Bonding method for aluminium alloy material
A technology of aluminum alloy materials and joining methods, applied in the direction of welding/cutting media/materials, welding media, welding equipment, etc., can solve the problems of inability to set hollow parts, uneven joints, high temperatures, etc., and achieve small dimensional changes and low strength Effects of embrittlement and joint performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment A( Embodiment 1~30 and comparative example 31~36
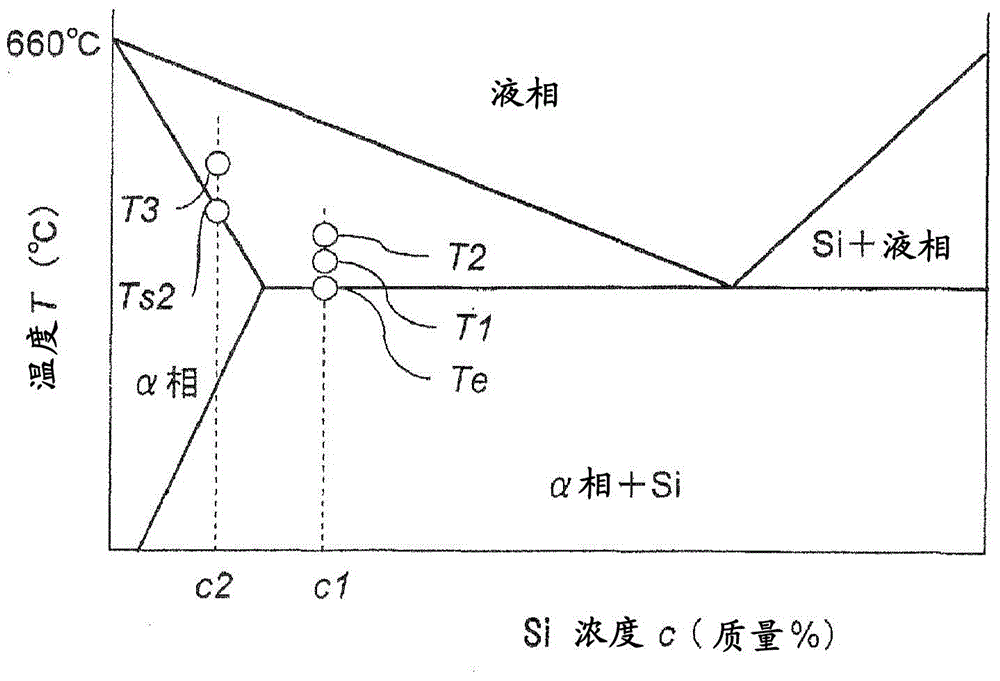
[0111] After preparing ingots with the alloy compositions shown in Table 1, rolled sheets with a thickness of 1 mm were obtained by hot rolling and cold rolling. After the rolled sheet was placed in a leveler, it was annealed at 380° C. for 2 hours to obtain a rolled sheet sample. Using the thus-produced rolled sheet samples, they were joined by heating in the air using a chloride-based flux, and the joining rate and deformation rate were evaluated.
[0112] [Table 1]
[0113]
[0114] (1) Engagement rate evaluation
[0115] Two plates with a width of 20mm x a length of 50mm were cut out from the above-mentioned rolled plate sample, and the respective end faces were smoothed with a milling cutter, and the upper plate and the lower plate of the aluminum alloy material were combined to produce Image 6 Inverted T-shaped joint test piece shown in . For the upper plate and the lower plate of the test piece, aluminum alloy plates having the compositions shown in Table 1 were ...
Embodiment B
[0147] Example B (Examples 37-46 and Comparative Examples 47-49)
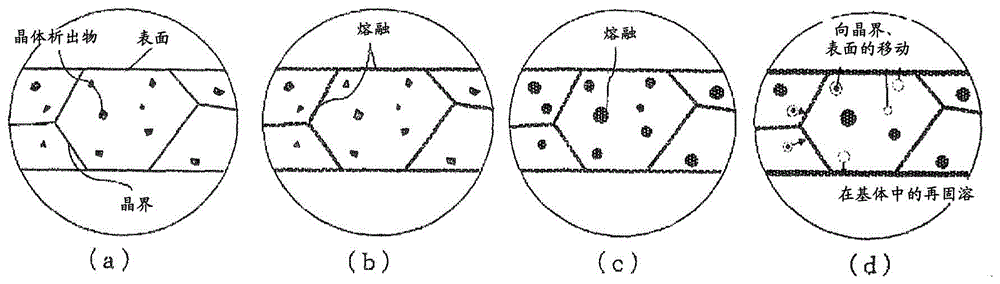
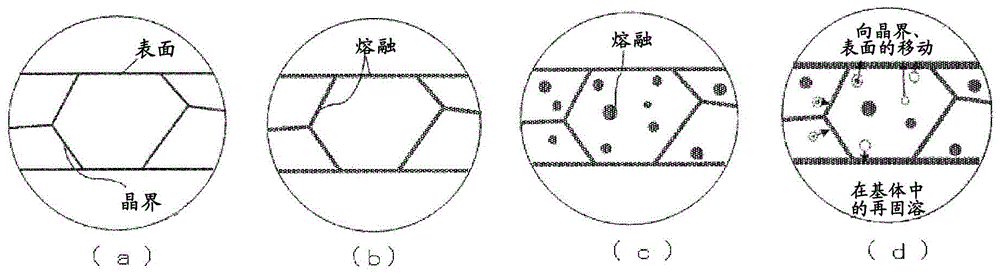
[0148] In the same manner as in Example A, the rolled sheet samples of the alloys shown in Table 1 were joined without using flux by heating in the air, and the joining rate and deformation rate were evaluated.
[0149] (1) Engagement rate evaluation
[0150] Two plates of 20 × 20 mm and 10 × 10 mm were cut out from the above-mentioned rolled plate sample, and made Figure 8 The bonding rate evaluation test piece shown in . Table 3 shows combinations of the upper plate and the lower plate of each test piece. The composition of the aluminum alloy of the upper plate and the lower plate is the same, and the upper plate and the lower plate are stacked without applying flux, and fixed by applying a pressure of 100 kPa with a spring, and used as a joint rate evaluation sample.
[0151] [table 3]
[0152]
[0153] The above-mentioned test pieces were heated up to a predetermined temperature in an air atmosphere...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com