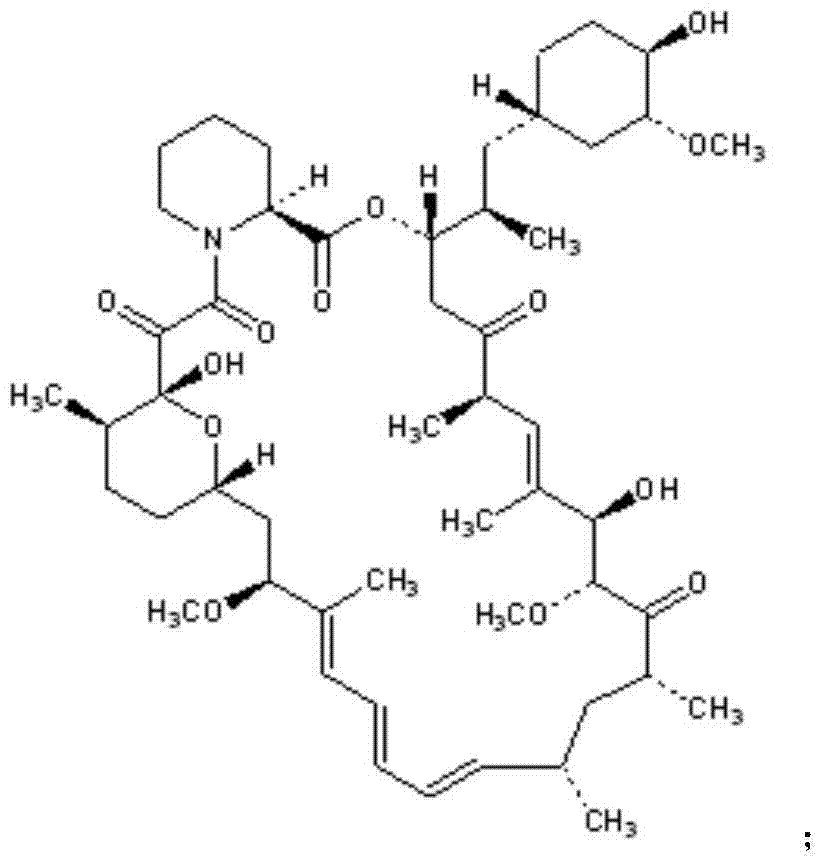
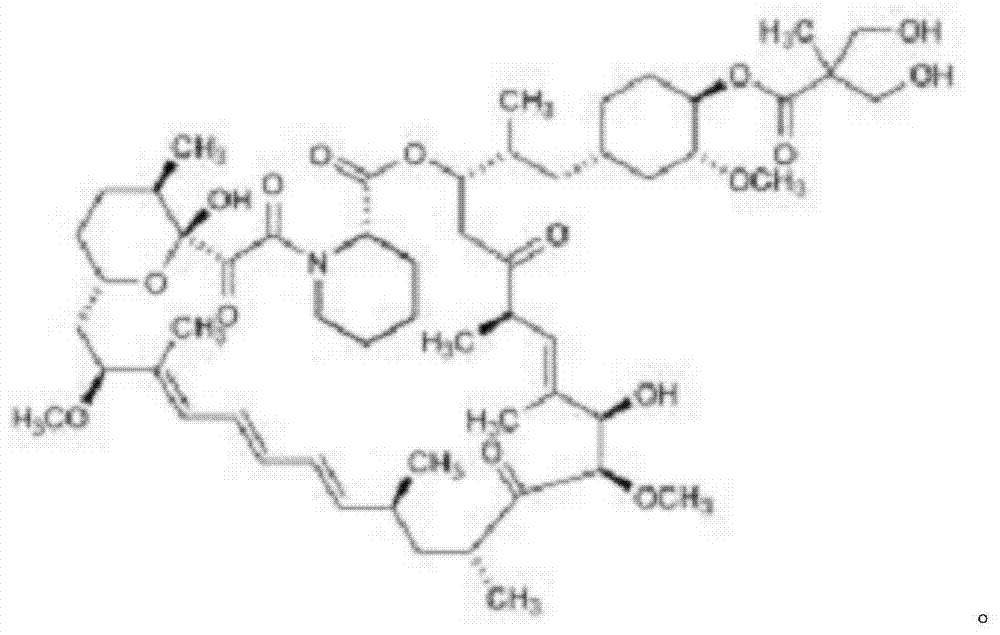
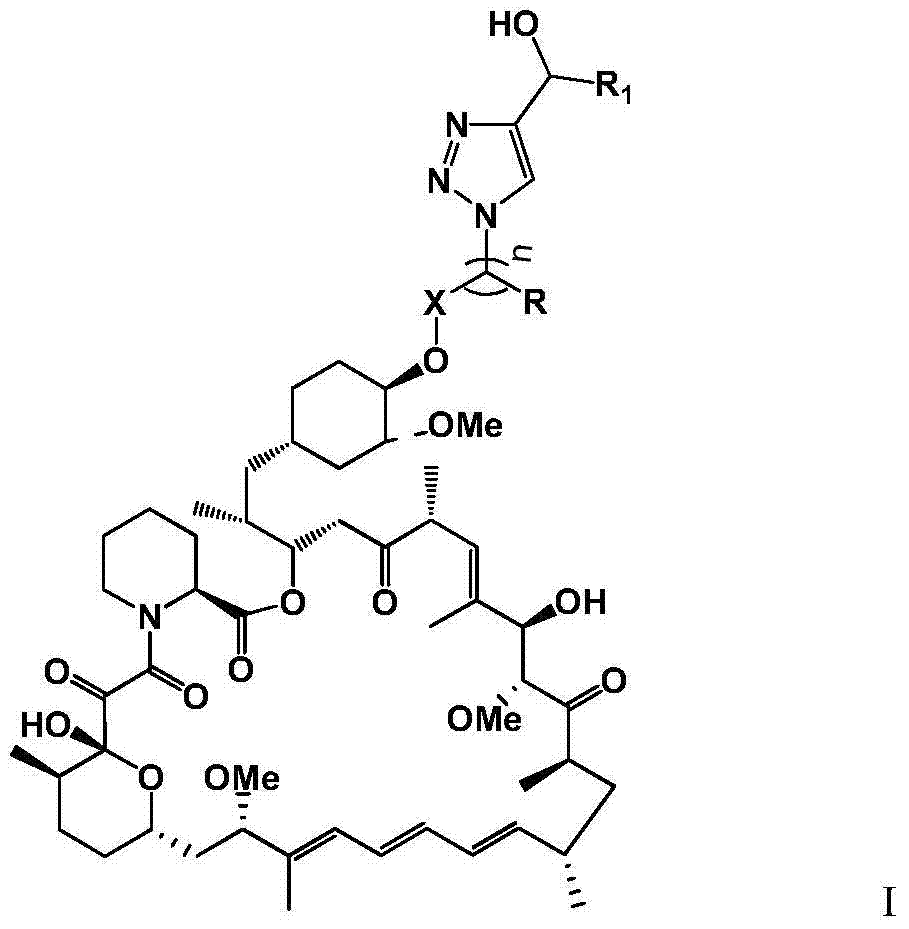
Triazole derivatives of rapamycin and application
A halogen and compound technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as low selectivity, easy drug resistance, and large toxic and side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0118] Example 1: 40-O-(2-(4-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)acetyl)oxyrapamycin (X-42) preparation
[0119] (prepared according to synthetic routes A and C)
[0120] Step A: Preparation of 28-oxytrimethylsilyl-rapamycin
[0121] Add rapamycin (5.5mmol, 5.0g) and imidazole (1.5g) into ethyl acetate (80mL) solution respectively, cool to 0-5°C after addition, add trimethylchlorosilane (mmol, 4.3g), heat preservation reaction for 2 hours. When the bissilyl ether protected product was formed, dilute sulfuric acid (15 mL, 1N H 2 SO 4 ), continue to stir and react for about 16h. After the reaction is completed, the reaction solution is washed with saturated sodium bicarbonate and saturated brine respectively. The organic layer is dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated to dryness to obtain 5.1 g of a white foamy solid with a yield of 47%. MS(ESI)m / z:1008.5(M+Na) + ..
[0122] Step B: Preparation of 28-oxytrimethylsilyl-43-O-(2-chloroacetyl)-oxrapamycin ...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Example 2: 40-O-(2-(4-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)isopropionyl)oxrapamycin (X-60)
[0134] (prepared according to synthetic routes A and C)
[0135] Step A: Preparation of 28-oxytrimethylsilyl-43-O-(2-bromoisopropionyl)-oxrapamycin
[0136] 28-OTMS-rapamycin (2.5g, 2.5mmol) and anhydrous dichloromethane (40mL) were added to a three-necked flask, triethylamine (3mL) was added, and 2- Isopropionyl chloride (1.1g, 5mmol) was added and reacted at 0-5°C for 8h. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was poured into 300 mL of water, extracted with dichloromethane, the extracts were combined, washed with water, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate. Evaporate to dryness to obtain 1.9 g of white solid, yield: 77.2% MS (ESI) m / z: 1142.5 (M+Na) + .
[0137] Step B: Preparation of 43-O-(2-bromoisopropionyl)-oxrapamycin
[0138] Add 28-OTMS-43-O-(2-bromoisopropionyl)-oxrapamycin (1.9g, 1.7mmol) into acetone (40mL) solution, cool to 0-5°C afte...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Example 3: 40-O-(2-(4-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)ethyl)oxrapamycin (X-51)
[0147] (prepared according to synthetic routes A and B)
[0148] Step A: Preparation of 43-O-(2-bromoethyl)-oxrapamycin
[0149] Add rapamycin (6g, 6.6mmol) and diisopropylethylamine (4.2g, 33mmol) to 50mL of toluene solution, add 2-bromoethylsulfonate side chain (5g, 19.6mmol), After the addition was completed, the temperature was raised to 60°C for 3 hours. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, respectively, in dilute hydrochloric acid, saturated sodium bicarbonate and saturated brine, the organic layer was dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and evaporated to dryness to give a light yellow solid, which was finally separated by column chromatography to obtain 2.9g White solid, yield: 82.6%, 1042.5 (M+Na) + .
[0150] Step B: Preparation of 43-O-(2-azidoethyl)-oxrapamycin
[0151] 43-O-(2-bromoethyl)-oxrapamycin (5.9g, 5.7...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com