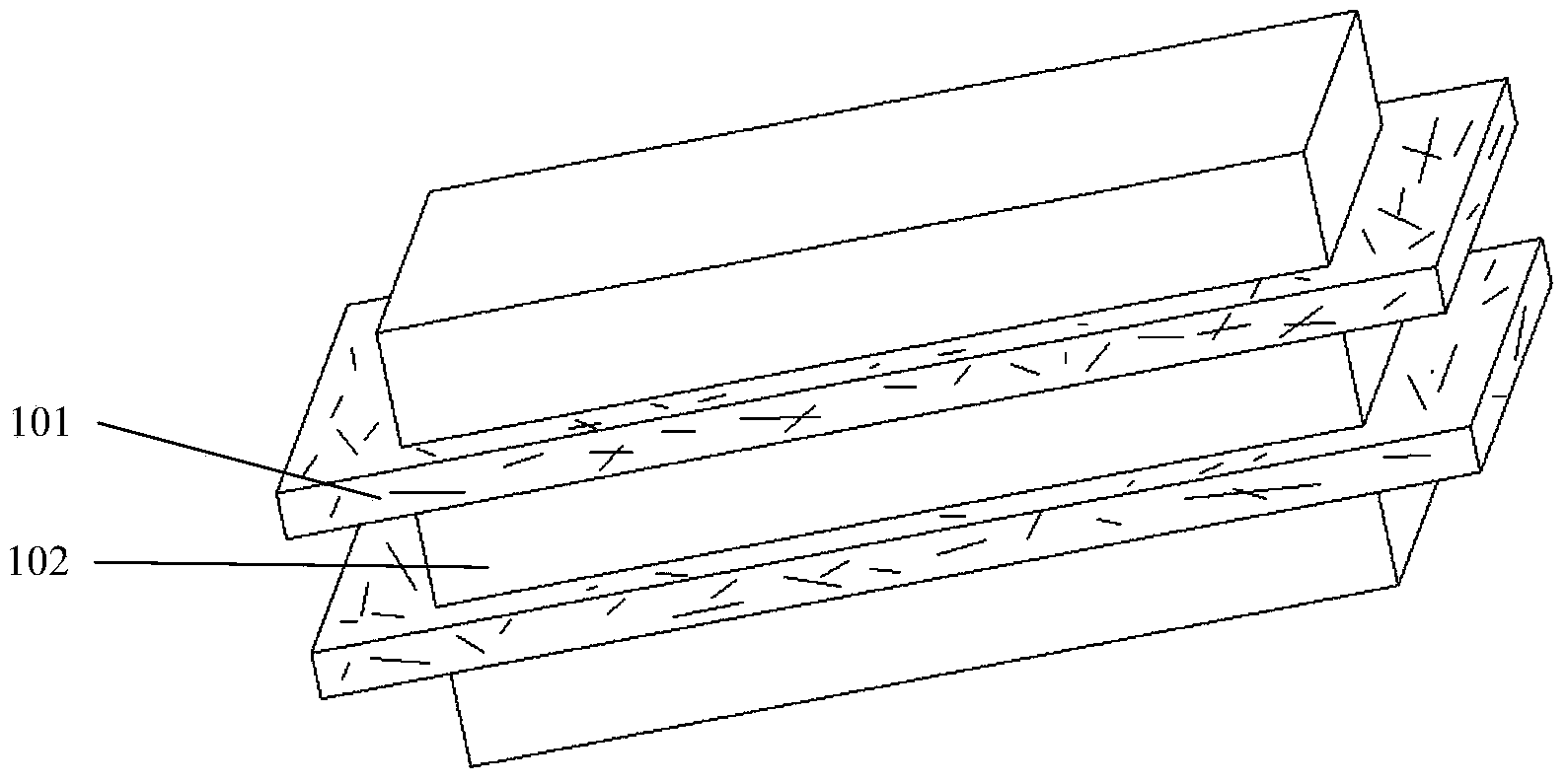
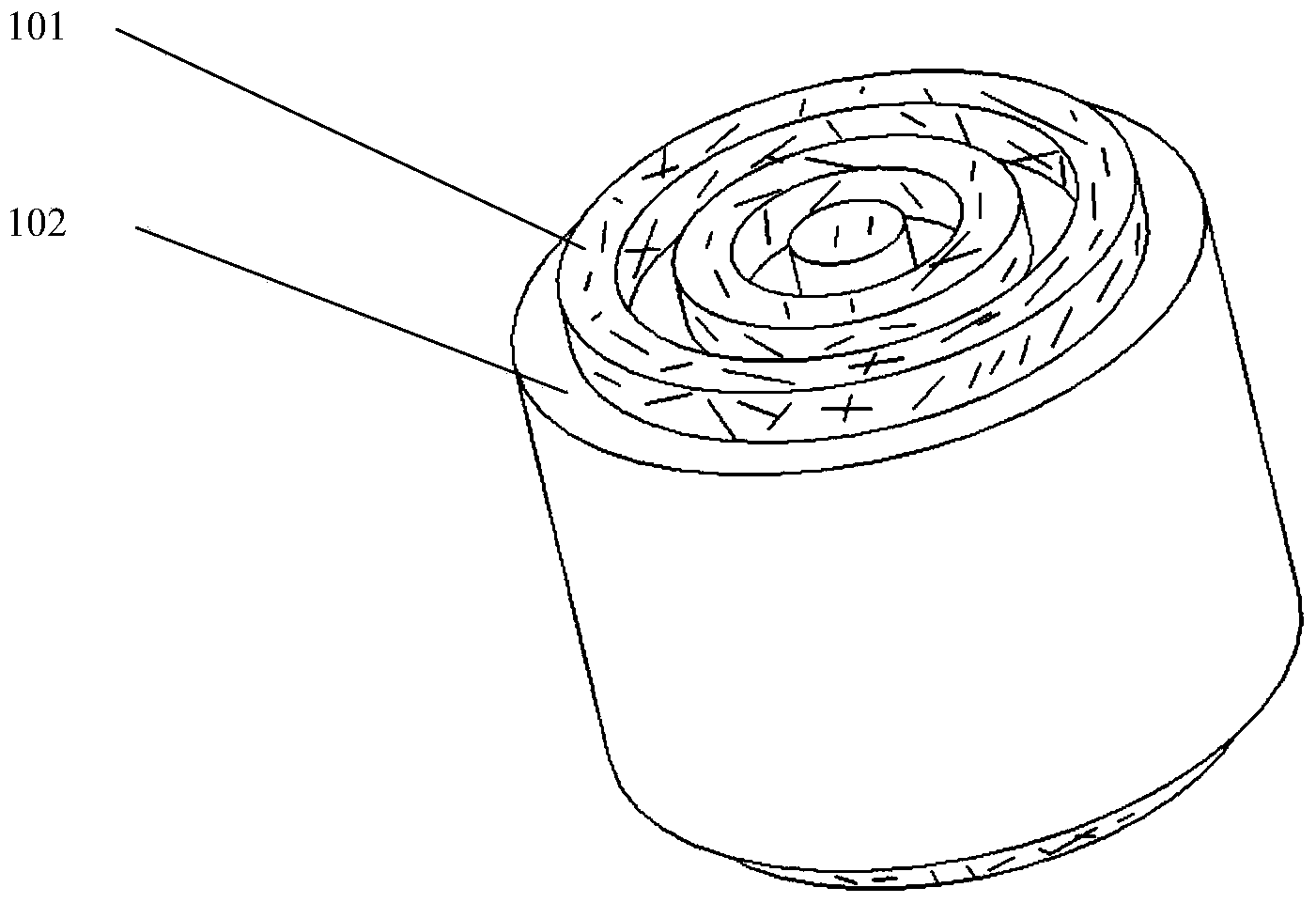
Tough tissue structure and 3D printing forming device and method thereof
A tissue structure, 3D printing technology, applied in the direction of ligaments, prostheses, muscles, etc., can solve the problem of incomplete recovery of damaged tissues, and achieve the effect of low immune rejection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0054] The present invention uses the above-mentioned 3D printing forming equipment to prepare a tough tissue structure. The preparation method includes a direct printing forming method in vivo or an external printing forming method. The method includes the following steps:
[0055] 1) In vivo direct printing and forming:
[0056]a) A three-dimensional model of the tough tissue structure is designed by a computer, or a three-dimensional model of the tough tissue structure is obtained by scanning the lesion with a scanning imaging system, and the computer assigns a printing path; the signal obtained by scanning the lesion is scanned by the scanning imaging system Send to the control system 404 for processing to obtain the instruction signal, and send the instruction signal to the rapid prototyping system 402 and the transmission system 403; b) prepare the prepared polymer hydrogel and polymer fiber with a mass volume concentration of 0.1-20% The raw materials are respectively l...
Embodiment 1
[0060] Example 1: Using 3D printing technology to prepare a ligament tissue structure in vitro and implant it in vivo.
[0061] 1) Preparation of cells and hydrogel: extract human fibroblasts, subculture the fibroblasts for later use; dissolve gelatin powder in phosphate buffer to prepare a hydrogel with a mass volume fraction of 15%; mix the fibroblasts into the above hydrogel to obtain a cell concentration of 1 x 10 6 Each / mL cell-hydrogel material system; the cell-hydrogel material is loaded into a 3D printed screw extrusion nozzle;
[0062] 2) Preparation of fiber material: heat polycaprolactone to melt it, and put the melted polycaprolactone into the 3D printed electrospinning nozzle for standby;
[0063] 3) Model design: design a three-dimensional model of the ligament tissue structure, and distribute the printing paths of the fiber layer and the hydrogel layer by the computer;
[0064] 4) Forming process: the 3D printing equipment is controlled by a computer. First, t...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Example 2: Using 3D printing technology to prepare a ligament tissue structure in vitro and implant it in vivo.
[0067] 1) Preparation of cell suspension: extract human fibroblasts, subculture the fibroblasts for later use, prepare the cell suspension of the cells, and the cell concentration is 1×10 6 cells / mL, the cell suspension is loaded into the spray nozzle of the 3D printing device;
[0068] 2) Preparation of hydrogel: dissolving gelatin powder in phosphate buffer solution to prepare hydrogel with a mass volume fraction of 15%, and loading the hydrogel into the screw extrusion nozzle of the 3D printing device;
[0069] 3) Preparation of fiber material: dissolving polyurethane material in tetraethylene glycol solution to obtain a solution with a mass volume fraction of 10%, and putting the solution into the screw extrusion nozzle of the 3D printing equipment;
[0070] 4) Model design: the patient's ligament injury site is scanned by the scanning imaging system to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com