Method and device for treating nitrobenzene wastewater through ultrasonic wave/iron-carbon micro-electrolysis-Fenton oxidation method
A technology of nitrobenzene wastewater and iron-carbon micro-electrolysis, applied in water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, multi-stage water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of reduced treatment efficiency, weakened anode reaction, low efficiency, etc. Achieve the effect of increasing reaction rate, reducing H2O2, and removing easy passivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
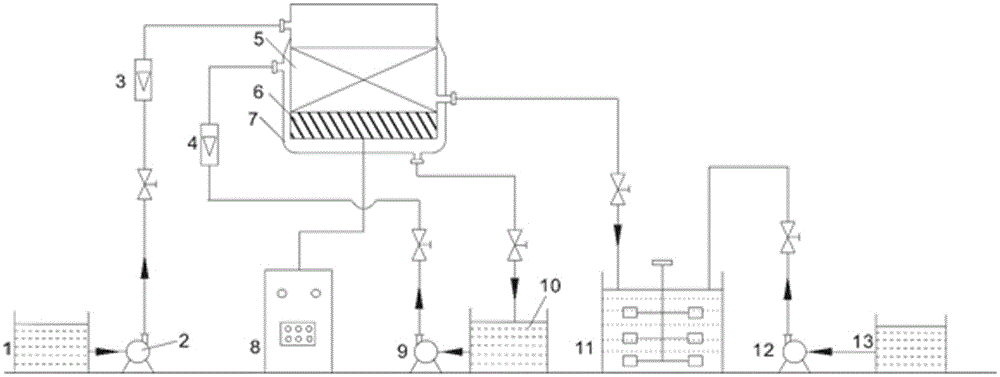
[0032] Example 1: Using figure 1 The flow chart of the device shown is for the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. The concentration of nitrobenzene in the water sample is 350 mg / L, and the pH value is 2. Inject 2 cubic meters of nitrobenzene wastewater into the micro-electrolyzer, the concentration of scrap iron is 10g / L, the mass ratio of iron to carbon is 1:1, the ultrasonic output power is 6kW, and the flow rate of cooling water circulating inside and outside the jacket is 45L / h , reacted for 40 min, 90% of nitrobenzene was reduced to aniline, the reaction rate was 8 times higher than that of the traditional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, and the free Fe in the wastewater 2+ Concentration increased by 6.8 times. At this time, inject the wastewater in the micro-electrolyzer into the stirred reaction tank, and add H at the same time 2 o 2 The concentration is 0.025mol / L, the stirring rate of the agitator is 200 rpm, and after 25 minutes of reaction, ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2: Using figure 1 The flow chart of the device shown is for the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. The concentration of nitrobenzene in the water sample is 500 mg / L, and the pH value is 3. Inject 2 cubic meters of nitrobenzene wastewater into the micro-electrolyzer, the concentration of scrap iron is 30 g / L, the mass ratio of iron to carbon is 3:1, the ultrasonic output power is 8kW, and the flow rate of cooling water circulating inside and outside the jacket is 25 L / h, reacted for 40 min, 96% of nitrobenzene was reduced to aniline, the reaction rate increased by 10 times compared with the traditional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, and the free Fe in the wastewater 2+ Concentration increased by 8 times. At this time, inject the wastewater in the micro-electrolyzer into the stirred reaction tank, and add H at the same time 2 o 2 The concentration is 0.04mol / L, the stirring rate of the agitator is 300 rpm, and the mineralization rate of ...
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: Using figure 1 The flow chart of the device shown is for the treatment of wastewater containing nitrobenzene. The concentration of nitrobenzene in the water sample is 300mg / L, and the pH value is 4. Inject 2 cubic meters of nitrobenzene wastewater into the micro-electrolyzer, the concentration of scrap iron is 20 g / L, the mass ratio of iron to carbon is 1:3, the ultrasonic output power is 4kW, and the flow rate of cooling water circulating inside and outside the jacket is 25 L / h, reaction 35 min, 95% of nitrobenzene is reduced to aniline, the reaction rate is 6 times higher than the traditional iron-carbon micro-electrolysis method, and the free Fe in the wastewater 2+ Concentration increased by 5 times. At this time, inject the wastewater in the micro-electrolyzer into the stirred reaction tank, and add H at the same time 2 o 2 The concentration is 0.01mol / L, the stirring speed of the stirrer is 100 rpm, and after 30 minutes of reaction, the mineralizat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com