Micro-interface hydroxyl free radical characterization method based on fluorescence imaging analysis
A fluorescence imaging and free radical technology, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by optical means, analysis of materials, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of large influence of the instrument, low oxidation selectivity, and wrong evaluation of the catalytic ability of the surface of the material, etc. Achieve the effect of strong anti-interference and simple operation steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1 characterizes the catalytic oxidation performance of carbon nanotubes
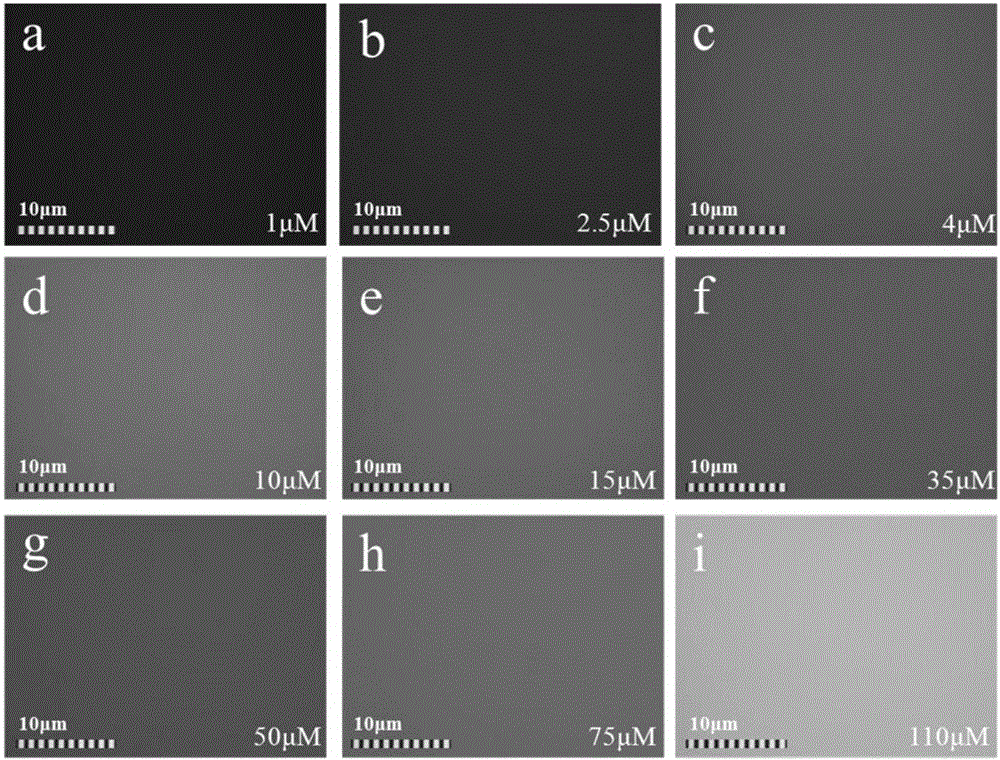
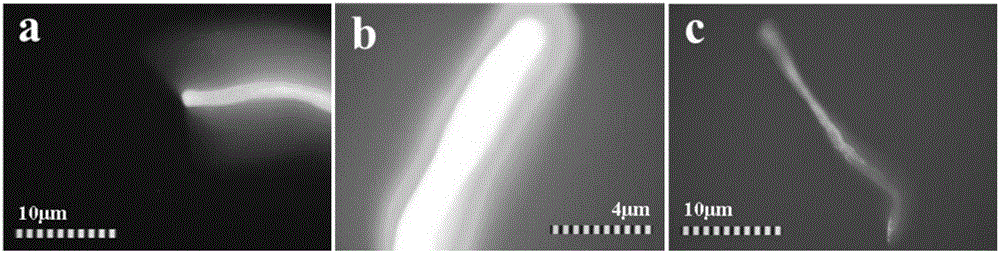
[0033] figure 2 It is a fluorescence micrograph of carbon nanotubes as a solid-phase catalyst. From figure 2 a It can be observed that there is a highly recognizable blue area around the carbon nanotubes, indicating that a high-intensity catalytic ozone reaction has occurred on the surface of the carbon nanotubes, and a large number of hydroxyl radicals (concentration is about 60 μM) have been generated. From figure 2 b is the picture of carbon tubes under increased magnification. It can be clearly seen that there is a higher intensity cyan free radical area (concentration is about 110 μM) in the blue area, reflecting that the carbon tube surface catalyzes ozone in situ to generate a large amount of HO. Then it concentrates and diffuses to a certain extent in a very small interface area. figure 2 c is a sample diagram of the catalytic ozone reaction in a strong alkaline solution...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 characterizes the catalytic oxidation performance of graphite, activated carbon and iron oxide
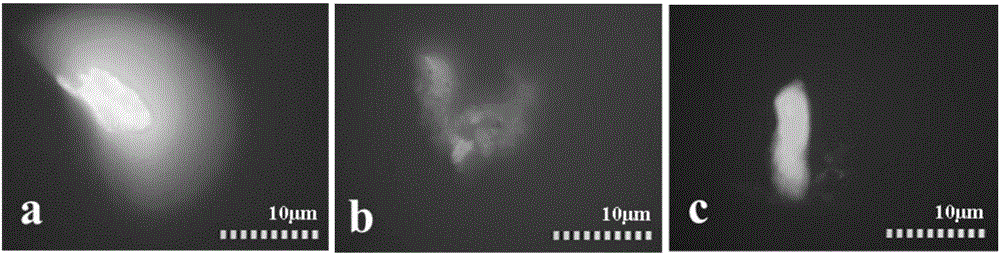
[0035] image 3 a is a fluorescence microscopic image of graphite as a solid-phase catalyst. It can be observed that graphite has a free radical generation state similar to that of carbon nanotubes, that is, the cyan region of the inner layer is a highly concentrated state of free radicals, and the blue region of the outer layer is Radical condensed states at solid-liquid interfaces. In contrast, the catalytic ozone ability of activated carbon decreased significantly ( image 3 b) On the one hand, the blue light intensity on the surface is obviously weakened, indicating that the amorphous carbon structure has a relatively weak ability to catalyze ozone to generate HO. On the other hand, the uneven color distribution reflects the arrangement of catalytic functional groups on the surface of amorphous carbon uneven. Iron oxide is also one of the emerging catalyt...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Example 3 comparative characterization research on the catalytic oxidation performance of carbon materials
[0037] Figure 4 It is a 400-fold magnified fluorescence micrograph of catalytic materials in an ozone environment under the conditions of parallel catalytic experiments. The comparison results clearly show that carbon nanotubes ( Figure 4 a) and graphite ( Figure 4 b) Both can rapidly promote the conversion of ozone on the surface to generate HO. In contrast, although activated carbon can also show a certain catalytic effect, the fluorescence intensity reflecting free radicals is significantly weaker. Compared Figure 4 a and Figure 4 b. Carbon nanotubes have more efficient catalytic properties. On the one hand, they have an active surface layer of graphene, and on the other hand, they are highly stable mesoporous materials, and their mass transfer and contact are significantly better than graphite. The results of this fluorescence imaging analysis furthe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com