, and then a line-shaped groove is prepared by a wet etching method. The groove width is 5μm, the line-to-line spacing is 1mm, and the line-shaped groove The depth is equal to the thickness of the deposited sacrificial layer (that is, the sapphire substrate is exposed at the trench);
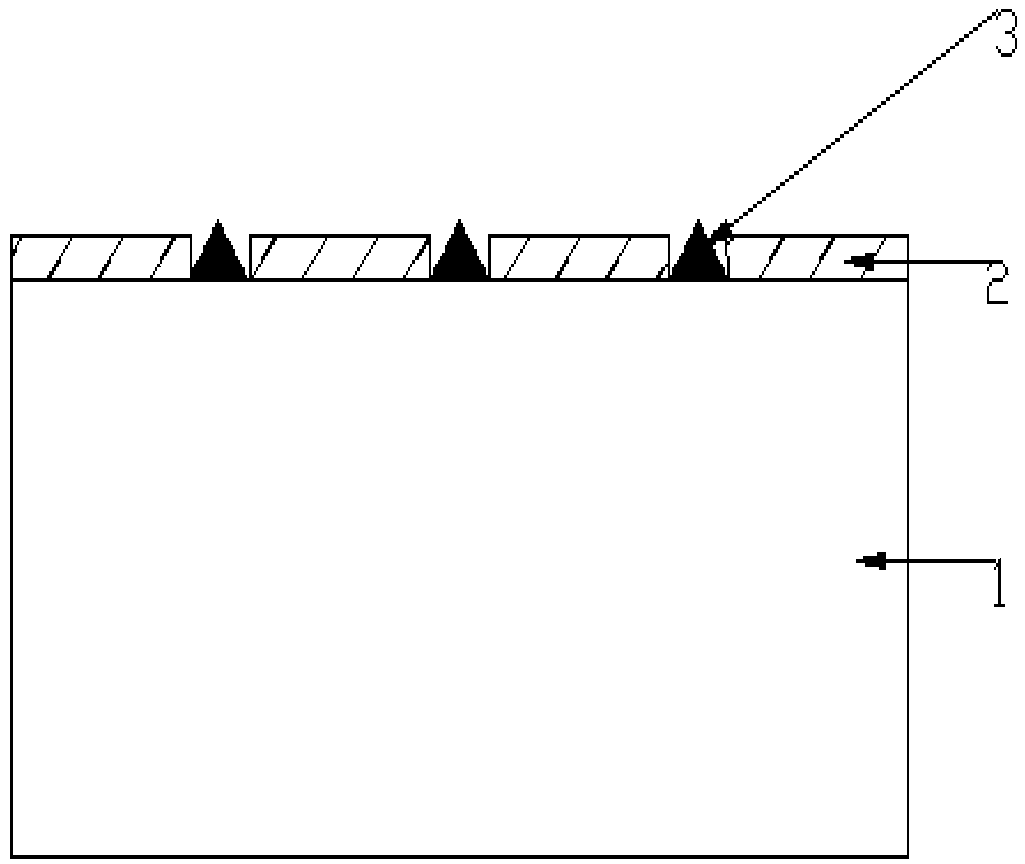
[0053] The third step is to use the Metal-organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) method. Firstly, the GaN b...
Embodiment 2
[0064] The method for preparing a vertical LED chip of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0065] Except for the first step, Si is prepared on the sapphire substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD, PlasmaEnhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition). 3 N 4 Sacrificial layer, power 40W, substrate temperature 300℃, working pressure 500mTorr, SiH 4 Flow 30sccm, NH 3 The flow rate is 120sccm, the deposition time is 110s; the thickness of the sacrificial layer is 50nm; in the second step, the sacrificial layer is coated, exposed, and developed to prepare a groove pattern, and then a line-shaped groove is prepared by a wet etching method. The groove width is 3μm, the line-to-line spacing is 0.5mm, and the line-shaped groove depth is equal to the thickness of the deposited sacrificial layer; the third step is to use MOCVD to grow a GaN buffer layer in the groove revealing the sapphire substrate, and then On the basis of the GaN buffer layer, an undoped GaN layer is...
Embodiment 3
[0067] The method for preparing a vertical LED chip of this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0068] Except for the first step, Si is prepared on the sapphire substrate by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD, PlasmaEnhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition). 3 N 4 Sacrificial layer, power 20W, substrate temperature 300℃, working pressure 500mTorr, SiH 4 Flow 30sccm, NH 3 The flow rate is 120sccm, the deposition time is 390s; the thickness of the sacrificial layer is 80nm; the second step, the sacrificial layer is coated, exposed, and developed to prepare a groove pattern, and then the Si in the groove is removed by wet etching 3 N 4 The sacrificial layer is completely removed, the trench width is 10μm, the line-to-line spacing is 3mm, and the line-shaped trench depth is equal to the thickness of the deposited sacrificial layer; the third step is to grow a GaN buffer in the trench that exposes the sapphire substrate by MOCVD Then, based on the GaN buffer layer, an und...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com