Method for preparing star-shaped styrene thermoplastic elastomer
A thermoplastic elastomer and styrene technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of star-shaped styrene thermoplastic elastomers, and can solve problems such as restricting applications.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
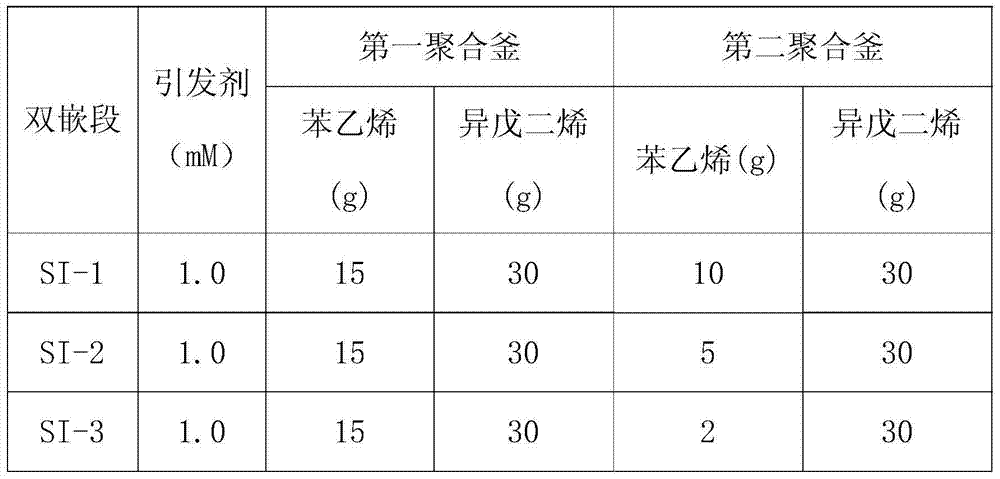
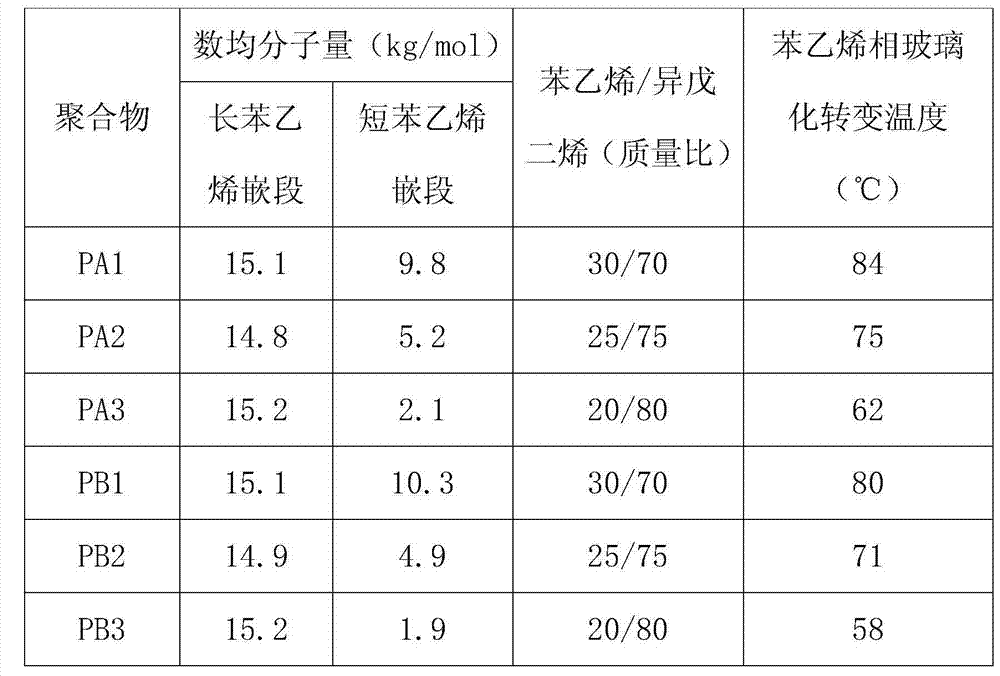
[0014] In the two polymerization kettles filled with argon gas are added metered cyclohexane, styrene monomer, and tetrahydrofuran, the temperature of the kettle is adjusted to 40-60°C and then the initiator n-butyllithium is added. After 30 minutes of reaction, the measured isoprene was added to the first and second polymerization tanks respectively, as shown in Table 1, SI-1, and the temperature of the tank was controlled at 50-70°C. After reacting for 60 minutes, the glue in the two polymerizers was introduced into the third polymerizer at a molar ratio of 1:1 to the active chain, and mixed, and then the coupling agent silicon tetrachloride was added. After reacting for 60 minutes, the reaction was stopped. The product was coagulated, washed, and dried to obtain the polymer PA1 shown in Table 2. The monomer feed ratio in the second polymerizer was changed respectively, as shown in SI-2 and SI-3 in Table 1, and the above experiment was repeated to obtain polymers PA2 and PA3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0018] In the two polymerization kettles filled with argon gas are added metered cyclohexane, styrene monomer, and tetrahydrofuran, the temperature of the kettle is adjusted to 40-60°C and then the initiator n-butyllithium is added. After 30 minutes of reaction, the measured isoprene was added to the first and second polymerization tanks respectively, as shown in Table 1, SI-1, and the temperature of the tank was controlled at 50-70°C. After reacting for 60 minutes, the glue in the two polymerizers was introduced into the third polymerizer according to the active chain molar ratio of 1:2, mixed, and then the coupling agent silicon tetrachloride was added. After the reaction for 60 minutes, the reaction was stopped. The product was coagulated, washed, and dried to obtain the polymer PB1 shown in Table 2. The monomer feed ratio in the second polymerizer was changed respectively, as shown in SI-2 and SI-3 in Table 1, and the above experiment was repeated to obtain polymers PB2 and...
Embodiment 3
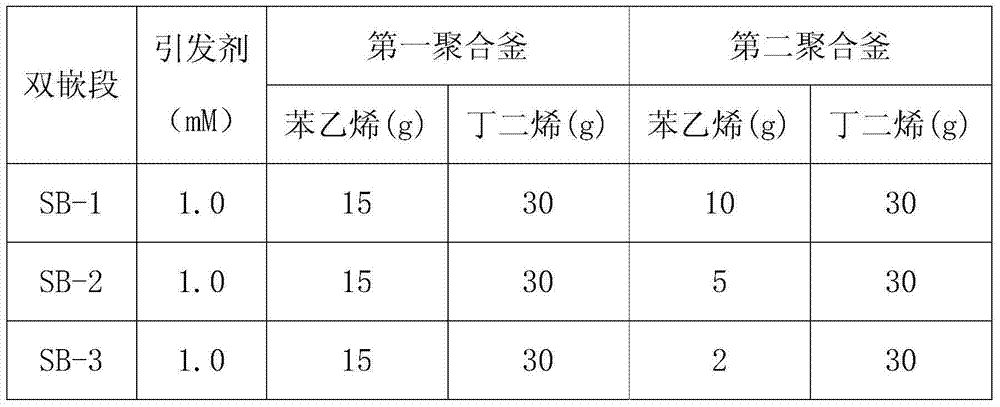
[0022] Table 3 Synthesis conditions of styrene-butadiene diblock
[0023]
[0024] In the two polymerization kettles filled with argon gas are added metered cyclohexane, styrene monomer, and tetrahydrofuran, the temperature of the kettle is adjusted to 40-60°C and then the initiator n-butyllithium is added. After reacting for 30 minutes, the measured butadiene was added to the first and second polymerization tanks respectively, as shown in SB-1 in Table 3, and the temperature of the tank was controlled at 50-70°C. After reacting for 60 minutes, the glue in the two polymerizers was introduced into the third polymerizer at a molar ratio of 1:1 to the active chain, and mixed, and then the coupling agent silicon tetrachloride was added. After reacting for 60 minutes, the reaction was stopped. The product was coagulated, washed, and dried to obtain the polymer PC1 shown in Table 4. The monomer feed ratio in the second polymerizer was changed respectively, as shown in SB-2 and SB-3 in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com