Phosphorous graphite ferrum-based powder metallurgy antifriction material
An iron-based powder metallurgy and friction-reducing material technology, applied in the field of powder metallurgy materials, can solve the problems affecting the material pressing uniformity and sintering effect, affecting the performance of the material, low density, etc. Anti-friction and self-lubricating properties, improve wear resistance and load-carrying capacity, and improve the effect of anti-friction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The formula is as follows: the iron-based powder is divided into units of measurement by weight, the copper-plated flake graphite is 4%, ordinary graphite powder is 0.5%, zinc stearate is 1%, phosphorus is 0.1%, and the balance For iron powder.
[0024] Concrete preparation operation steps are as follows:
[0025] (1) mixed
[0026] Take the raw materials according to the formula, stir and mix for 3 minutes at a speed of 3000r / min, add a binder whose mass is 2%~3% of the mixed powder, and stir for 2 minutes to obtain the mixed powder; the mixed powder passes through a 100-mesh sieve to obtain Dough granules are dried for 30 minutes at a temperature of 100°C, passed through a 100-mesh sieve for the second time, and dried for 1 hour at a temperature of 100°C to obtain dry powder particles; the binder is epoxy resin, polyethylene Alcohol and ethanol are prepared in a volume ratio of 1:1:10;
[0027] (2) suppression
[0028] Send the powder into the product mold of the ...
Embodiment 2
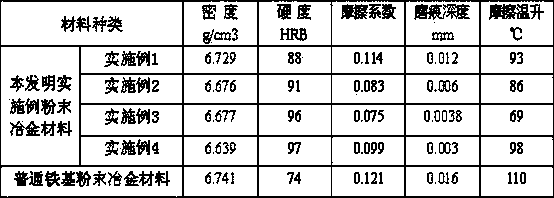
[0033] The powder metallurgy formula of the present invention is as follows: the iron-based powder is divided into units of measurement by weight, the copper-plated flake graphite is 3%, ordinary graphite powder is 0.4%, zinc stearate is 0.8%, phosphorus 0.2%, and the balance is iron powder. Preparation method and operation steps are identical with embodiment 1; The density of this material is 6.676g / cm 3 , The hardness is 91HRB, the friction coefficient is 0.083, the wear scar depth is 0.006mm, and the friction temperature rise is 86°C. The results show that the density of the formula material in this example is slightly reduced, but it has better anti-friction and wear resistance than Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The powder metallurgy formula of the present invention is as follows: the iron-based powder is divided into measurement units by weight, the copper-plated flake graphite is 4%, ordinary graphite powder is 1%, zinc stearate is 1.5%, phosphorus 0.3%, and the balance is iron powder. Preparation method and operation steps are identical with embodiment 1; The density of this material is 6.677g / cm 3 , The hardness is 96HRB, the friction coefficient is 0.075, the wear scar depth is 0.0038mm, and the friction temperature rise is 69℃. Compared with Examples 1 and 2, the anti-friction, wear-resistant, and anti-adhesion properties of the powder metallurgy material formulated in this example are significantly better.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wear scar depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com