Glucooligosaccharide and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of oligoglucosaccharide and glucose, which is applied in the field of agricultural application, can solve the problems of long enzymatic hydrolysis cycle, low efficiency and high production cost, and achieves the effects of low cost, simple preparation process, and easy separation and purification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
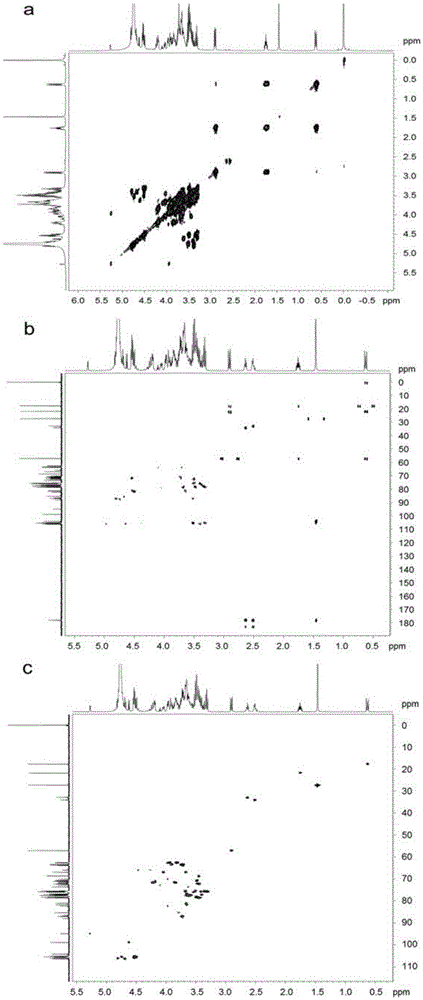
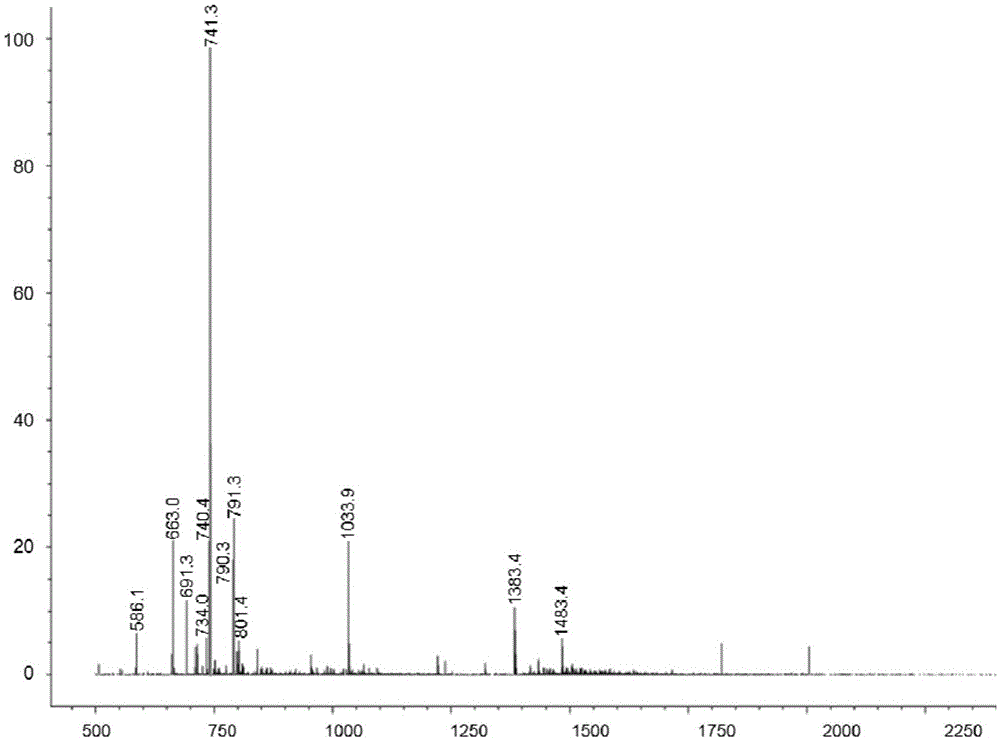
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] This example illustrates the method of obtaining glucooligosaccharides through mixed culture and fermentation of Agrobacterium ZX09 and Paenibacillus S09.
[0033] a. Preparation of seed liquid: Inoculate a single colony of ZX09 bacteria into an inorganic salt-sucrose liquid medium, and culture it with shaking at 30°C for 24 hours. The medium composition is: 20g sucrose, 0.5g sodium nitrate, 0.5g potassium dihydrogen phosphate, Anhydrous calcium chloride 0.1g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.3g, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.02g, zinc chloride 0.003g, manganese sulfate 0.001g, water 1000mL, pH7.0. Autoclave at 121℃ for 20min. Inoculate a single colony of S09 bacteria into LBO liquid medium, shake and culture at 35°C for 24h, the medium composition is 0.5g of sodium chloride, 0.5g of yeast extract, 1.0g of peptone, 0.5g of oat flour, and sterilize by high pressure steam at 121°C 20min.
[0034] b. Mixed bacteria culture: Inoculate the seed liquid of the cultivated ZX0...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Preparation of oligoglucose derivatives.
[0039] Prepare the purified oligosaccharides into 10mg / mL aqueous solution, add NaOH with a final concentration of 0.2M to react for 2-5h, neutralize with HCl, desalt through SephadexG25, collect the eluted peak samples of oligosaccharides, and obtain the removal Oligodextrose derivative II with succinyl modification group. The purified oligoglucose was prepared into an aqueous solution of 10 mg / mL, added HCl with a final concentration of 0.5M to react for 5 hours, neutralized with NaOH, desalted through SephadexG25, collected eluted peak samples of oligoglucose, and obtained amber removal at the same time Acyl- and pyruvate-modified oligodextrose derivatives III.
Embodiment 3
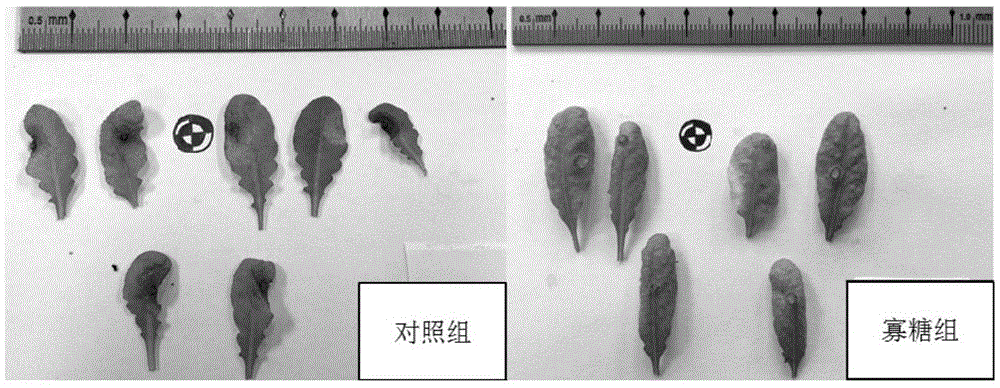
[0041] Control of Botrytis cinerea infection in Arabidopsis by gluco-oligosaccharides.
[0042] Prepare a 0.2-1.0 g / L gluco-oligosaccharide aqueous solution, and spray evenly on the leaves of Arabidopsis plants that have grown to a suitable size, spray once a day, and spray with clear water as a control. Two days after the pretreatment of the gluco-oligosaccharide, the cultured Botrytis cinerea was punched on the solid medium, and the mold agar block was pasted on the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana for infection culture. After 1-3 days, observe the degree of infection of the leaves of the plants in the control group and the gluco-oligosaccharide group.
[0043] The results showed that spraying the gluco-oligosaccharide solution in advance could reduce the infection rate of Arabidopsis plant leaves, and the plaques of the bacteria were significantly smaller. image 3 Shown are the leaves of Arabidopsis plants after spraying clear water and spraying 0.5g / L gluco-oligosaccharide...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com