Wood-plastic floor and manufacturing method thereof
A wood-plastic floor and base material technology, which can be used in buildings, building structures, floors, etc., and can solve problems such as low mechanical properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] The present invention provides a kind of preparation method of wood-plastic floor, comprises the following steps:
[0045] Melting and extruding the components included in the base material to obtain the base material;
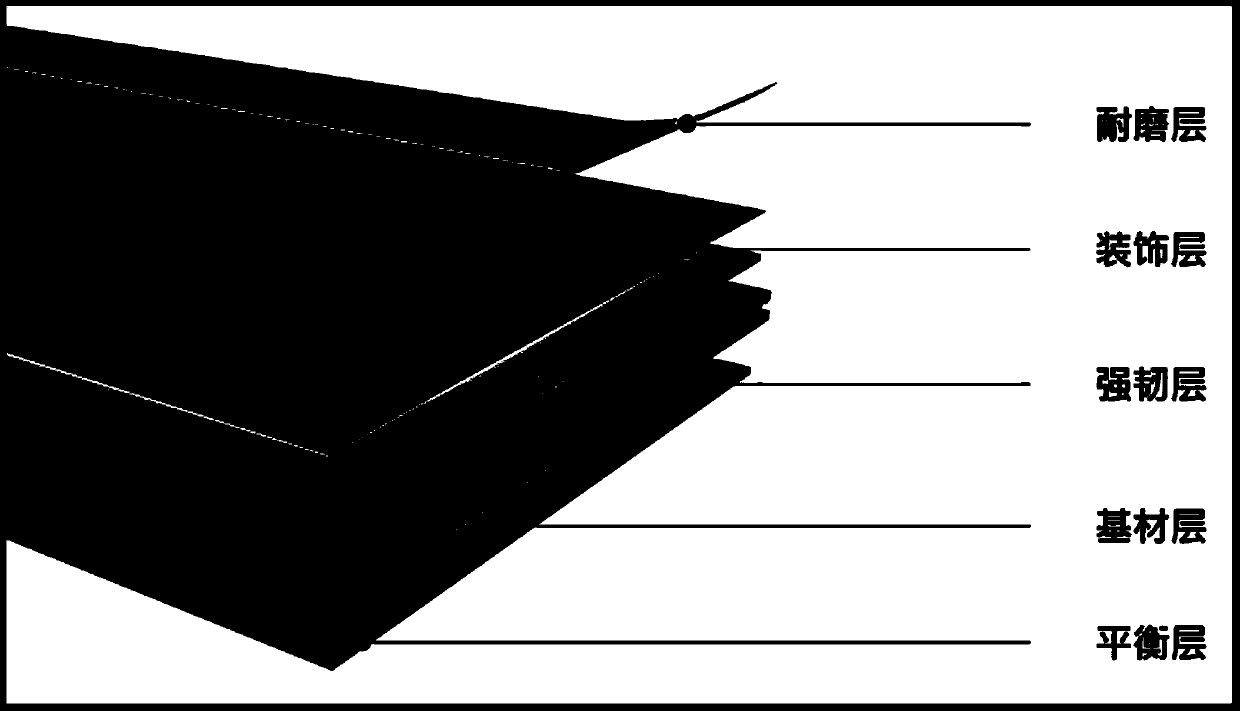
[0046] A tough layer, a balance layer, a decorative layer and a wear-resistant layer are provided, and a base material, a tough layer, a decorative layer and a wear-resistant layer are sequentially arranged on the balance layer to obtain a wood-plastic floor.
[0047] The present invention has no special limitation on the components of the base material, and the base material well-known to those skilled in the art for preparing wood-plastic flooring can be used. In order to obtain the wood-plastic floor with antibacterial and antiviral properties, in parts by weight, preferably 30.0 to 50.0 parts of modified plant powder, 100 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 30.0 to 50.0 parts of calcium carbonate, 5.0 to 7.0 parts 1 part of the first composite stabilizer,...
Embodiment 1
[0108] Add 30.0 parts of wood powder with a fineness of 60 meshes into the mixer and start the operation. When the temperature rises to 100°C, open the cover and stop, and add silane coupling agent with 1.1% of the wood powder mass into the mixer within 3 minutes. In the middle, after starting up for another 3 minutes, put the obtained material into the cold mixer to run, and the temperature drops below 45°C to obtain modified wood powder;
[0109] The modified sawdust powder is mixed with 100 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 30.0 parts of activated calcium carbonate with a fineness of 600 meshes, 2.0 parts of calcium stearate, 3.0 parts of tribasic lead sulfate, 10.0 parts of foam regulator, 1.0 parts of even Nitrogendiformamide, 3.0 parts of chlorinated polyethylene (CPE), and 3.0 parts of polyethylene wax were added to the mixer, and the mixing temperature was adjusted to 110°C. Five minutes before the end of the temperature rise, 5.0 parts of 60-mesh Put it into the mixer, and...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Add 50.0 parts of wood powder with a fineness of 80 meshes into the mixer and start the operation. When the temperature rises to 110°C, open the cover and stop, and add 1.3% silane coupling agent of wood powder into the mixer within 5 minutes. In the middle, after starting up for another 3 minutes, put the obtained material into the cold mixer to run, and the temperature drops below 45°C to obtain modified wood powder;
[0130] Mix the modified sawdust powder with 100 parts of polyvinyl chloride, 50 parts of activated calcium carbonate with a fineness of 1200 mesh, 3.0 parts of zinc stearate, 4.0 parts of dibasic lead phosphate, 16.0 parts of foam regulator, 0.8 parts of even Nitrogendiformamide, 4.0 parts of chlorinated polyethylene (CPE), and 6.0 parts of polyethylene wax were added to the mixer, and the mixing temperature was adjusted to 110 ° C. 4 minutes before the end of the temperature rise, 10.0 parts of 80-mesh Put it into the mixer, and then turn it on for 5 m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com