Porous material supported nano alloy catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of porous materials and nano-alloys, applied in the field of nano-materials and catalysis, can solve the problems of high reaction temperature, reduced stability, material waste, etc., and achieve the effects of high catalytic activity, improved stability, low consumption and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
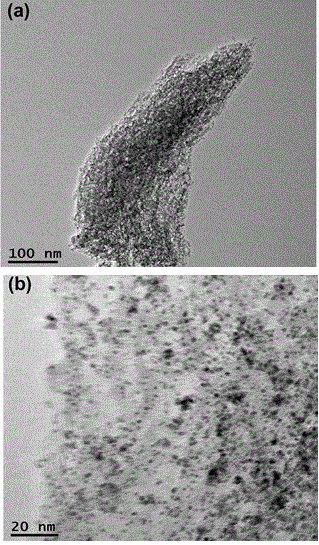
[0041] Using supercritical CO 2 Technology, using mesoporous carbon with a pore size of ~5 nm as a carrier to prepare PtFe nanoalloy composites.
[0042] The preparation steps are as follows:
[0043] a) Preparation of mesoporous carbon-supported Pt and Fe precursors.
[0044] 1) Pt(acac) with a total mass of 50 mg 2 and Fe(acac) 2 Precursor is put into the reaction kettle that volume is 20 mL, and described Pt(acac) 2 and Fe(acac) 2 The molar ratio of the substances is 1:1.
[0045] 2) Put 20 mg of mesoporous carbon material into the reaction kettle.
[0046] 3) Add 500 microliters of tetrahydrofuran into the reaction kettle.
[0047] 4) Close the reactor and press into 150 atm supercritical CO 2 In the reaction kettle, heated to 60 °C and kept warm for 2 h, then slowly released the pressure to obtain the preparation of mesoporous carbon-supported Pt and Fe precursors.
[0048] b) Reduction of the precursor in a) to obtain mesoporous carbon-supported PtFe nanoalloys....
Embodiment 2
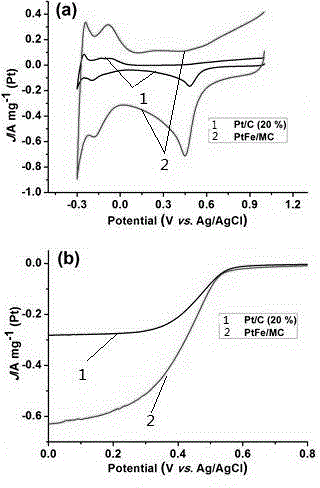
[0057] The electrochemical performance and catalytic performance for oxygen reduction of the mesoporous carbon-supported PtFe catalyst in Example 1 were tested using CHI and rotating disk electrodes, in which commercial Pt / C (Pt: 20 wt%) was used as a control experiment.
[0058] figure 2 a is the cyclic voltammetry curve (CV) diagram of the catalyst prepared in Example 1. It can be seen from the figure that the current density of the catalyst for catalyzing oxygen reduction is much greater than that of commercial Pt / C; figure 2 The polarization curve results of the oxygen reduction reaction of the catalyst in b also show that the catalyst prepared in the example has higher catalytic activity.
Embodiment 3
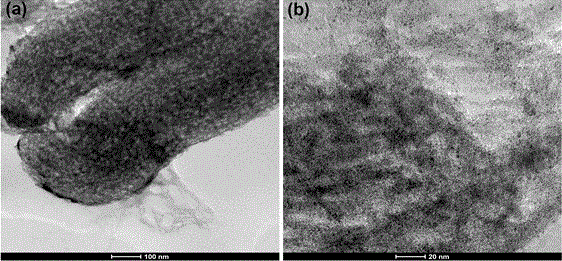
[0060] The steps of Example 3 are the same as those of Example 1, except that the mass of the mesoporous carbon material in 2) in step a) is reduced to 10 mg, and the morphology of the obtained PtFe / MC catalyst is shown in image 3 shown.
[0061] Comparing the TEM image in Example 1, it can be clearly seen that more PtFe nanoparticles are evenly distributed on the mesoporous carbon, and the result of ICP shows that the mass loading of PtFe particles is 23%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com