High-compactness boron carbide composite ceramic material preparation method
A technology of composite ceramics and boron carbide, which is applied in the field of preparation of boron carbide composite ceramic materials, can solve problems such as unclear function, large shrinkage, and heavy loss of green body
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The invention belongs to the field of preparation of special materials, and in particular relates to a method for preparing a boron carbide composite ceramic material. The formula contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of boron carbide powder; 20-50 parts of boride powder, 1-20 parts of transition metal carbide, preferably the content of the boride powder in the raw material powder is 20- 40 parts; 1-20 parts of transition metal oxide powder, preferably 2-6 parts; and according to the reduction reaction of transition metals, add carbon or precursor substances that can generate carbon, generally 1-15 parts, preferably The amount of addition should be determined according to calculation and experimental results; wherein: the average particle size of boron carbide powder is 0.1-3.0 microns, preferably 0.5-1 microns; the particle size of transition metal boride powders is 0.1-10 microns, preferably 1-5 microns. The above raw materials are mixed ...
Embodiment 1
[0048] Boron carbide powder 300 grams, average particle size 0.5 micron, titanium boride powder (d 50 =1μm) 90 grams, titanium oxide powder (d 50 =0.3 μm) 20 grams, 10 grams of carbon black powder, add 250 grams of absolute ethanol, ball mill for 2 hours, add 20 parts of 10% PVB aqueous solution, continue ball milling for 1 hour, dry, and pass through a 120 mesh sieve. The above-mentioned mixed powder is pressed into a 6×8×45mm test strip, sintered under the pressure of 0.01MPa argon gas, the holding temperature is 2120°C, and the holding time is 1 hour. Material density 2.70g / cm 3 (relative density 97%), strength 420MPa, hardness 33GPa, toughness 4.5MPa m 1 / 2 ;
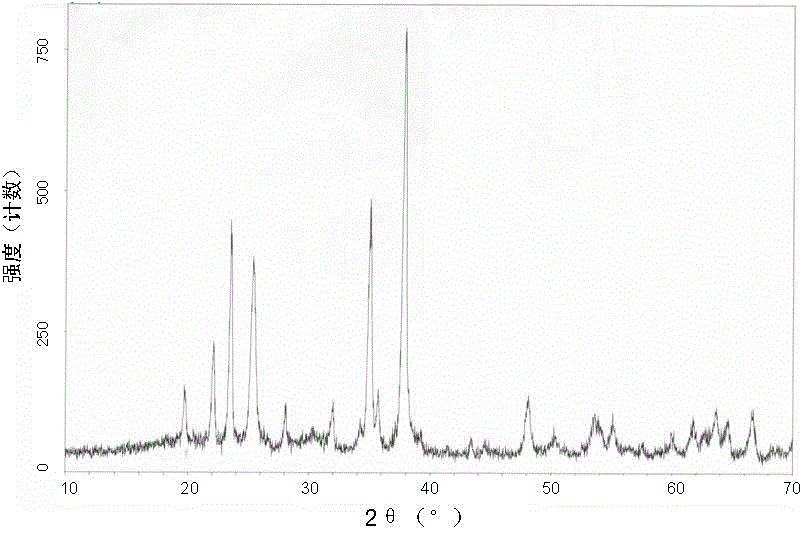
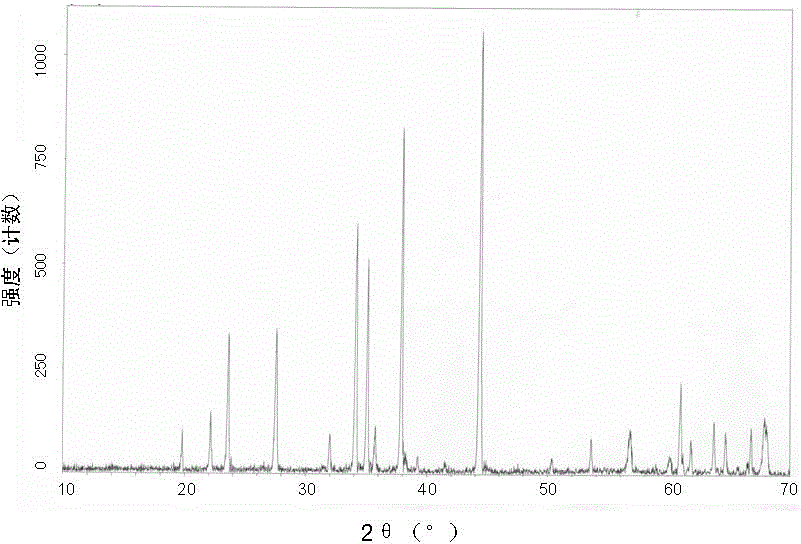
[0049] Figure 1a with Figure 1b The XRD patterns of the raw material powder and the prepared boron carbide composite ceramic material in Example 1 are shown respectively, and it can be seen from the figure that the components of the raw material are indeed composited to form ceramics after sintering.
Embodiment 2
[0053] 300 grams of boron carbide powder, average particle size 0.5 micron, vanadium boride powder (d 50 =1μm) 90 grams, titanium carbide powder (d 50 =2μm) 20 grams, zirconia powder (d 50 =1 μm) 20 grams, 10 grams of carbon black powder, add 300 grams of water, ball mill 2 hours, add 12 parts of 8% PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) aqueous solution, continue ball mill 1 hour, dry, cross 120 mesh sieves. The above-mentioned mixed powder is pressed into a test bar of 6×8×45 mm, sintered under vacuum condition, the holding temperature is 2100° C., and the holding time is 1 hour. Material density 2.75g / cm 3 , strength 410MPa, hardness 32GPa, toughness 4.9MPa m 1 / 2 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com