Semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor
A technology for semiconductors and devices, applied in the field of semiconductor devices and their preparation, can solve the problems of increasing parasitic gate-source capacitance and parasitic resistance, increasing parasitic gate-source capacitance and parasitic resistance, and increasing on-resistance, etc. Breakdown voltage, reduce parasitic gate-source capacitance and parasitic resistance, reduce leakage effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
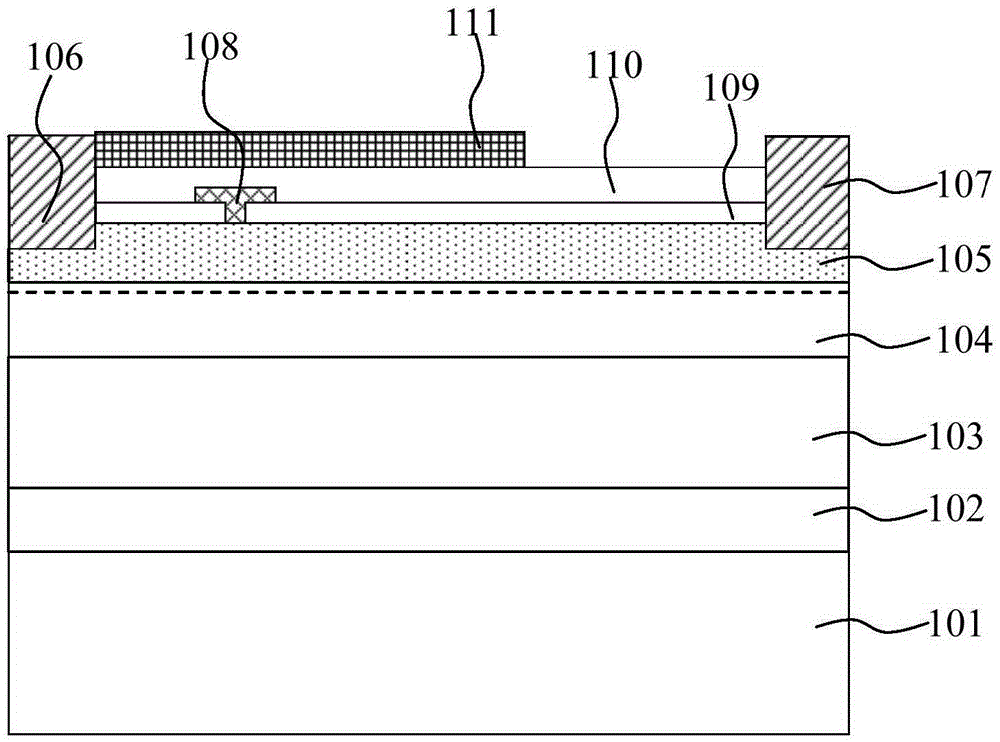
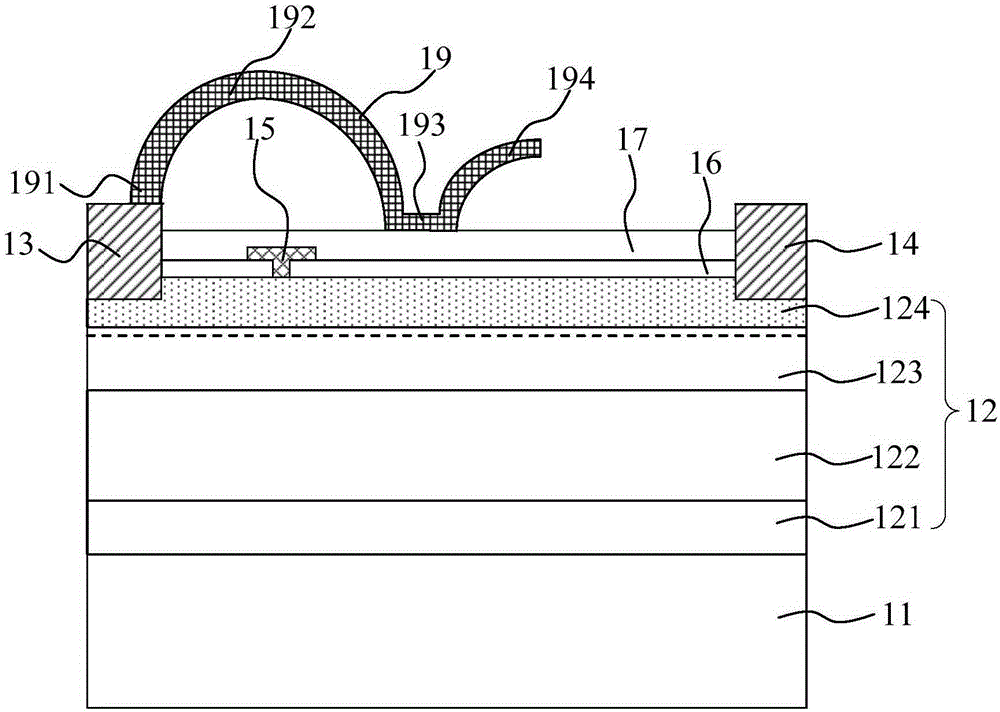
[0033] Figure 2a-Figure 2c is a schematic cross-sectional view of a semiconductor device with a dielectric layer provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, image 3 It is a top view of the semiconductor device provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as Figure 2a-Figure 2c As shown, the semiconductor device includes a substrate 11; a semiconductor layer 12 on the substrate 11; a source 13 on the semiconductor layer 12, a drain 14, and a gate 15 between the source 13 and the drain 14; The source field plate 19 located on the semiconductor layer 12 includes in turn an initial portion 191 electrically connected to the source level 13, a first intermediate portion 192 with air between the semiconductor layer 12, and covering between the gate 15 and the drain 14. The second middle portion 193 on the semiconductor layer 12 and the tail portion 194 where air exists between the semiconductor layer 12 . Wherein, the material of the source field plate 19 is a...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Figure 6 It is a schematic cross-sectional view of a semiconductor device with a sloped groove wall provided in Embodiment 2 of the present invention. This embodiment is optimized on the basis of the above-mentioned embodiments, as shown in Figure 6 As shown, the semiconductor device may include: a substrate 11; a semiconductor layer 12 on the substrate 11; a source 13 on the semiconductor layer 12, a drain 14, and a gate between the source 13 and the drain 14 15; the first dielectric layer 16 and the second dielectric layer 17 on the semiconductor layer 12; the groove 18 on the second dielectric layer 17 between the grid 15 and the drain 14, the groove 18 passes through the air bridge light Formed by a self-aligned etching process; the source field plate 19 located on the second dielectric layer 17, the initial portion 191 of the source field plate 19 is electrically connected to the source 13, and the first middle portion 192 of the source field plate 19 is connecte...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Figure 8 A schematic cross-sectional view of a semiconductor device in which the dielectric layer is one layer provided for Embodiment 3 of the present invention, as shown in Figure 8 As shown, this embodiment is based on the above-mentioned embodiments, and the second dielectric layer 17 is removed, which is equivalent to the gate region, the region between the gate and the source, and the second part of the region between the gate and the drain. Dielectric layer 17 is replaced by air of equal thickness, can further reduce parasitic capacitance and parasitic resistance like this, groove 18 is etched on the first dielectric layer 16 simultaneously, covers the second middle part 193 distances in groove 18 The closer the electric field area, the more effective the modulation of the electric field between the gate and the drain is.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com