Photoresist pattern formation method, transistor gate formation method
A technology of photoresist and photoresist layer, which is applied in the formation of photoresist patterns and the formation of transistor gates, and can solve the problems of reducing the low-frequency line width roughness of photoresist patterns
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0031] like figure 1 As shown, a substrate 100 is provided.
[0032] The substrate 100 may be a commonly used substrate such as a silicon substrate, a silicon germanium substrate, a gallium arsenic substrate, and the like.
[0033] Continue to refer to figure 1 A gate material layer 102 is formed on a substrate 100 as shown
[0034] In this embodiment, the material of the gate material layer 102 is polysilicon, and the formation method of the gate material layer 102 is chemical vapor deposition.
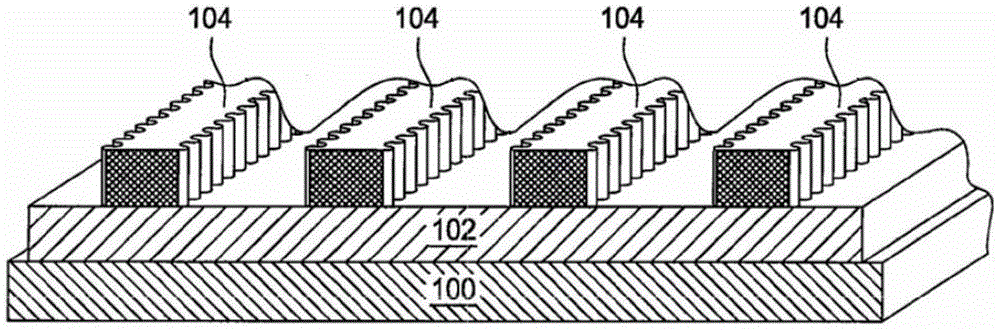
[0035] Continue to refer to figure 1 As shown, a photoresist pattern 104 is formed on the gate material layer 102 .
[0036] The photoresist pattern 104 is used to define the transistor gate. The method for forming the photoresist pattern 104 includes: forming a photoresist layer on the gate material layer 102 ; and patterning the photoresist layer to form the photoresist pattern 104 .
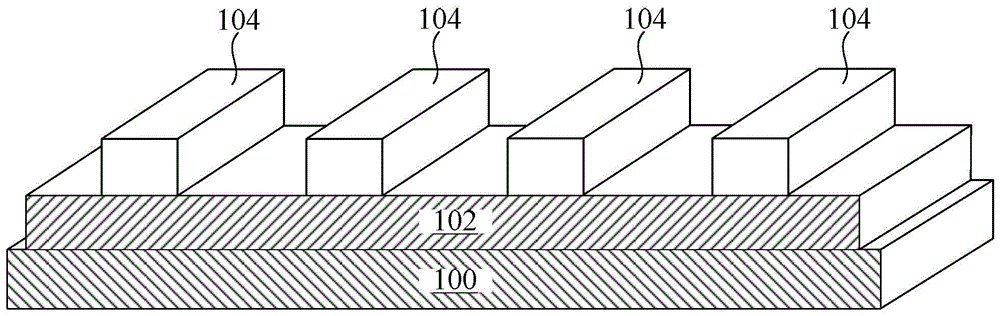
[0037] In this embodiment, the photoresist pattern 104 is basically a cuboid.
[0038] ...
no. 2 example
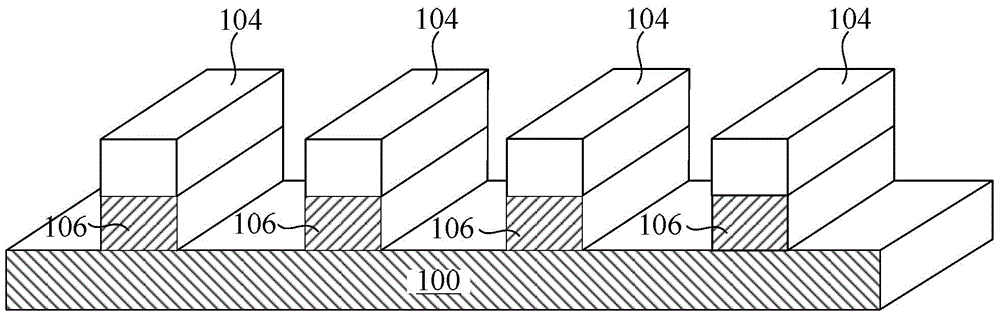
[0058] The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the second embodiment, as Figure 4 As shown, there are also formed between the photoresist pattern 104 and the gate material layer 102: a hard mask layer 108 above the gate material layer 102, an amorphous carbon layer (amorphous carbon) above the hard mask layer 108 110 , a dielectric antireflection layer (Darc) 112 on the amorphous carbon layer 110 , and a bottom antireflection layer (Barc) 114 on the dielectric antireflection layer 112 .
[0059] On the basis of the first embodiment, the technical solution of the second embodiment can bring the following further beneficial effects: by sequentially setting a hard mask layer between the photoresist pattern and the gate material layer, the amorphous The carbon layer, the dielectric antireflection layer and the bottom antireflection layer can reduce the thickness of the photoresist pattern.
[0060] In this embodiment, the method for formi...
no. 3 example
[0068] The difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that in the third embodiment, the H 2 The gases also include: CH 2 f 2 、CH 3 One or more of F.
[0069] On the basis of the first embodiment, the technical solution of the third embodiment can bring the following further beneficial effects: 2 f 2 、CH 3 Under the action of F, a layer of polymer layer will be formed on the surface of the photoresist pattern, which can prevent the photoresist pattern from reflowing and prevent the photoresist pattern from being unable to flow due to the large degree of reflow. Keep the basic shape.
[0070] In this example, the H 2 The gas also includes CH 2 f 2 and CH 3 F, the process parameters of the first plasma treatment include: the pressure is 2 to 100mtorr, the power of the first radio frequency power supply is 10 to 1000W, the first bias voltage is 0 to 500V (inclusive), H 2 The flow rate is 10 to 500sccm, CH 2 f 2 and CH 3 The flow rate of F is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com