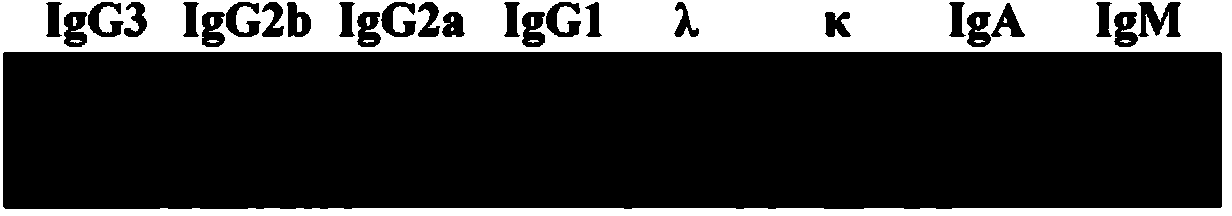Therapeutic monoclonal antibody for resisting escherichia coli infection, hybridoma cell strain generating monoclonal antibody and use of therapeutic monoclonal antibody
A hybridoma cell line, monoclonal antibody technology, applied in antibacterial immunoglobulins, applications, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as slow progress in research on bacteriolysis mechanism
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
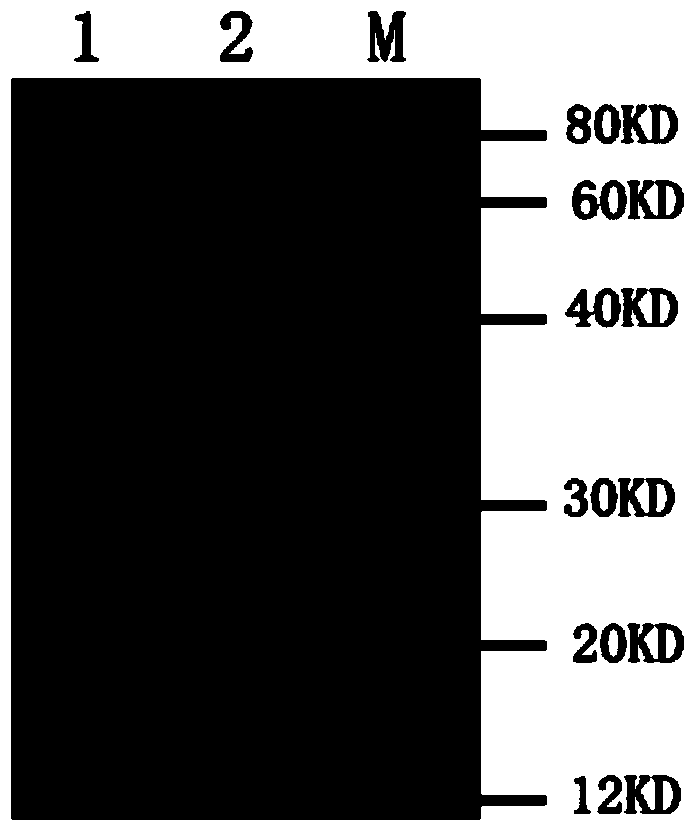
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1: Construction of MraY hydrophilic region fusion protein prokaryotic expression vector
[0045] Using Escherichia coli DH5α genomic DNA as a template, a 96bp fragment a (shown in SEQ ID NO.3) and a 99bp b fragment (shown in SEQ ID NO.4) were amplified by PCR, and the two fragments were amplified by overlapping PCR. The fragments were fused, cut with restriction enzymes (Bam H I and Sal I), ligated with pGEX-6P-1 (purchased from Amersham), and transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3) (purchased from Merck). And the recombinant plasmid pGEX-6p-M-ab was obtained after digestion and PCR identification.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Expression and purification of embodiment 2 fusion protein
[0047] (1) Induction of recombinant protein
[0048] Pick out the single clone colonies containing the plasmid, inoculate them in 5ml of LB medium containing ampicillin, shake overnight at 220rpm at 37°C. The next day, dilute 1:100 into 500ml LB medium containing the corresponding antibiotics, culture at 37°C until OD 600 About 0.6, add IPTG to make the concentration 1mM, induce for 4 hours at 37°C, and collect the precipitate by centrifugation.
[0049] (2) Deformation of urea to extract inclusion bodies
[0050] 1) Suspend the precipitate with 12mL resuspension solution (20mM Tris, 150mM NaCl) according to the ratio of 4ml / 100ml bacterial solution (the bacterial solution volume is the bacterial solution volume during IPTG induction);
[0051] 2) Ultrasound for 30 minutes, each ultrasonic wave is 5 seconds, the interval is 15 seconds, the amplitude is 30%, and the operation is performed on ice;
[0052] 3...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Preparation of embodiment 3 antiserum
[0065] After mixing and emulsifying the purified GST-M-ab fusion protein with an equal volume of Freund's complete adjuvant (purchased from Sigma Company), subcutaneously immunized 6-8 week-old female BALB / c mice (purchased from China Agricultural Experimental Animal Center, Harbin Veterinary Research Institute, Academy of Sciences), the injection dose was 100 μg / animal; a total of three immunizations, the latter two with an equal volume of Freund’s incomplete adjuvant (purchased from Sigma Company), the immunization dose was also 100 μg / animal. Seven days after the third immunization, blood was collected from the tail vein, and serum was separated as positive serum. Measure titer by indirect ELISA method, when reaching 10 -4 Then ready to blend. Three days before fusion, booster immunization was carried out by intraperitoneal injection of protein without adjuvant, and the dose was also 100 μg per mouse.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com