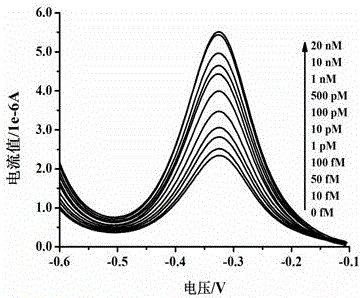
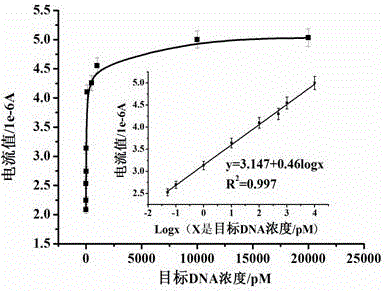
Method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and nucleic acid probe
An exonuclease and nucleic acid probe technology, applied in the field of electrochemical detection of specific single-stranded DNA concentration, can solve problems such as low sensitivity, radioactive contamination, and expensive detection instruments.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1. K-ras proto-oncogene fragment as the target DNA sequence to be detected.
[0035] K-ras gene is a proto-oncogene about 35kb long located on chromosome 12, the expression of this gene can regulate the normal growth of cells. Mutations in this gene will lead to abnormal cell growth, excessive cell proliferation and spread to cause cancer. According to statistics, the probability of K-ras gene mutation in patients with pancreatic cancer is as high as 90%-100%. K-ras gene mutations often occur in the early stage of canceration. The 12th codon base of the wild-type K-ras gene is GGT, and it is easy to mutate into GTT, GAT, GCT and other mutant types. GAT mutant type is the most common mutation. The type can be used as a marker to characterize pancreatic cancer. It is of great significance for the early screening of pancreatic cancer to develop a sensitive detection method using the gene fragment where the mutation site is located as the detection target sequence....
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2. Specificity Analysis of Electrochemical DNA Sensors
[0042] Still taking the above-mentioned K-ras proto-oncogene fragment as an example, replace the original target DNA with DNA with single-base mismatch and three-base mismatch to participate in the hybridization reaction, and the specific steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0043] The target DNA (TD) sequence is: 5'-TGGAGCTGGTGGCGTAGGCA-3'
[0044] The single base mismatch sequence is: 5'-TGGAGCTG A TGGCGTAGGCA-3'
[0045] The three-base mismatch sequence is: 5'-TGGAGCT CCA GGCGTAGGCA-3'
[0046] Compare the signal response in the presence of target DNA, single-base mismatch DNA, and triple-base mismatch DNA in the presence of three different DNAs. Such as Figure 4 , the sensor can produce a clear comparison of DPV signal intensity in the recognition of single-base mutation and three-base mutation sequence of the target DNA. Single-base (b) and triple-base mismatches (c) produce much lower signal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com