Method for fountain codes under binary erasure channel
A technology for deleting channels and fountain codes, applied in the coding field, can solve problems such as defects in information security guarantee, and achieve the effect of reasonable design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
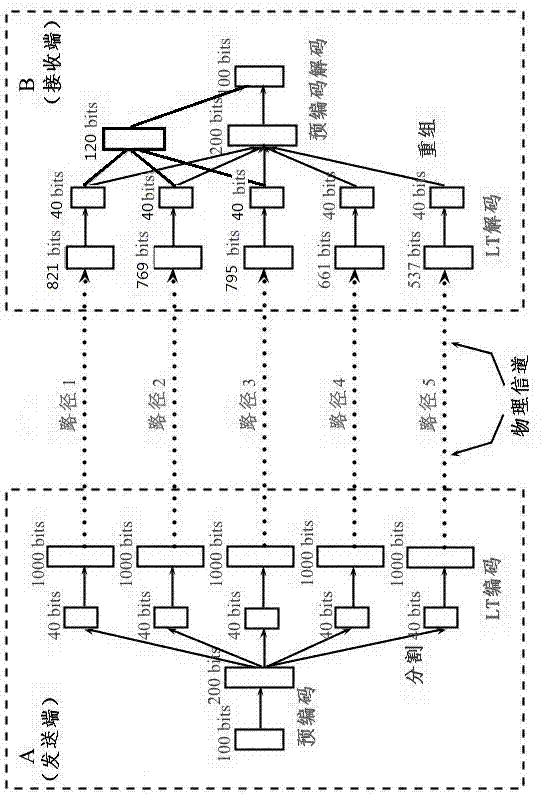
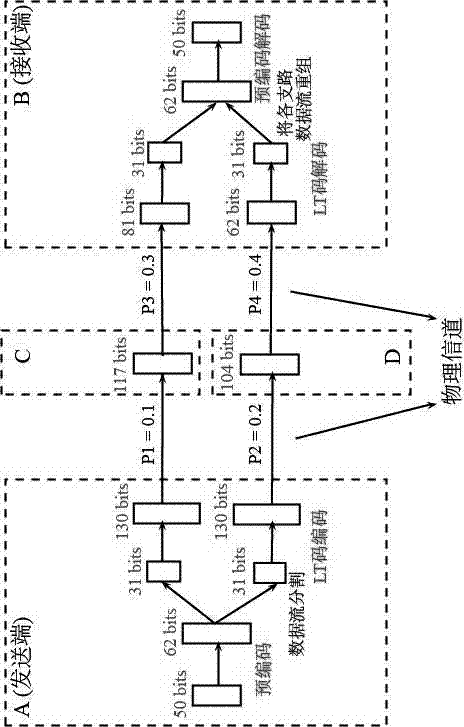
[0035] Embodiment 1, a fountain code method under a binary erasure channel, its steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Use block codes to pre-encode the original data stream, c = dG; where c is the pre-encoded data packet, d is the original data packet, G is the generator matrix, and a sparse matrix with a density of 0.2 is selected for pre-encoding Obtain precoded data as a generator matrix; the generator matrix is composed of many small sparse matrices, and then shuffled by row and column respectively;
[0037] (2) Segment the data stream obtained after precoding, and divide it into several information streams as required;
[0038] (3) Encode each branch of information flow according to the definition of LT code. When LT encoding, the selection range of "degree" Ω parameter is 1 < Ω < K; where K is the length of the original data packet;
[0039] (4) Send the information flow of each branch according to the pre-established routing scheme;
[0040] (5) At the decoding end, us...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Embodiment 2, in the fountain code method under the binary erasure channel described in Embodiment 1: in step (3), the selection range of "degree" Ω is 1 < Ω < 6.
Embodiment 3
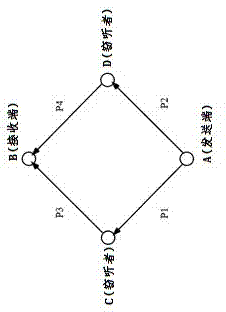
[0044] Embodiment 3, in the fountain code method under the binary erasure channel described in Embodiment 1 or 2: the routing scheme formulated in step (4) considers the channel erasure probability of each path, and ensures that the physical distance is the shortest and the packet loss phenomenon It is best to avoid, the specific routing scheme is as follows:
[0045] (1) According to the length of each path, a simulated channel erasure probability Pi=di / dtotal is associated with it; where Pi is the erasure probability of the path, di is the length of the path, and dtotal is the The straight-line distance from end to origin;
[0046] (2) Calculate all possible paths of the detected node positions between the receiving end and the sending end in the network;
[0047] (3) Calculate the packet loss rate for all these paths; that is: apply the channel erasure probability obtained in the first step to each path, and calculate the packet loss when using each possible route; Packet...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com