Method for measuring antioxidant activity of lactic acid bacteria based on cellular level
A cell-level, lactic acid bacteria technology, applied in the field of microbiology, can solve problems such as animal difficulties, cumbersome operations, and inability to respond to physiological conditions, and achieve the effects of short exposure time, good repeatability, and high-efficiency research
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Determination of antioxidant capacity of Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus fermentum
[0035] 1 cell culture
[0036] Human hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) was grown in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium-high glucose (DMEM) medium (containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U / mL penicillin, 100 μg / mL streptomycin) environment, and at 37 °C, 5% CO 2 cultured under conditions. The number of generations of cells used in the present embodiment is 12-20 generations;
[0037] 2 Quercetin standard curve establishment
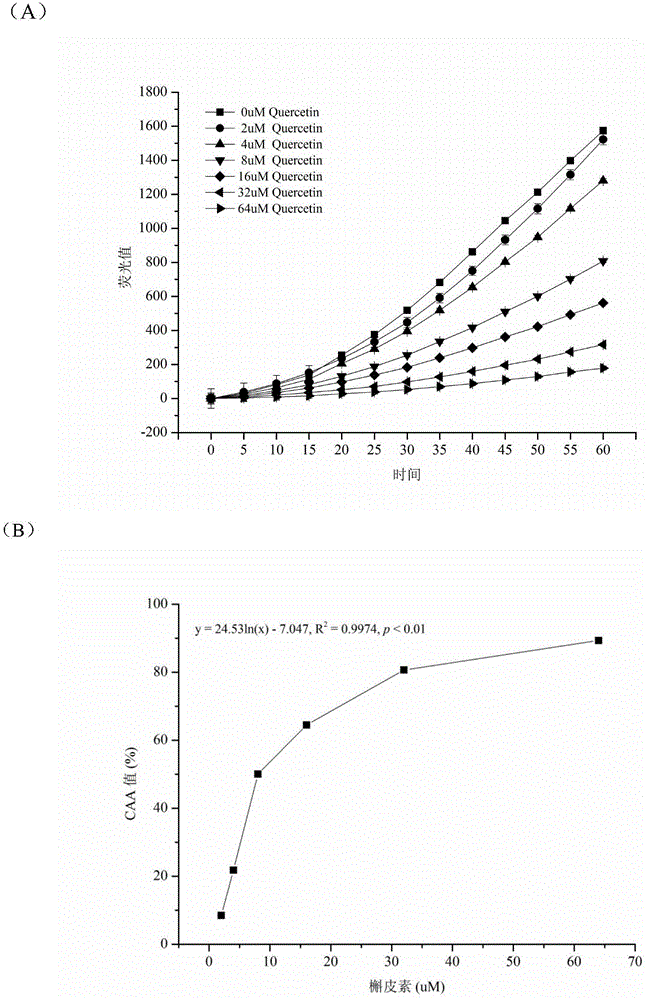
[0038] ① Accurately weigh quercetin [4H-1-Benzopyran-4-one,2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-Flavone], prepare mother solution (100μM) with 95% ethanol, and use Dilute the DMEM medium without antibiotics and fetal bovine serum into a reaction solution with gradient concentrations (2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 μM) to form a quercetin solution;
[0039] ② On a 96-well plate wit...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2 adopts the method for measuring the antioxidant capacity of different measures to measure the antioxidant capacity of lactic acid bacteria
[0055] 1 Determination of lactic acid bacteria DPPH scavenging free radical ability
[0056] Take 1 mL of the cell-free extract of lactic acid bacteria and add it to a test tube, then add 1 mL of 0.2 mmol / L DPPH-absolute ethanol solution, mix well, and react in the dark for 30 minutes, then take the supernatant and measure the absorbance at 517 nm to determine An equal volume of PBS was used as a control group instead of the sample solution.
[0057] Calculate according to the following formula: DPPH free radical scavenging rate=(1-A 517样品 / A 517对照 )×100%, where: A 517样品 and A 517对照 are the absorbance values measured at 517nm of the sample group and the control group, respectively
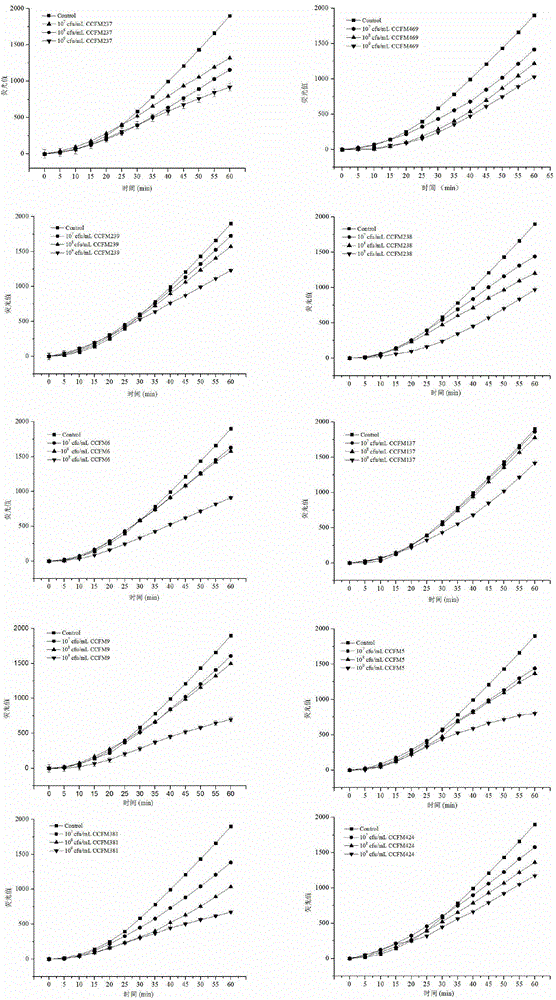
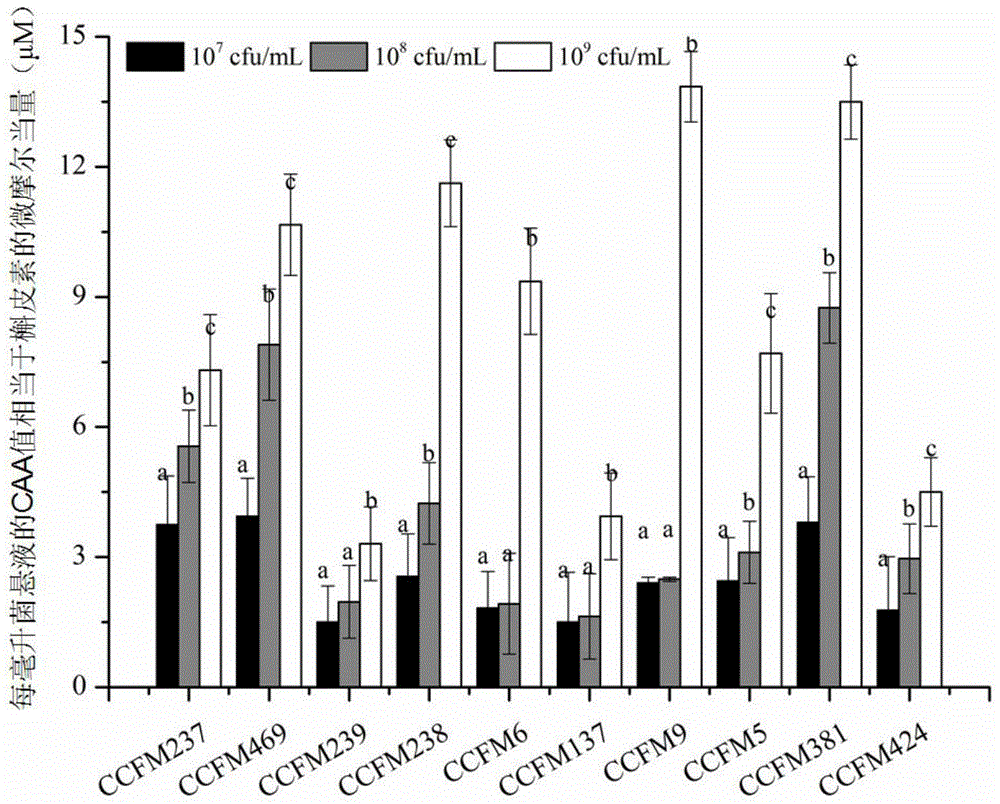
[0058] We are used for the analysis of the antioxidant activity of 5 kinds of 10 strains of lactic acid bacteria shown in table 1 w...
Embodiment 3
[0069] The coefficient of variation of embodiment 3 CAA method measurement result
[0070] For determining the reproducibility of the CAA method of the present invention, we compared the coefficient of variation of the antioxidant capacity of quercetin and 10 strains of lactic acid bacteria determined by the CAA method, the results are as shown in table 4, and the coefficient of variation of visible quercetin and 10 strains of lactic acid bacteria The range is 1.23-3.25%, which is lower than 10%, indicating that the method of the present invention has good repeatability.
[0071] Table 4 Coefficient of variation of different sample determination results
[0072]
[0073] After the quercetin standard curve of the present invention is established, it can be applied to the determination of each sample in the future, and can measure the antioxidant capacity of different species of lactic acid bacteria in batches in a very short time, and the determination speed is about 10 time...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com