Technology for preparing tribasic copper chloride and tetrabasic zinc chloride by utilization of brass slag and zinc-containing flue ash
A technology of copper chloride and zinc chloride, which is applied in the direction of copper chloride, copper halide, zinc halide, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in controlling pH, difficulty in controlling the end point, increasing the difficulty and cost of wastewater treatment, and improving the utilization , The effect of reducing processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
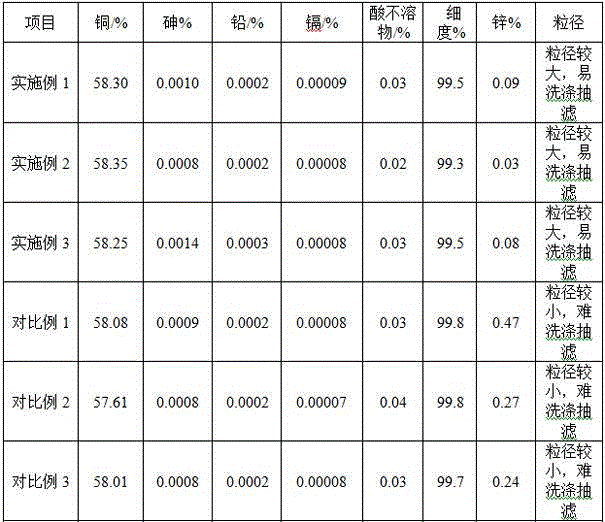
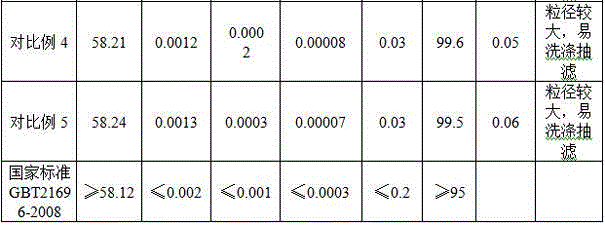
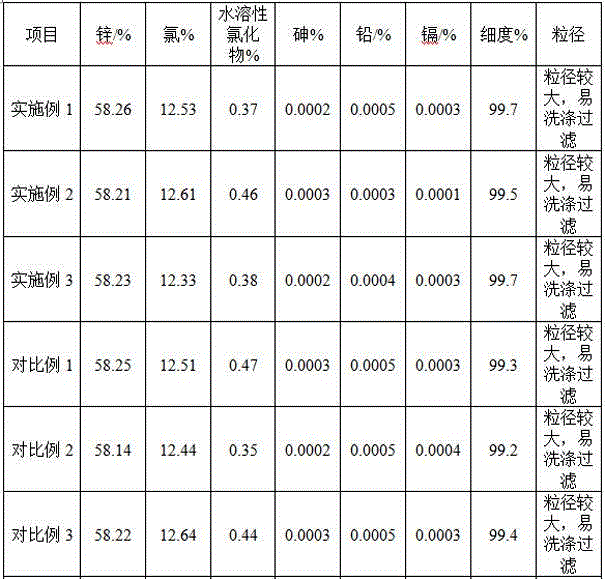
[0063] S12. Mix the above filter residue with 505g brass slag containing 28.36% copper and 39.55% zinc, then add 1600mL31% hydrochloric acid, stir for 1 hour under the condition that the circulating cooling water keeps the reaction temperature below 40°C, and slowly add 250mL hydrogen peroxide , keep the reaction temperature below 40°C. Suction filter and rinse the filter residue, and mix the obtained filtrate with washing water, which is about 2500mL copper-zinc mixed acid solution, containing 60.8g / L copper and 80g / L zinc.
[0064] S21. Adjust the pH of the copper-zinc mixed acid solution to 1 with 1840 mL of ammonia etching waste liquid containing 90 g / L of copper, then add an appropriate amount of impurity remover, and react for 20 minutes to remove toxic metals such as lead, arsenic, chromium, and mercury. Obtained 4330 mL of copper and zinc mixed solution after removing impurities, containing 73.33 g / L of copper and 46.18 g / L of zinc;
[0065] S22. React the copper-zinc...
Embodiment 2
[0070] S12. Mix the above filter residue with 776g brass slag containing 29.68% copper and 37.72% zinc, then add 3100mL31% hydrochloric acid, stir for 1.5 hours under the condition that the circulating cooling water keeps the reaction temperature below 40°C, and slowly add 580mL8% Sodium hypochlorite, keep the reaction temperature below 40°C. Suction filter and rinse the filter residue, and mix the obtained filtrate with washing water to form a copper-zinc mixture of about 3600mL, containing 76.75g / L copper and 81g / L zinc.
[0071] S21. Adjust the pH of the copper-zinc mixed solution to 1.5 with 20% ammonia water 2200mL, then add an appropriate amount of impurity remover, and react for 20 minutes to remove toxic metals such as lead, arsenic, chromium, mercury, etc., and obtain a mixed mixture of copper and zinc after impurity removal. Liquid 5800mL, containing copper 47.63g / L, zinc 50.27g / L;
[0072] S22. React the copper-zinc mixture after impurity removal with 1740mL of 5% ...
Embodiment 3
[0077]S12. Mix the above filter residue with 1060g brass slag containing 29.68% copper and 37.72% zinc, then add 5300mL31% hydrochloric acid, stir for 2 hours under the condition that the circulating cooling water keeps the reaction temperature below 40°C, and slowly add 1060mL27. 5% hydrogen peroxide, keep the reaction temperature below 40°C. Suction filter and rinse the filter residue, and mix the obtained filtrate with washing water to form a copper-zinc mixture solution of about 6800mL, containing 53.6g / L copper and 61.2g / L zinc.
[0078] S21. Adjust the pH of the copper-zinc mixture to 2 with 650mL of 50% sodium hydroxide solution, then add an appropriate amount of impurity remover, and react for 20 minutes to remove toxic metals such as lead, arsenic, chromium, mercury, etc., and obtain copper after impurity removal. , Zinc mixture 7400mL, copper 48g / L, zinc 56g / L;
[0079] S22. React the copper-zinc mixed solution after impurity removal with 1850mL of 4% ammonia water,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com