Method for Transformation and Expansion of Double Negative T Cells
A double-negative, cell-based technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biological preparations for removing bad cells, animal cells, etc., can solve the problems of small number of initial DNT cells, influence of DNT cell immune function, long culture time, etc. Achieve significant immunosuppressive function, prevention and treatment of autoimmune diseases, and short culture period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 Expansion and transformation method of DN T cells according to the present invention
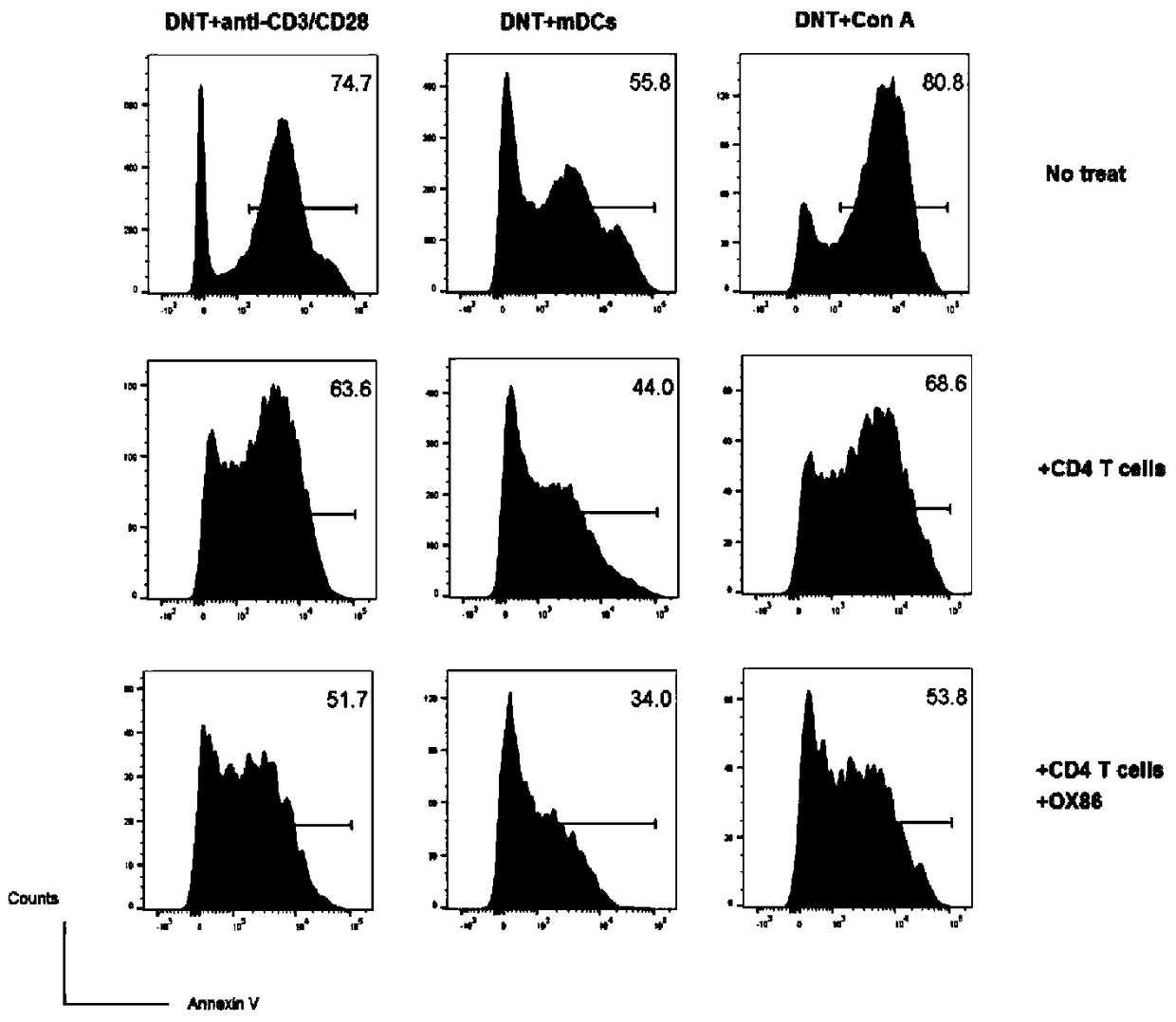
[0047] (1) Obtain EDTA anticoagulated whole blood from C57BL / 6 mice, and separate peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) with lymphocyte separation medium. Lymph nodes and spleens of C57BL / 6 mice were separated, ground and filtered through a 70um filter, and erythrocytes were lysed with erythrocyte lysate to obtain mononuclear cells (spleen cells, Splenocytes). Depletion of CD8 in mononuclear cells by immunomagnetic bead negative selection + T cells (anti-CD8 antibody-magnetic bead sorting, to remove CD8 positive cells) and NK cells (anti-NK1.1 antibody-magnetic bead sorting, to remove NK cells), but without CD4 isolation + T cells, and there is no need to isolate native DN T cells. like figure 1 As shown, the left column is the composition of initial T lymphocytes, and the right column is the composition of T lymphocytes after negative selection of CD8 and NK cells...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2 Expansion and transformation method of DN T cells according to the present invention
[0051] (1) Lymph nodes and spleens of C57BL / 6 mice were separated, ground and filtered through a 70um filter, and red blood cells were lysed with red blood cell lysate to obtain mononuclear cells. Depletion of CD8 in mononuclear cells by immunomagnetic bead negative selection + T cells (anti-CD8 antibody-magnetic bead sorting, to remove CD8 positive cells) and NK cells (anti-NK1.1 antibody-magnetic bead sorting, to remove NK cells), but without CD4 isolation + T cells, and there is no need to isolate native DN T cells.
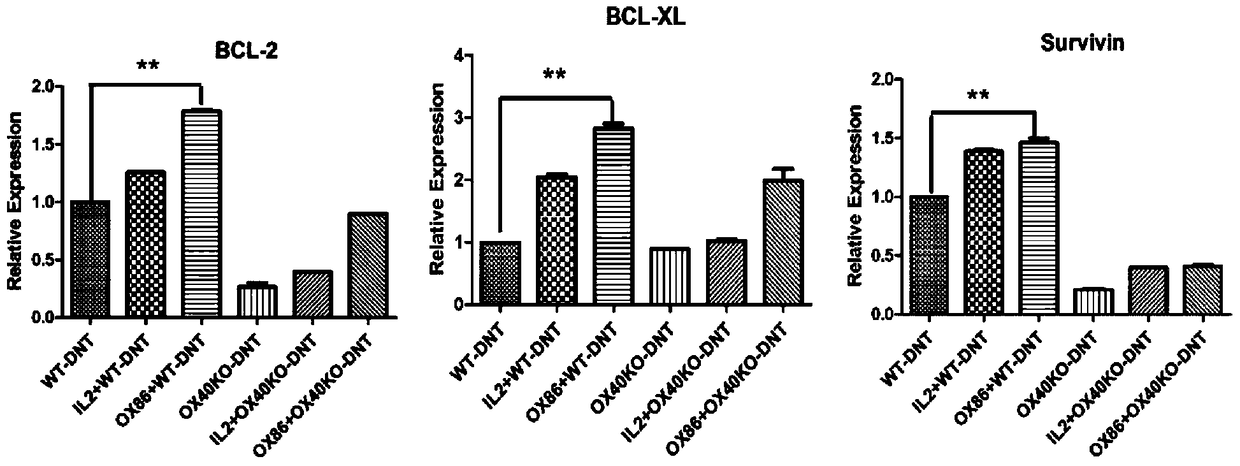
[0052] (2) The mixed cells separated by negative selection in step (1) were stimulated to proliferate with mature dendritic cells in vitro (the ratio of mature dendritic cells to the mixed cells in step (1) was 1:4, and OX40 was added at the same time Activation antibody OX86, 100ug / ml and IL-220ng / ml. Culture selection 1640 medium + 10% fetal bovine se...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3 Expansion and transformation method of DN T cells according to the present invention
[0055] (1) Lymph nodes and spleens of C57BL / 6 mice were separated, ground and filtered through a 70um filter, and red blood cells were lysed with red blood cell lysate to obtain mononuclear cells. Depletion of CD8 in mononuclear cells by immunomagnetic bead negative selection + T cells (anti-CD8 antibody-magnetic bead sorting, to remove CD8 positive cells) and NK cells (anti-NK1.1 antibody-magnetic bead sorting, to remove NK cells), but without CD4 isolation + T cells, and there is no need to isolate native DN T cells.
[0056] (2) The mixed cells separated by negative selection in step (1) are stimulated to proliferate in vitro with CD3 / CD28 antibody (the dosage of CD3 antibody is 5ug / ml, and in another embodiment the dosage is 1ug / ml; the dosage of CD28 antibody is 2ug / ml, in another embodiment, the amount used is 0.5ug / ml;), while adding the OX40 activation antibody...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com