Degradable flame-retardant wood-plastic composite material and preparation method thereof
A technology of wood-plastic composite materials and composite flame retardants, applied in the field of composite materials, can solve the problems of poor flame retardancy and high production costs of wood-plastic composite materials, and achieve the effects of cost saving, simple production methods, and environmental protection costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
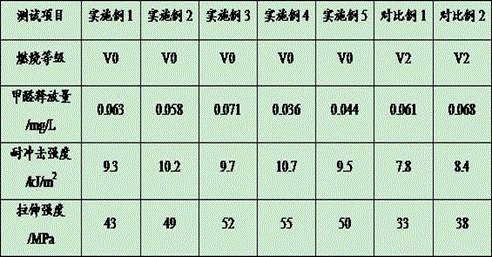
[0029] The degradable flame-retardant wood-plastic composite material described in this embodiment includes the following components by weight: 22 parts of waste polypropylene, 32 parts of waste low-density polyethylene, 10 parts of nano-kaolin, 8 parts of polyhydroxybutyrate, poly 5 parts of ethylene glycol naphthalate, 11 parts of modified cotinus wood powder, 7 parts of shell powder, 6 parts of glass fiber, 8 parts of quartz fiber, 4 parts of bornyl acetate, 3 parts of itaconic acid, 2 4 parts of disodium acid, 7 parts of ethylene bis stearic acid amide, 4 parts of composite flame retardant, 1 part of titanate coupling agent, and 2 parts of stabilizer;
[0030] The composite flame retardant is a mixture of antimony trioxide, ferrocene and magnesium oxide in a weight ratio of 2:1:1;
[0031] The stabilizer includes calcium stearate, antioxidant DLTP and ultraviolet absorber UV-1084 in a weight ratio of 5:2:1.
[0032] The preparation method of the degradable flame-retardant...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The degradable flame-retardant wood-plastic composite material described in this embodiment includes the following components by weight: 37 parts of waste polypropylene, 45 parts of waste low-density polyethylene, 18 parts of nano-kaolin, 15 parts of polyhydroxybutyrate, poly 13 parts of ethylene glycol naphthalate, 20 parts of modified cotinus wood powder, 16 parts of shell powder, 14 parts of glass fiber, 17 parts of quartz fiber, 10 parts of bornyl acetate, 8 parts of itaconic acid, 2 9 parts of disodium acid, 15 parts of ethylene bis stearic acid amide, 9 parts of composite flame retardant, 3 parts of aluminate coupling agent, and 5 parts of stabilizer;
[0040] The composite flame retardant is a mixture of antimony trioxide, ferrocene and magnesium oxide in a weight ratio of 2:1:1;
[0041] The stabilizer includes calcium stearate, antioxidant DLTP and ultraviolet absorber UV-1084 in a weight ratio of 5:2:1.
[0042] The preparation method of the degradable flame-...
Embodiment 3
[0049] The degradable flame-retardant wood-plastic composite material described in this embodiment includes the following components by weight: 30 parts of waste polypropylene, 38 parts of waste low-density polyethylene, 14 parts of nano-kaolin, 12 parts of polyhydroxybutyrate, poly 9 parts of ethylene glycol naphthalate, 16 parts of modified cotinus wood powder, 12 parts of shell powder, 10 parts of glass fiber, 12 parts of quartz fiber, 7 parts of bornyl acetate, 5 parts of itaconic acid, 2 6 parts of disodium acid, 11 parts of ethylene bis stearic acid amide, 6 parts of composite flame retardant, 2 parts of silane coupling agent, 3 parts of stabilizer;
[0050] The composite flame retardant is a mixture of antimony trioxide, ferrocene and magnesium oxide in a weight ratio of 2:1:1;
[0051] The stabilizer includes calcium stearate, antioxidant DLTP and ultraviolet absorber UV-1084 in a weight ratio of 5:2:1.
[0052] The preparation method of the degradable flame-retardant...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| impact strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com