Phenolate lignin tackiness agent and preparing method of phenolate lignin tackiness agent
A technology of phenolic lignin and adhesives, applied in the field of natural polymers, can solve the problems of inconvenient production and application of lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesives, affecting the application and popularization of lignin-modified phenolic resin adhesives, and slow curing reaction rate, etc. Achieve the effect of convenient construction, good storage stability and good fluidity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
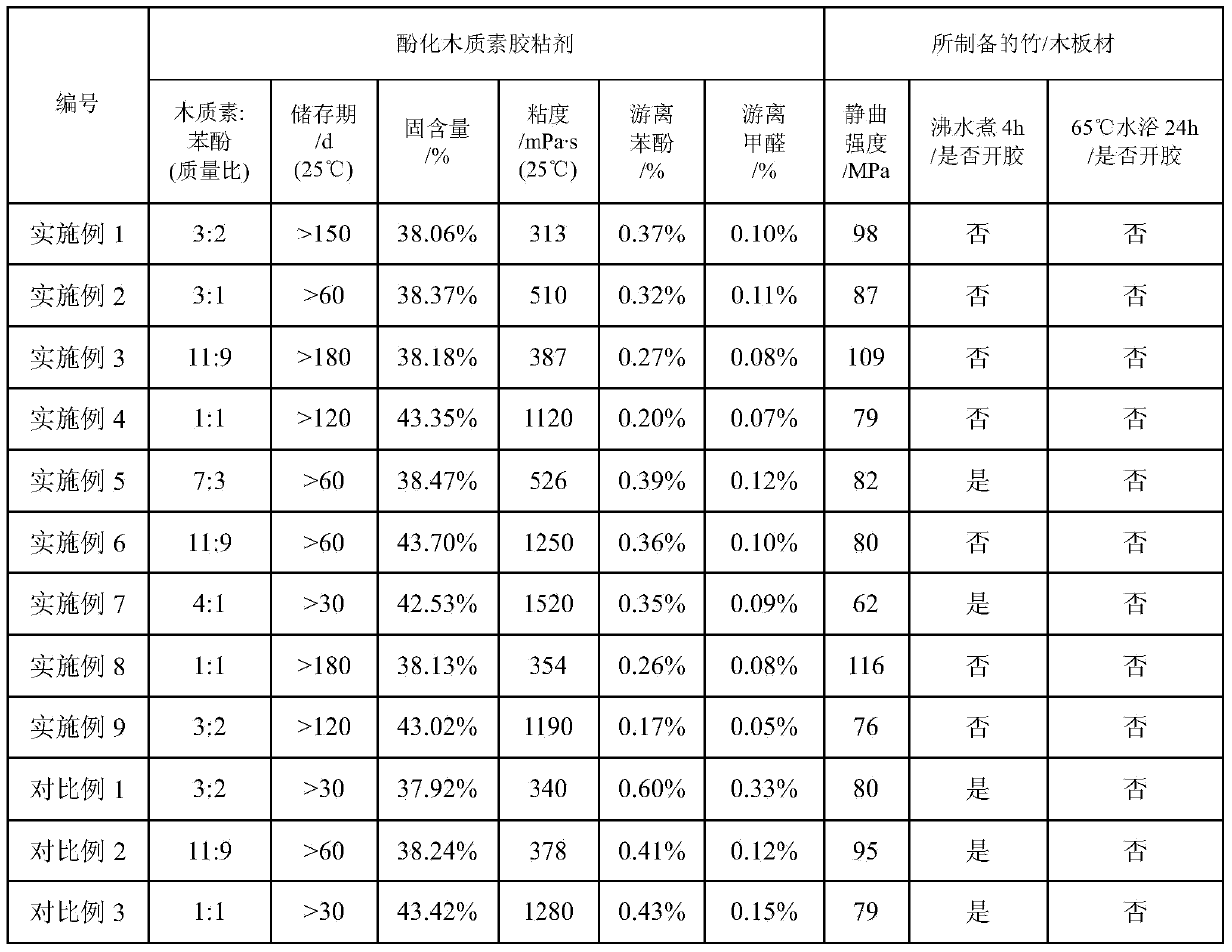
Embodiment 1
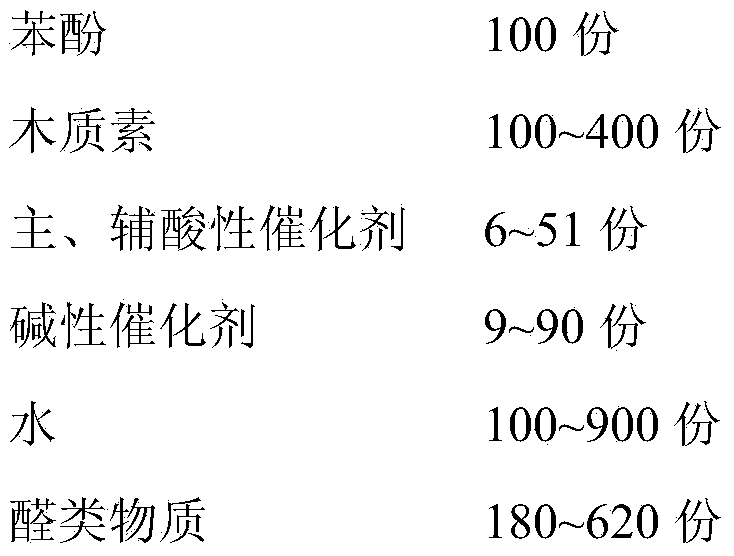
[0030] Add 200.0g of phenol into a 2500mL five-neck flask equipped with polytetrafluoroethylene stirring, spherical condenser, and tantalum alloy temperature sensor, raise the temperature to 60-65°C, and add 100.0g of sulfonated bamboo pulp alkali lignin, 6.0 g trifluoropropionic acid, 24.0 g of sulfuric acid of 9 mol / L, 50.0 g of sulfonated bamboo pulp alkali lignin, heat preservation reaction for 10 minutes, heat up to 80-85 °C, add 75.0 g of sulfonated bamboo pulp alkali lignin, heat preservation reaction for 5 minutes, Then add 75.0g of sulfonated bamboo pulp alkali lignin, raise the temperature to 105-115°C, keep the temperature for 30 minutes, cool down rapidly to below 45°C, add 193.3g of lye (58.0g of sodium hydroxide dissolved in 135.3g of water), water 125.0g, keep warm at 35-55°C for 10min, add 300.0g of formaldehyde and 12.0g of acetaldehyde, slowly heat up to 90°C, add 132.0g of formaldehyde, 5.4g of acetaldehyde, keep warm at 90°C for 10min, then add formaldehyde ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Add 125.0g of phenol to a 2500mL five-necked flask equipped with polytetrafluoroethylene stirring, a spherical condenser, and a tantalum alloy temperature sensor, raise the temperature to 75-80°C, and add 70.0g of sodium lignosulfonate and 9.0g of sodium lignosulfonate in sequence. Trifluoropropionic acid, 27.0g of 12mol / L sulfuric acid, 15.0g concentrated hydrochloric acid, 90.0g sodium lignosulfonate, keep warm for 15 minutes, heat up to 85-90°C, add 90.0g sodium lignosulfonate, keep warm for 10 minutes, Then add 70.0g sodium lignosulfonate, heat preservation reaction for 5min, then add 55.0g sodium lignosulfonate, heat up to 115~120℃, heat preservation reaction for 45min, rapidly cool to below 45℃, add lye 283.0g (85.0g Potassium hydroxide (dissolved in 198.0g of water), 125.0g of water, keep warm at 35-55°C for 20min, add 280.0g of formaldehyde, slowly heat up to 92°C, add 123.5g of formaldehyde, keep warm at 90°C for 15min, then add 70.0g of formaldehyde, heat pres...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Add 225.0g of phenol into a 2500mL five-necked flask equipped with polytetrafluoroethylene stirring, a spherical condenser, and a tantalum alloy temperature sensor, raise the temperature to 60-70°C, and add 100.0g of sodium lignosulfonate and 5.0g of sodium lignosulfonate in sequence. Trifluoropropionic acid, 20.0g concentrated hydrochloric acid, 60.0g sodium lignosulfonate, keep warm for 5min, heat up to 85~90℃, add 60.0g sodium lignosulfonate, keep warm for 10min, then add 55.0g lignosulfonate Sodium, heat up to 110-115°C, keep warm for 25 minutes, quickly cool down to below 45°C, add 213.0g of lye (64.0g sodium hydroxide dissolved in 149.0g of water), 125.0g of water, keep warm at 35-55°C After 15 minutes, add 330.0g of formaldehyde, slowly heat up to 85°C, add 145.0g of formaldehyde, keep it at 90°C for 30 minutes, then add 82.5g of formaldehyde, keep it at 90°C for 15 minutes, then add 104.5g of formaldehyde, slowly heat up to 90°C Insulation reaction, at intervals...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com