Lactobacillus plantarum having anti-diabetic function and application thereof
A technology of Lactobacillus plantarum and anti-diabetes, which is applied in the biological field and can solve problems such as large differences in probiotic activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
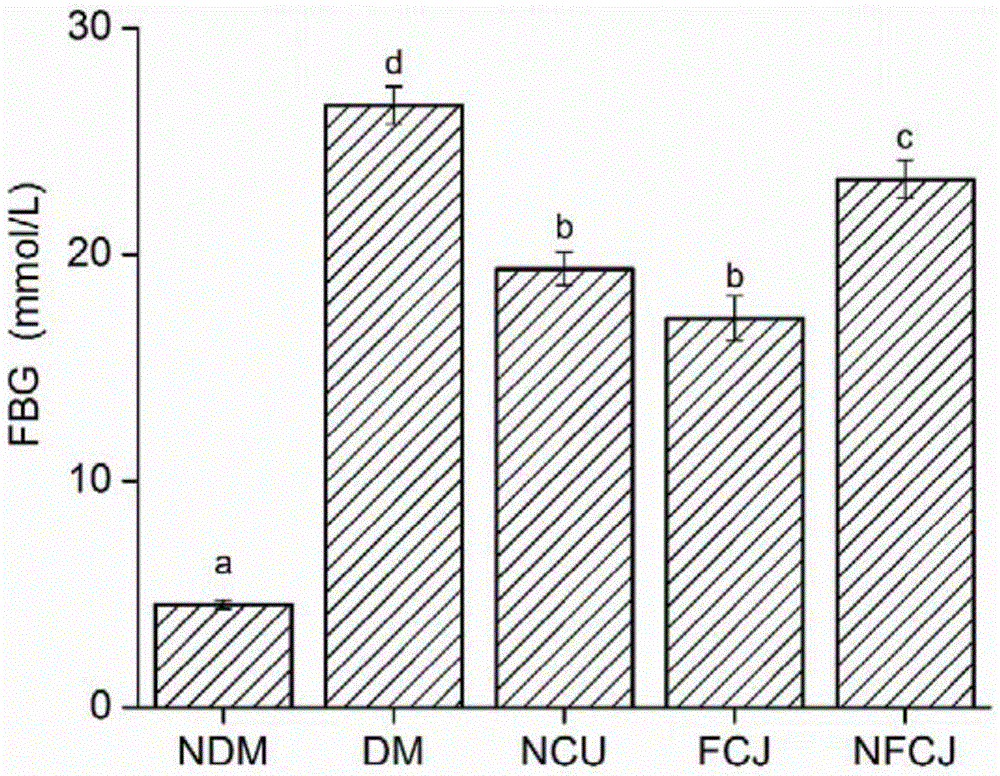
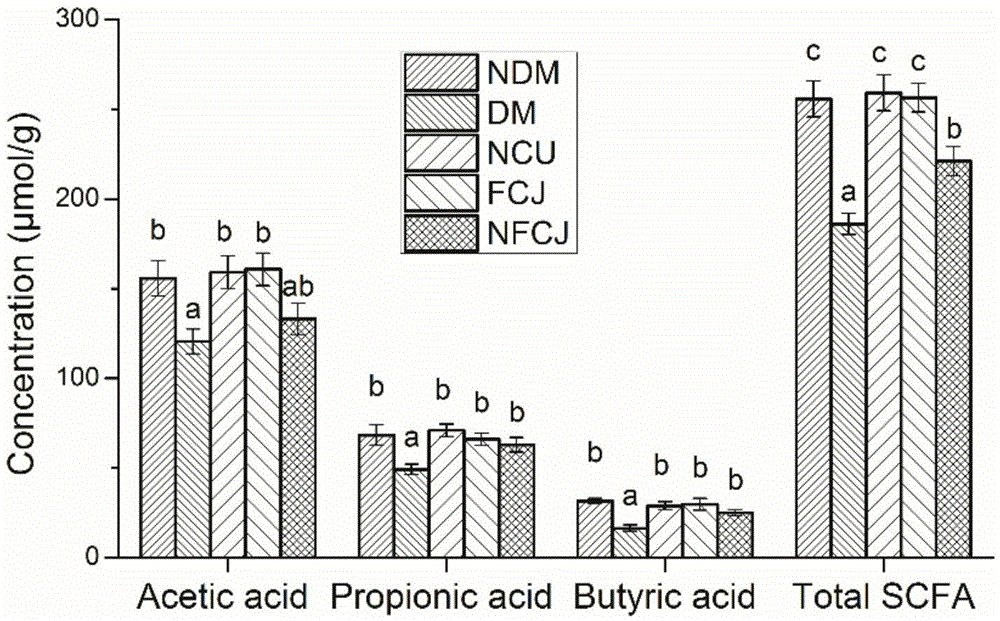
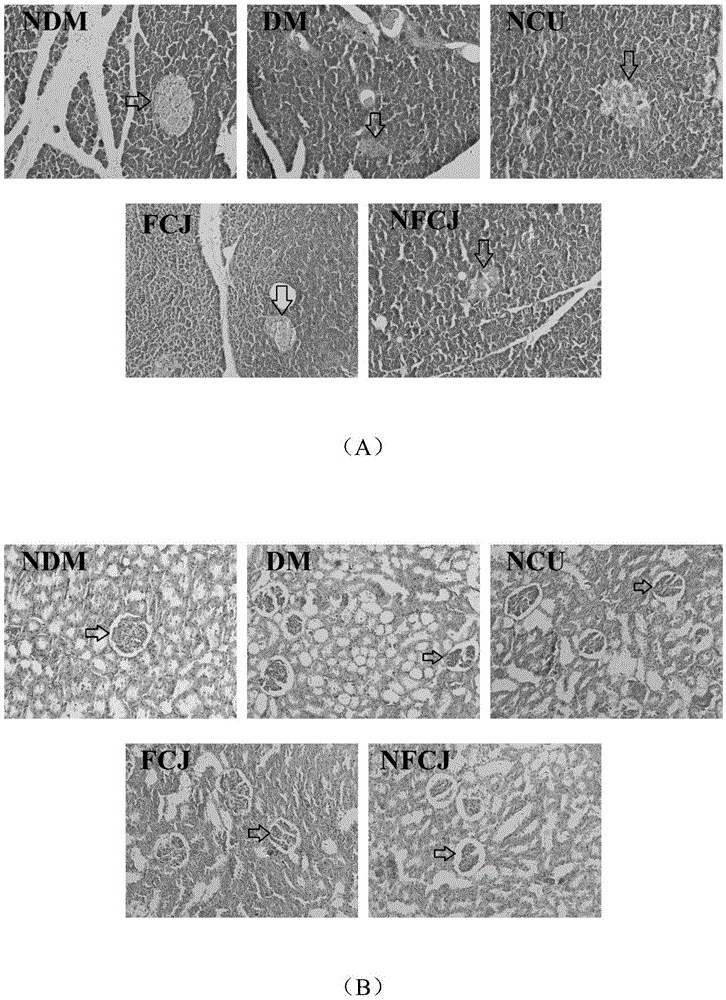
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Screening and preservation of bacterial strains.
[0029] The Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 of the present invention is obtained by separation and screening from traditional Chinese kimchi old liquid, and the specific separation and identification steps are as follows:
[0030] (1) Isolation and cultivation of strains.
[0031] The traditional Chinese kimchi old solution from different sources was inoculated into the vegetable juice enrichment medium according to the inoculum amount of 3%, and anaerobically cultured at 37°C for 24h. Pipette 1mL of the vegetable juice enrichment culture solution, adopt the 10-fold gradient dilution method, select an appropriate dilution, spread it on the primary screening plate medium, and culture it anaerobically at 37°C for 48 hours. , large colonies, and large yellow bacterial circles. The strains selected by the primary screening were transferred to the secondary screening plate medium and cultured anaerobically at 37°C...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Gastrointestinal tolerance test of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116.
[0051] By simulating the human digestive tract environment, the survival ability of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 in the gastrointestinal tract was explored, so as to provide a reference for whether this strain of lactic acid bacteria can play a health-promoting role in the human digestive tract environment.
[0052] (1) Artificial gastric juice tolerance.
[0053] Take the freeze-dried bacterial powder of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116, inoculate 1% of the inoculum into artificial gastric juice with pH values of 1.5, 2.5, 3.5 and 4.5, mix well, and shake at 100r / min at 37°C Cultivate, take samples after 0, 1, 2 and 3 hours respectively, count live lactic acid bacteria, and measure the light transmittance at a wavelength of 600nm.
[0054]
[0055] (2) Tolerance of artificial intestinal juice.
[0056] Take the freeze-dried bacterial powder of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116, inoculat...
Embodiment 3
[0063] Example 3: Adhesion performance test of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116.
[0064] Simulating the human intestinal environment, the in vitro cell model human colon cancer cell line HT-29 was used to investigate the adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116, and the effects of different factors on the adhesion of NCU116 to HT-29 were studied. The human intestinal environment is neutral, so the sterile PBS buffer solution with pH 7.30 is used to simulate the intestinal environment, and the bacterial concentration is adjusted to 1.0×10 8 CFU / mL, co-incubated with HT-29 cells for 2.0 hours in an anaerobic incubator at 37°C, the number of adhered bacteria was 4.78±0.21CFU / cell (number of adherent bacteria / HT-29), the adhesion ability of Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 strong.
[0065] (1) Use sterile PBS buffer (pH7.30) to adjust the concentration of bacteria to 1×10 5 , 1×10 6 , 1×10 7 , 1×10 8 , 1×10 9 CFU / mL, co-incubated with the cells for 2.0h, calculated the number...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com