Applicaton method of scrap tires in process of steadily converting alga type lake into grass type lake
A waste tire conversion technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, coastline protection, etc., can solve the problems of increased water chaos, reduced transparency, and few engineering applications, and achieve ecological environment improvement , reduce the transmittance, and solve the effect of difficult rooting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
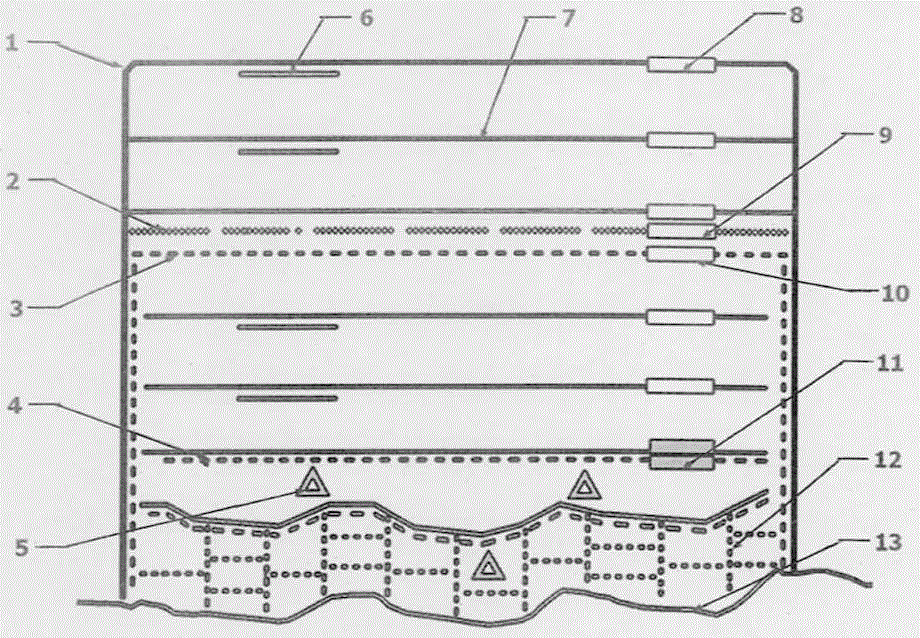
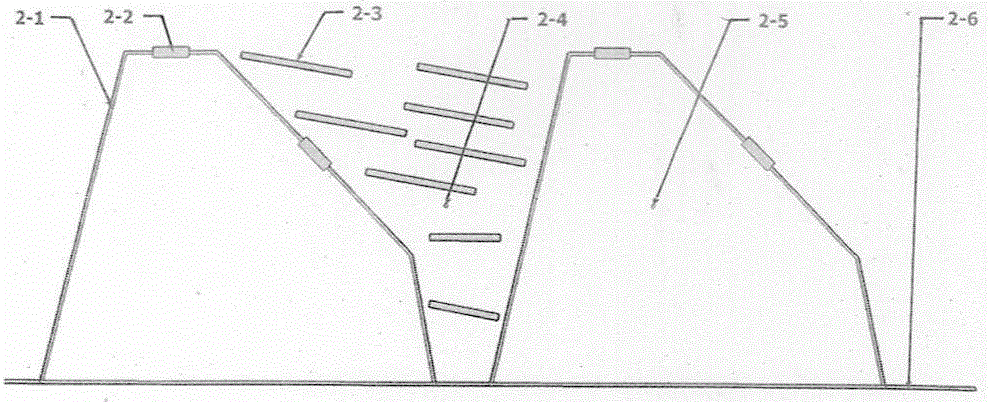
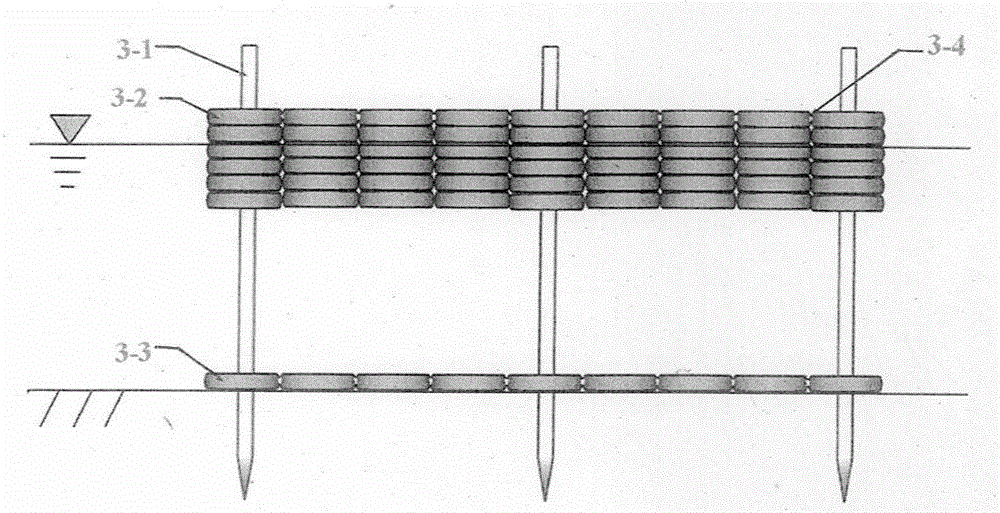
[0094] Avoid wharves, waterways and key waters, and set up multiple floating raft-type waste tire wave-dissipating belts in the entire shallow water area of the lake where waves need to be dissipated, and the distance between them is 50-250 meters; On one side of the raft-type waste tire wave-dissipating belt, 1-2 floating raft-type waste tire wave-dissipating belts with a width of 0.6-6.00 meters and a length of 50-150 meters are attached every 200-400 meters, thus forming a motorized floating Raft type waste tire wave dissipation belt; due to the influence of landform, wind direction and other reasons, the water dissipation between floating raft type waste tire wave dissipation belt, floating raft type waste tire wave dissipation belt and floating waste tire permeable breakwater There are still some wave-dissipation blind areas in the wave water area. After discovering the wave-dissipation blind area, untie the rope in time, transfer the motorized floating raft type waste t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com