Purification, gene cloning, and enzymatic characteristic identification of chitosanase
A technology of chitosanase and chitosan, used in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, biochemical equipment and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Cultivation of chitosanase-producing strains: We isolated a miscellaneous bacterium from the contaminated yeast culture solution, Gram staining and morphological observation showed that it was a Gram-positive bacillus ( figure 1 ), tentatively named Bacillussp.TK-02. The strain was first cultured overnight on LB solid medium (30°C), and then a single clone was picked and inoculated in LB liquid medium for shaking culture at 30°C for 24 hours. The bacterial solution was centrifuged (5000g, 10min), and the supernatant was collected.
Embodiment 2
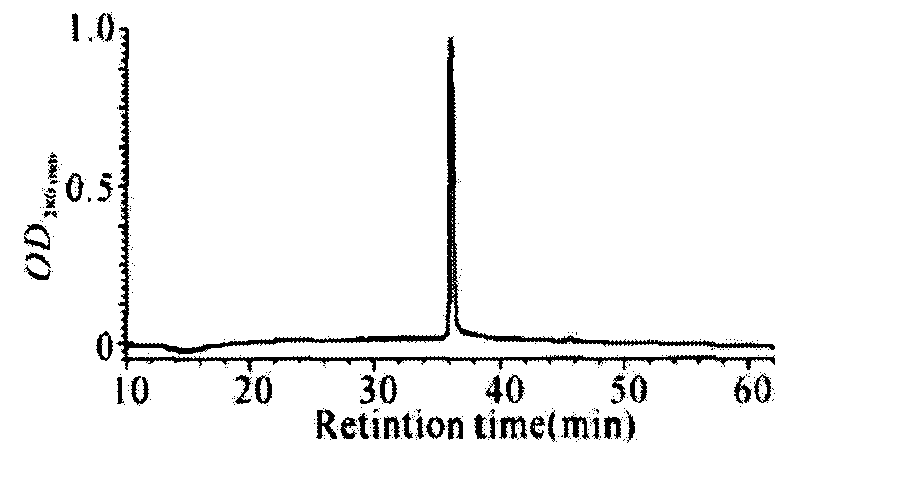
[0014] Purification of chitosanase and determination of N-terminal amino acid sequence: the composition of the supernatant of the fermentation broth of this bacterium is relatively simple, and the secreted expression product is mainly the chitosanase ( figure 2 A). After the culture supernatant is concentrated, it is separated and purified. First, the chitosanase is separated from the large-volume fermentation supernatant by hydrophobic chromatography. The SDS-PAGE identification shows that the chitosanase obtained in this step is purified. It mainly contains a heteroprotein with a large molecular weight ( figure 2 B, lane 1). Accordingly, purifying by molecular sieves, high-purity chitosanase ( figure 2 B, lane2). The purity of the chitosanase was further identified by C3 reverse phase HPLC. Such as image 3 As shown, the enzyme has only one peak on HPLC, and its purity is greater than 95%. The molecular mass of the eluted chitosanase was determined by electrospray m...
Embodiment 3
[0017] Cloning of chitosanase gene: According to the DNA sequence of other chitosanases, take the conserved gene sequence before the signal peptide and the termination signal TAA, and design primers as follows: Primer 1:
[0018] 5'-tta-aaaggagctgacaacataat3'; Primer 2: 5'-ttaatatcgtatccttcataaattgca-3'. The bacterial genome DNA was used as a template, and the above primers were used for PCR amplification. A sequence of about 1.3 kb was amplified, and then cloned into a T-vector for DNA sequence determination. Through searching online (http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / BLAST), its sequence has high homology with other 11 kinds of chitosanases, reaching 96%-98%, and their numbers in GenBank are respectively: AAQ 75085, ZP00240544, AAK 07481, YP 084010, NP 832437, NP845032, BAB 19277, AAQ 75084, AAQ 19679, AAO49750, and AAQ 19678. They all belong to the glycoside hydrolase 8 family, and all are derived from the genus Bacillus. The gene encodes 453 amino acids, of which the N-termin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com