Biological ink material for 3D printing and preparation method and application thereof
A bio-ink and 3D printing technology, applied in additive processing, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of immature biological 3D soft tissue printing technology, slow cellularization and vascularization, low immunogenicity of dermal matrix, etc. , to achieve vascularization and overall performance improvement promotion, promote adhesion growth, and achieve individual targeted effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The bio-ink material used for 3D printing described in this embodiment is prepared from the following raw materials by mass concentration percentage:
[0044] Biomacromolecule 5%
[0045] Water 93.5%
[0046] Coagulant 1.5%.
[0047] And the above-mentioned bio-ink materials will be washed and cross-linked to shape after printing.
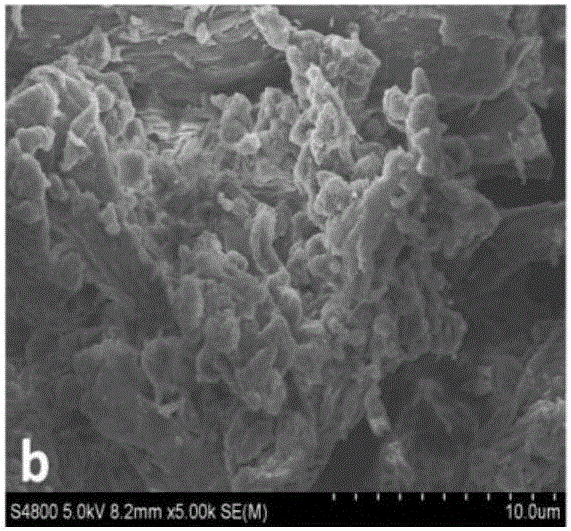
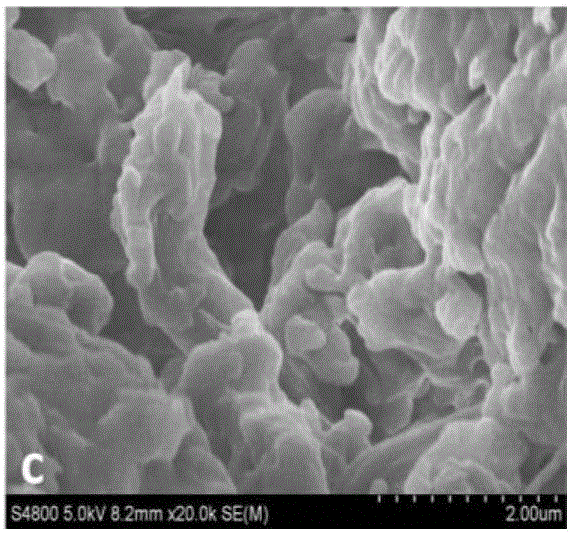
[0048] The biomacromolecule is pig dermis-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder.
[0049] The water is ultrapure water.
[0050]The coagulant is hydrochloric acid solution, and the molar concentration of hydrochloric acid is 3mol / L.
[0051] A preparation method for a bio-ink material for 3D printing is carried out as follows: at normal temperature, use an electronic analytical balance to weigh the biomacromolecule (i.e. pig dermis-derived ECM nanofiber micropowder) in a beaker, Add the formula amount of ultrapure water, then add a small magnetic bead, place the entire beaker on a magnetic stirrer, adjust the rotation speed to 8...
Embodiment 2
[0060] The characteristics of this embodiment are: the bio-ink material used for 3D printing described in this embodiment is prepared from the following raw materials in terms of mass concentration percentage:
[0061] Biomacromolecule 18%
[0062] Water 76%
[0063] Coagulant 6%.
[0064] And the above-mentioned bio-ink material ink will be washed and cross-linked to shape after printing.
[0065] The biomacromolecule is pig dermis-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder.
[0066] The water is ultrapure water. The coagulant is hydrochloric acid solution, and the molar concentration of hydrochloric acid is 3mol / L.
[0067] The crosslinking agent is glutaraldehyde solution, and the mass concentration of glutaraldehyde is 10%.
[0068] The difference in its preparation method is that the pH is adjusted to 1 during gelation, and other specific operation steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0070] The characteristics of this embodiment are: the bio-ink material for 3D printing described in this embodiment is prepared from the following raw materials in terms of mass concentration percentage:
[0071] Biomacromolecules 8.5%
[0072] water 90%
[0073] Coagulant 1.5%.
[0074] And the above-mentioned bio-ink material ink will be washed and cross-linked to shape after printing.
[0075] The biomacromolecule is pig dermis-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder.
[0076] The water is ultrapure water.
[0077] The coagulant is hydrochloric acid solution, and the molar concentration of hydrochloric acid is 3mol / L.
[0078] The crosslinking agent is glutaraldehyde solution, and the mass concentration of glutaraldehyde is 10%.
[0079] Other specific operation steps are the same as embodiment 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com