A strain of bacteria that efficiently degrades glyphosate
A glyphosate, bacterial technology, applied in the field of environmental biology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] [Example 1] Screening of efficient glyphosate pesticide degrading bacteria
[0024] The experimental soil and water samples were collected from the rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil samples around the new plant of Qinong Chemical Co., Ltd., Qizhou Town, Hubei Province, and the water samples were also collected from 5 drainage outlets of the plant. After the water samples were collected, they were immediately stored in the laboratory at -20°C to kill insects, plant tissues and some viruses in the soil. After 10 hours of treatment, it was thawed at 4°C, and the excess soil samples were stored in a 4°C refrigerator. Take 10g soil sample or 10mL water sample, add 100mL sterilized liquid enrichment medium (containing sterile glass beads) (enrichment medium composition: peptone 10g / L, NaCl 1.0g / L, KH 2 PO 3 1.0g / L, pH=7), shaking at 150rpm for 7 days. After culturing for 1 week, take 10 mL of the culture solution in the enriched medium, add them to the enriched medium ...
Embodiment 2
[0025] [Example 2] identification of bacterial strains
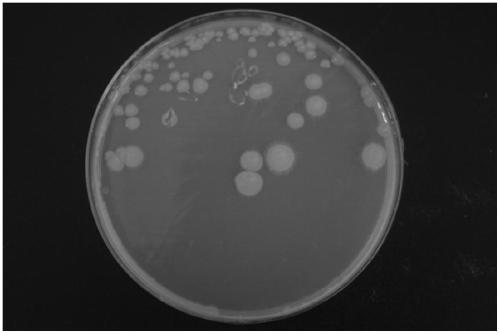
[0026] Inoculate the purified strain on solid LB medium (ingredients: tryptone 10g / L, yeast extract 1g / L, NaCl 1g / L, agar 20g / L, pH=7) and culture for 5 days to observe the colony of the strain on the solid plate Morphological characteristics: the colony is round, opaque, the diameter of the mature colony is about 0.8cm, light yellow to yellow, the colony is moist and sticky and easy to pick (such as figure 1 shown).
[0027] The physical and chemical properties of the strains were identified mainly by reference to the Physiological and Biochemical Tests of Berger Bacteria Identification. Record the results in a form.
[0028] Table 1: Physiological and biochemical assays of bacteria YU 1-1
[0029]
[0030] Note: "+" indicates a positive result after 5 days of culture, and "-" indicates a negative result
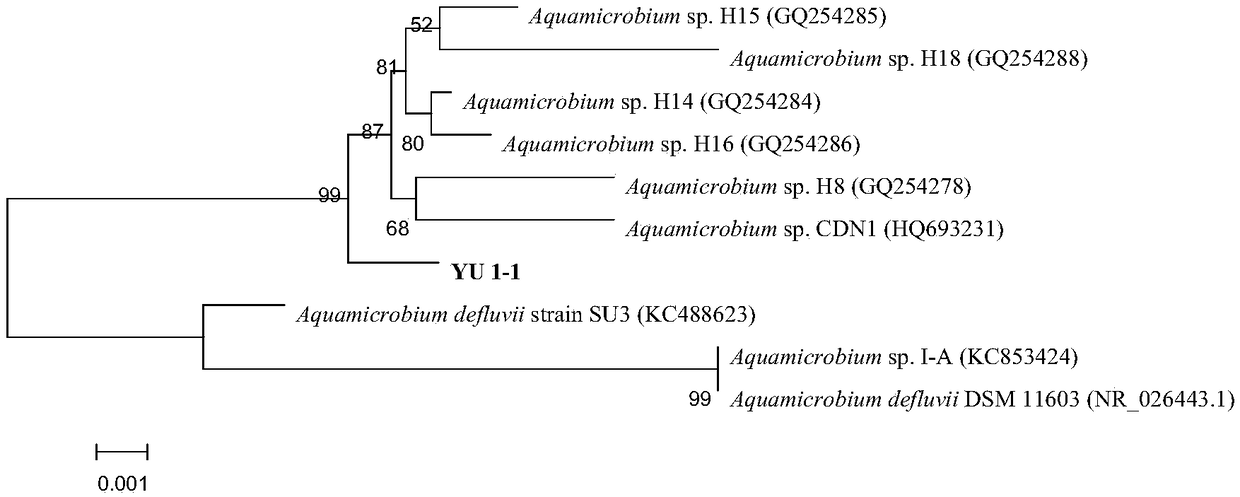
[0031] Bacterial 16S rDNA sequencing included strain DNA extraction, 16S rDNA amplification in vitro (using ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] [Example 3] Degradation rate analysis of bacterial strains to glyphosate
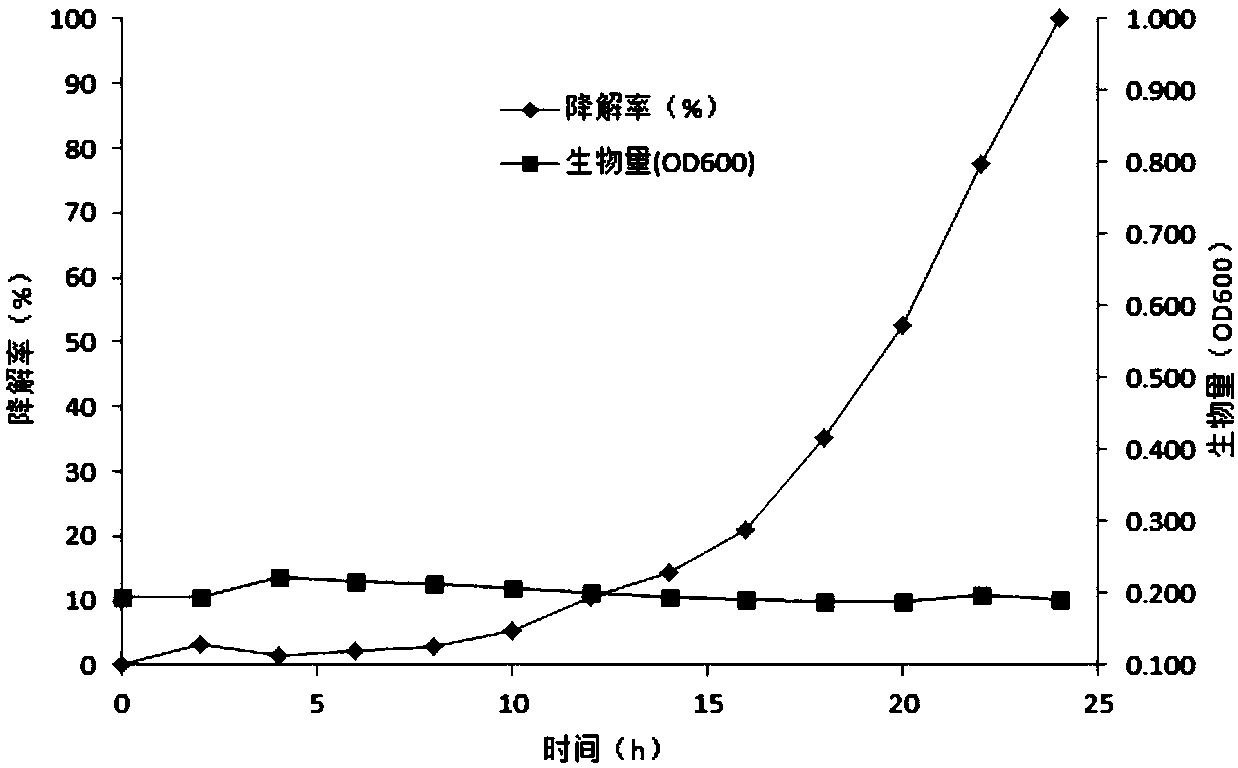
[0033] 1. Construction of degradation kinetic model
[0034] Liquid MSM medium was used, and the final concentration after adding glyphosate pesticide was set at 100mg / L. Before the determination, inoculate the strain in LB liquid medium for activation, activate and cultivate at 180rpm at 37°C for 24 hours, then take 2mL of the activated culture medium and measure the OD 600 Value, then add 2ml of sterile distilled water to make a uniform bacterial suspension, and add it to the medium at a volume ratio of 10%. All the cultures were shaken at 180rpm at 28°C for 24 hours, and the glyphosate content and strain OD in the supernatant were measured every 2 hours. 600 value, the supernatant was diluted, nitrosated to constant volume, filtered, and the residual amount of glyphosate was determined by the reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography analysis method. According to the change of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com