Anti-drug resistant tuberculosis compound targeting bacteria RNA polymerase
An RNA polymerase, compound technology, used in antibacterial drugs, pharmaceutical formulations, resistance to vector-borne diseases, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
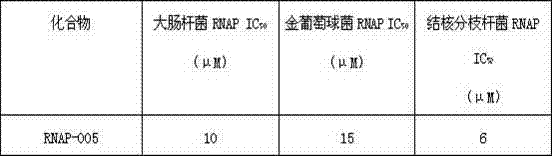
[0016] In vitro inhibition experiment of compound RNAP-005 (purchased from IBScreen Company) on bacterial RNA polymerase. For the compound RNAP-005 molecule, by detecting the reduction of the substrate ATP——Kool NC-45 RNAP Activity & Inhibitor Screening Kit (Epicentre Company): 2 μg of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and mycobacterium-binding RNA polymerase were mixed with The gradient diluted pyridoindole derivatives were reacted at 25°C for 20 minutes, and then 1002 μM ATP (total reaction volume 50 μL) was added. After acting at 25°C for 20 minutes, the reaction mixture was added to a 96-well microtiter plate, 50 μL per well, and Kool 50 μL of NC-45Reagent per well was allowed to stand at room temperature for 10 minutes, and the chemiluminescence value was read to indicate the amount of ATP remaining in the reaction. In the experiment, the group without compound was set as the control group. Finally, calculate the inhibitory rate of compound RNAP-005 on the activity...
Embodiment 2
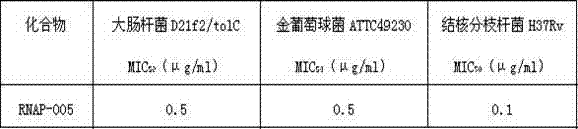
[0023] In vitro inhibition experiment of compound RNAP-005 on the growth of standard bacteria. Use the standard tube dilution method recommended by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI):
[0024] 1. Inoculate the bacteria in fresh MH liquid medium and culture overnight at 37°C;
[0025] 2. Correct the bacterial solution to the 0.5 McFarland turbidity standard with fresh MH liquid medium, then dilute it with MH liquid medium at 1:200, add 1 mL to each test tube, and add 1 mL of N-( (4-fluorobenzyloxy)methyl)-O-methyl-N-(6-(trifluoromethyl)-2,3,4,9-tetrahydropyridoindole)hydroxylamine and other 6 compounds (The final concentration of solvent DMSO is maintained at 1%), cultured at 37°C for 18 hours, with 1% DMSO + bacteria as the control, and sterile medium as the blank control;
[0026] 3. Take out the tube with the lowest concentration of no bacteria growth compared with the blank control, which is the minimum inhibitory concentration of the compound RNAP-005...
Embodiment 3
[0031] In vitro inhibition experiment of compound RNAP-005 on drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Using the experimental method described in Example 3, the compound RNAP-005 was used to carry out antibacterial experiments on three strains of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis collected clinically. At the same time, the commonly used clinical anti-binding drugs streptomycin (SM), ethambutol (EMB), kanamycin (KM), isoniazid (INH), rifampicin (RFP), levofloxacin (LVFX), Ofloxacin (OFLX), moxifloxacin (MOX), capreomycin (CPM), and amikacin (AMK) were used as controls.
[0032] The results showed that the compound RNAP-005 had obvious inhibitory effect on the growth of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis collected in clinic, and its MIC9 0 The values are shown in Table 3.
[0033] Strain number RNAP-005 SM RFP EMB INH CPM KM AMK OFLX LVFX MOX 1 0.3 64 64 16 1 4 2 1 0.5 0.25 0.06 2 0.5 64 64 4 8 1 1 0....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com