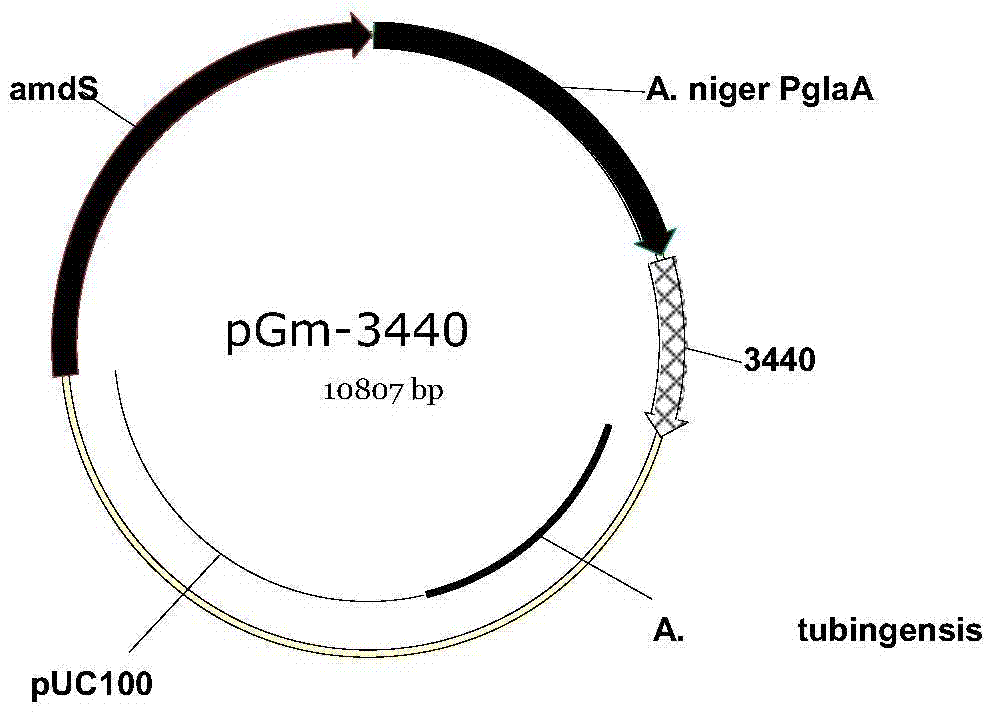
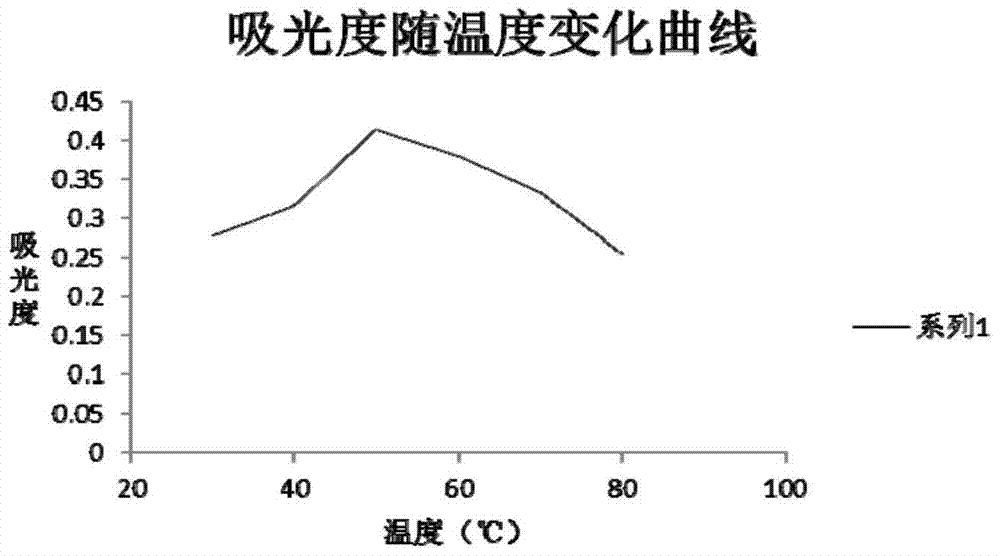
Glucamylase
A kind of technology of glucoamylase and glucose, applied in glucoamylase and its application field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Embodiment 1: Screening of glucoamylase gene
[0020] Through comparative proteomics, the pre-established glucoamylase sequence of our laboratory (Protein Expression and Molecular Biology Laboratory) and the predicted protein sequence of the whole genome of Glioma rosea were locally blasted to obtain some sequences with high homology . These highly homologous sequences were subjected to NCBI online Blastp and the comparison results were analyzed to determine the most likely glucoamylase sequence. Use SignalP4.1Server to analyze these possible sequences, and use the sequence containing the signal peptide as the target gene for cloning.
[0021] Cloning of the glucoamylase gene
[0022] The target gene was obtained by PCR amplification using the whole genome DNA of Glioma pink as a template, and the primers used in the PCR process were as follows:
[0023] Forward primer 5′-CCG CTCGAG AGGATGGTGAAGATAATTCCCACTGTGC-3′
[0024] reverse primer 5′-TGC TCTAGA TCATCGCCAG...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Embodiment 2: Recombinant plasmid transforms Aspergillus niger G1 strain and verification
[0031] Draw the Aspergillus niger G1 spore suspension in the center of the CMA plate (9cm petri dish), wait for the colony to cover the entire petri dish, cut 1 / 4 size of the culture based on 200mL CMA liquid medium, cultivate at 30°C and 200rpm for 14~ 16h.
[0032] Collect the bacteria with a sterile Miracloth filter cloth, rinse once with solution A, transfer it to 40ml of lysate with a cotton swab under sterile conditions, lyse at 30°C and 200rpm for two hours, and observe the protoplasts with a microscope the formation of.
[0033] Filter the above lysate with a sterile Miracloth filter cloth, collect protoplasts with two 50ml sterile centrifuge tubes and rinse with solution B to make each tube about 25ml. Centrifuge at 2000rpm for 5min to discard the supernatant, and wash the precipitate twice with 20ml solutionB. Resuspend the pellet in 10 mL of solution B, and count th...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: Fermentation verification of positive transformant strains.
[0049] Pick the above-mentioned positive transformant strains, inoculate them in 20ml TSB fermentation medium, and cultivate them at 30°C and 200rpm for 5 days; the obtained fermentation broth is filtered with 8 layers of gauze, and the filtrate is centrifuged at 14000g for 10min to collect the supernatant; The supernatant was electrophoresed on a 12% SDS-PAGE gel. Electropherogram as figure 2 .
[0050] TSB fermentation medium: 12g NaNO 3 , 0.5g KCl, 1.5g KH 2 PO 4 , 2.05g MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O, 3.5 g NaH 2 PO 4 ·H 2 O, 45g tryptic soybean broth, 70g sodium citrate, 1g Tween 80, 1mL trace elements (see below), add dlH 2 O to a final volume of 700 mL, after autoclaving, add 300 mL of 40% maltose sterilized by filtration with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane.
[0051] Trace elements: in 250mL dlH 2 Add 1g FeSO to O 4 ·7H 2 O, 8.8g ZnSO 4 · 7 h 2 O, 0.4g CuSO 4 ·5H 2 O, 0.15g MnSO 4 4H 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com