Heat-resisting sintered neodymium iron boron permanent magnet material and preparation method thereof
A permanent magnet material, NdFeB technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic material magnetism, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of limited application scope, remain unchanged, cannot be applied, etc., achieve small size, uniform grain size, The effect of high thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
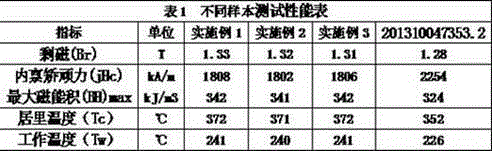
[0017] Example 1: (1) According to the weight percentage, Nd19.8%, B0.78%, Cu0.48%, Co0.98%, Ga0.43%, Nb0.69%, Dy2.8%, Al0.25%, and the balance is Fe ratio raw material , put the raw material into a vacuum quick-setting throwing belt furnace, and smelt it into thin slices with a thickness between 0.2 and 0.3 mm;
[0018] (2) Put the flakes in step (1) into a hydrogen furnace, and dehydrogenate them at 530°C for 4 hours to make a coarse powder; then pass through a jet mill to make a magnetic powder with an average particle size of 2.5-2.8 μm;
[0019] (3) Mix nano-iron powder with a particle size of 40-50nm and nano-strontium titanate with a particle size of 80-100nm at a ratio of 4:3 by weight, add it to the wi84564 nano-scale dispersion grinder, and grind and mix for 2-3 hours , to obtain nano-mixed powder A; the particle size is 40 ~ 50nm nano-vanadium nitride, the magnetic powder in step (2), mixed according to the ratio of 4:9 by weight percentage, added to wi84564 nano-sc...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: (1) According to the weight percentage, Nd 18.6%, B 0.73%, Cu 0.44%, Co 0.95%, Ga 0.41%, Nb 0.67%, Dy 2.6%, Al 0.23%, and the balance is Fe proportioning raw materials, Put the raw material into a vacuum quick-setting throwing belt furnace, and smelt it into thin slices with a thickness of 0.2-0.3mm;
[0023] (2) Put the flakes in step (1) into a hydrogen furnace, and dehydrogenate at 510-530°C for 4 hours to make coarse powder; then pass through jet mill to make magnetic powder with an average particle size of 2.5-2.8 μm;
[0024] (3) Mix nano-iron powder with a particle size of 40-50nm and nano-strontium titanate with a particle size of 80-100nm at a ratio of 4:3 by weight, add it to the wi84564 nano-scale dispersion grinder, and grind and mix for 2-3 hours , to obtain nano-mixed powder A; the particle size is 40 ~ 50nm nano-vanadium nitride, the magnetic powder in step (2), mixed according to the ratio of 4:9 by weight percentage, added to wi84564 nano-sca...
Embodiment 3
[0027] Example 3: (1) According to the weight percentage, Nd 23.1%, B 0.81%, Cu 0.53%, Co 1.03%, Ga 0.46%, Nb 0.73%, Dy 3.1%, Al 0.29%, and the balance is Fe proportioning raw materials, Put the raw material into a vacuum quick-setting throwing belt furnace, and smelt it into thin slices with a thickness of 0.2-0.3mm;
[0028] (2) Put the flakes in step (1) into a hydrogen furnace, and dehydrogenate at 510-530°C for 4 hours to make coarse powder; then pass through jet mill to make magnetic powder with an average particle size of 2.5-2.8 μm;
[0029] (3) Mix nano-iron powder with a particle size of 40-50nm and nano-strontium titanate with a particle size of 80-100nm at a ratio of 4:3 by weight, add it to the wi84564 nano-scale dispersion grinder, and grind and mix for 2-3 hours , to obtain nano-mixed powder A; the particle size is 40 ~ 50nm nano-vanadium nitride, the magnetic powder in step (2), mixed according to the ratio of 4:9 by weight percentage, added to wi84564 nano-sca...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com