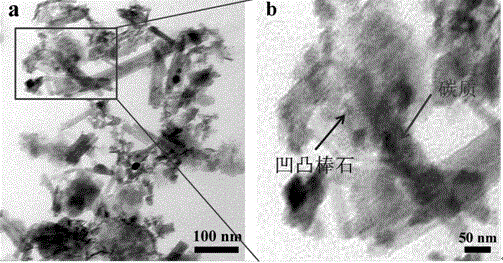
Method for preparing charcoal-supported attapulgite nano composite by using antibiotic wastewater
A technology for nanocomposite materials and antibiotic wastewater, applied in chemical instruments and methods, alkali metal compounds, alkali metal oxides/hydroxides, etc., can solve the problems of high operating costs, improve adsorption performance, realize reuse, improve The effect of adsorption performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
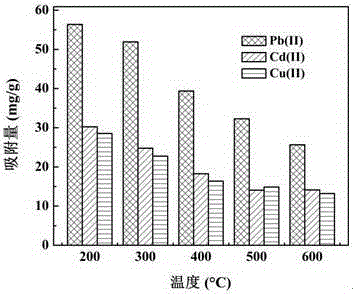
[0027] Under the condition of stirring at 200 rpm, 100kg of attapulgite clay was added to 1000L of the mixed solution of sulfuric acid and chloroacetic acid (the mass concentration of sulfuric acid was 0.6%, and the mass concentration of chloroacetic acid was 2.4%), stirred for 4 hours, and passed through a filter press. After pressure filtration, it is sent to a rotary kiln for calcination at 400°C for 2 hours, crushed, and treated with aureomycin-containing wastewater by dynamic adsorption for 24 hours (solid-liquid ratio is 1:10kg / L), and after pressure filtration, it is sent to a rotary kiln in a nitrogen atmosphere. , calcined and carbonized at 200°C for 1 h, and finally washed, dried, and sieved to obtain attapulgite nanocomposites loaded with biochar. The adsorption capacities of the composite for Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) were 56, 30 and 28 mg / g, respectively.
Embodiment 2
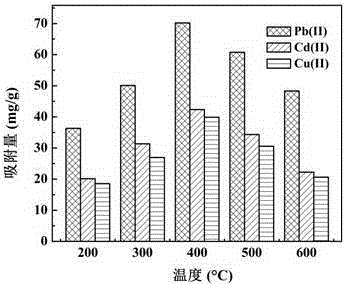
[0029]Under the stirring condition of 200 rpm, add 150kg of attapulgite clay into 1000L of the mixed solution of sulfuric acid and glycine (the mass concentration of sulfuric acid is 2%, the mass concentration of glycine is 8%), stir for 2 hours, and filter through the filter press After that, it is sent to the rotary kiln for calcination at 200°C for 1 hour, crushed, treated with oxytetracycline-containing wastewater by dynamic adsorption method for 12 hours (solid-liquid ratio is 1:15kg / L), and sent to the rotary kiln after pressure filtration, nitrogen atmosphere, 400 ℃ calcination and carbonization for 2 hours, and finally washed, dried, and sieved to obtain the attapulgite nanocomposite material loaded with biochar. The adsorption capacities of the composite for Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) were 70, 42 and 39 mg / g, respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Under the condition of stirring at 200 rpm, 200kg of attapulgite clay was added to 1000L of the mixed solution of sulfuric acid and glycine (the mass concentration of sulfuric acid was 4%, and the mass concentration of citric acid was 16%), stirred for 3 hours, and pressed by a filter press. After filtration, it is sent to the rotary kiln, calcined at 500°C for 2 hours, and after crushing, it is treated with wastewater containing tetracycline for 24 hours by dynamic adsorption method (solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:5kg / L), and then sent to the rotary kiln after pressure filtration. Roasting and carbonizing at 600°C for 4 hours, and finally washing, drying, and sieving to obtain the attapulgite nanocomposite material loaded with biochar. The adsorption capacities of the composite for Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cu(II) were 92, 48 and 45 mg / g, respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com