Aptamer afb1-22 of aflatoxin b1 and its application
An aflatoxin and nucleic acid aptamer technology, applied in the field of nucleic acid, can solve the problems of limited application scope and rapid development of immunological detection methods, short life of reagents, difficult to store, difficult antibody preparation, etc., and achieves simple and rapid in vitro screening and detection. Easy fixed-point modification mark, promising effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
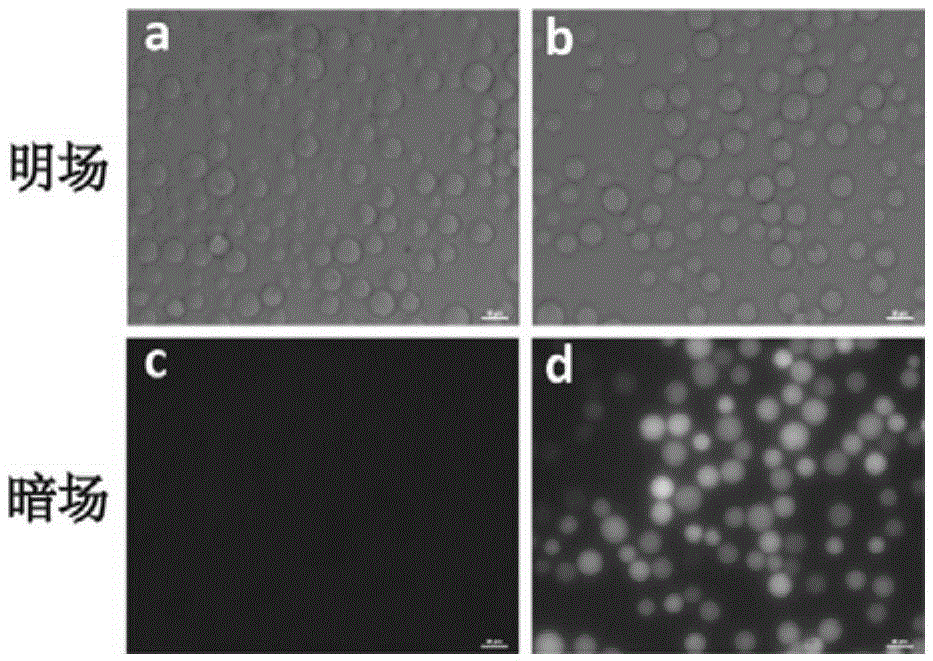
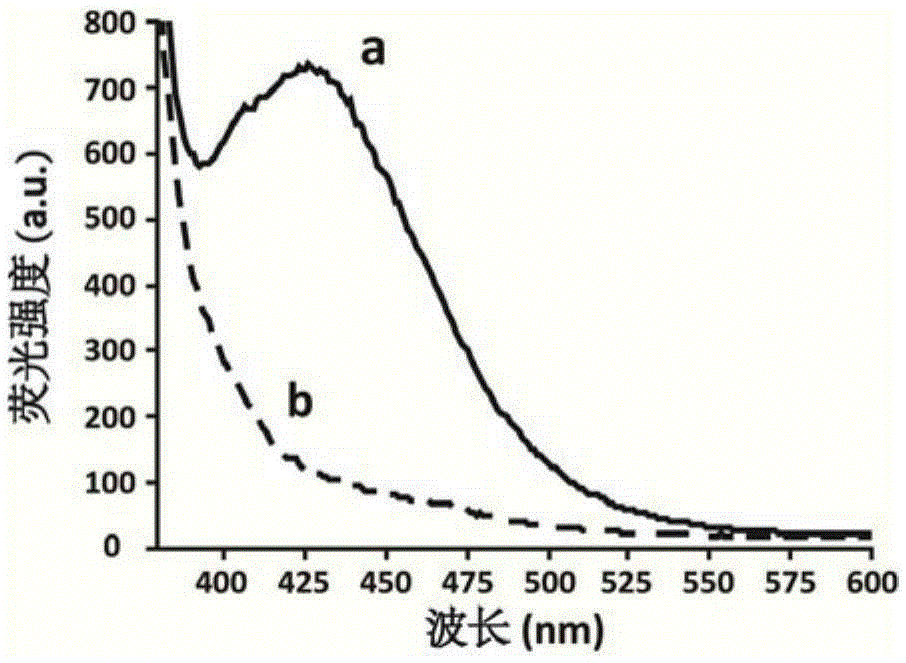
[0020] Example 1 Target AFB 1 Synthesis and characterization of -beads
[0021] Using agarose microbeads as the solid phase carrier of target molecules is beneficial to the separation of unbound or weakly bound and non-specific binding sequences, and is suitable for flow cytometry detection. will AFB 1 The synthetic route coupled to agarose microbeads is as follows:
[0022]
[0023] Take 7.6mg AFB 1 Dissolve in 4mL pyridine, add 35mg carboxymethylhydroxylamine hydrochloride, reflux at 80°C overnight, concentrate in vacuo and silica gel column chromatography (chloroform / methanol=10:1), isolate AFB 1 -oxime and dissolved in 3 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, added 5.4 mg of NHS, 9.6 mg of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 5 mg of dimethylaminopyridine, stirred overnight with a magnetic rotor, filtered and concentrated by evaporation to obtain AFB 1 -oxime activated esters (11. Chu, F.S.; Hsia, M.T.; Sun, P.S.: Preparation and characterization of aflatox-nB1-1-(O-carboxymethyl...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Embodiment 2 Aflatoxin B 1 Screening of specific aptamers
[0025] (1) Design and synthesis of random oligonucleotide library
[0026] Design and synthesize a random oligonucleotide library with fixed regions at both ends of 18 nucleotides and a random region of 45 nucleotides in the middle as follows: 5'-ATACCAGCTTATTCAATT-N45-AGATAGTAAGTGCAATCT-3', with a library capacity of 10 15 . The primer sequences used were forward primer (FP): 5'-ATACCAGCTTATTCAATT-3', reverse primer (RP): 5'-AGATTGCACTTACTATCT-3', fluorescent labeling primer (FFP): 5'-FAM-ATACCAGCTTATTCAATT-3 ', biotin-labeled primer (BRP): 5'-Bio-AGATTGCACTTACTATCT-3' (12.Shangguan, D.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cao, Z.C.; Chen, H.W.; Mallikaracchy, P.; Sefah, K.; Yang, C.J.; Tan, W. Aptamers evolved from living cells as effective molecular probes for cancers study. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006, 103, 11838-11843).
[0027] (2) Screening of nucleic acid aptamers
[0028] AFB 1 -beads are used as target molecules,...
Embodiment 3
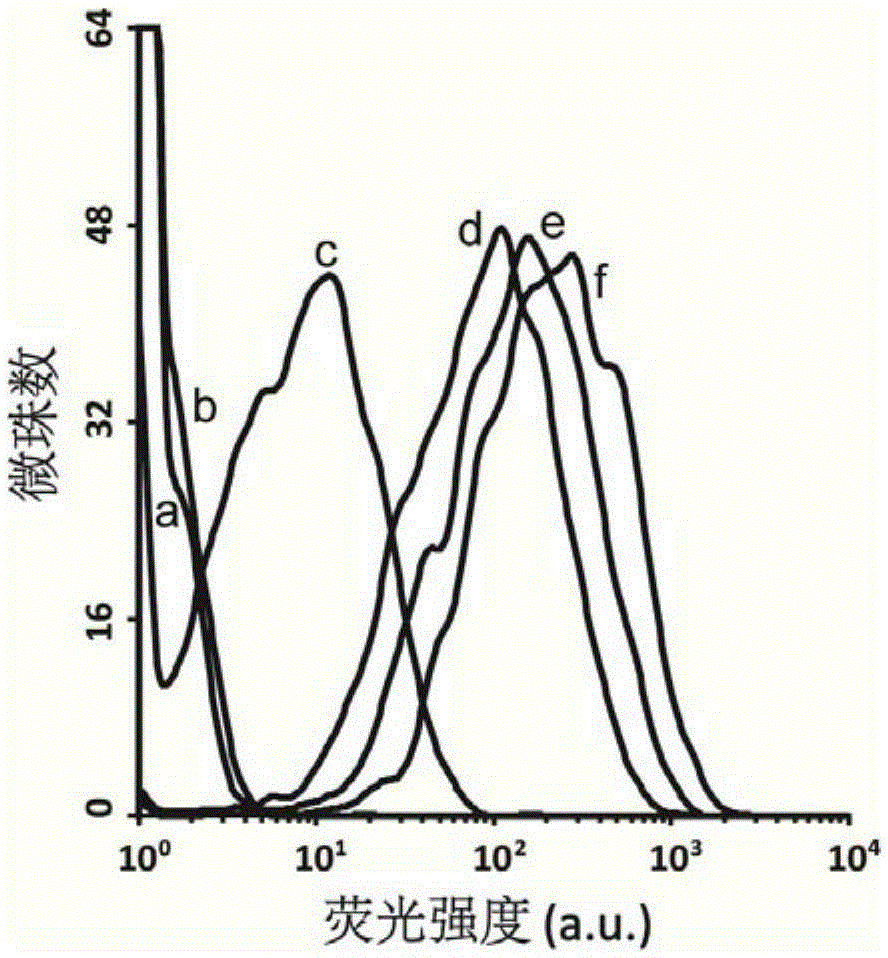
[0030] Affinity Characterization of Example 3 Nucleic Aptamers
[0031] Label the nucleic acid aptamer molecule with carboxyfluorescein (FAM) at the 5' end, prepare a 0-7000nM gradient solution in 200μL binding buffer, heat denature, and mix with 0.4μL AFB 1 -beads were incubated at room temperature for 30min. After washing with the binding buffer, the microbeads were suspended in the binding buffer, and the fluorescence intensity on the surface of the microbeads was measured by flow cytometry. Plot fluorescence intensity versus aptamer concentration using the formula Y=BmaxX / (K d +X) carrying out the fitting of the binding curve to determine the binding and dissociation constant K of the nucleic acid aptamer d . (see Figure 5 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com