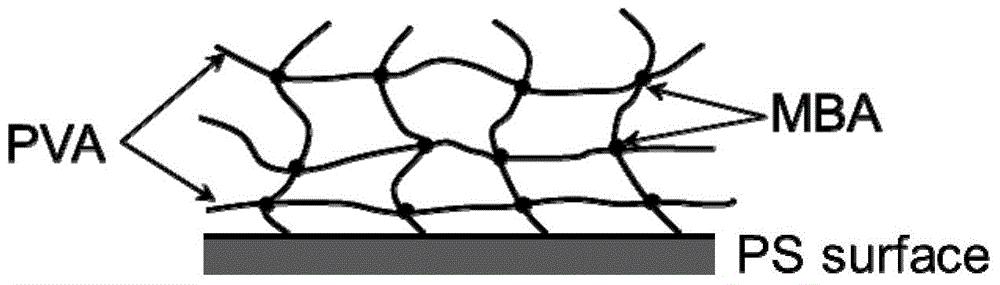
A method for hydrophilic modification of polystyrene material surface
A polystyrene and hydrophilic modification technology, which is applied in the field of perfusion chromatographic medium of biological macromolecules, polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel, and surface hydrophilic modification of polystyrene materials, can solve the problem of high protein adsorption and achieve Increased hydrophilicity, reduced non-specific adsorption capacity, and the effect of not falling off easily
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
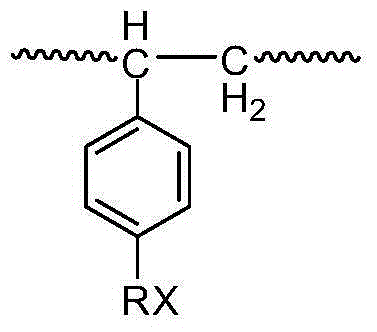
[0045] Chloroacetylation of polystyrene (PS-Cl)
[0046] Add 0.8g of polystyrene microspheres, 24ml of carbon disulfide, and 1.06g of anhydrous aluminum trichloride into a 50ml flask, stir with a magnet, and the solution turns yellow, then add 0.4ml of chloroacetyl chloride dropwise, and react in an oil bath at 50°C for 3h. The reaction solution was suction-filtered in anhydrous state, the separated solid matter was quickly poured into glacial hydrochloric acid and stirred, filtered again and washed with deionized water until neutral, finally washed and filtered with absolute ethanol, and dried in a vacuum oven.
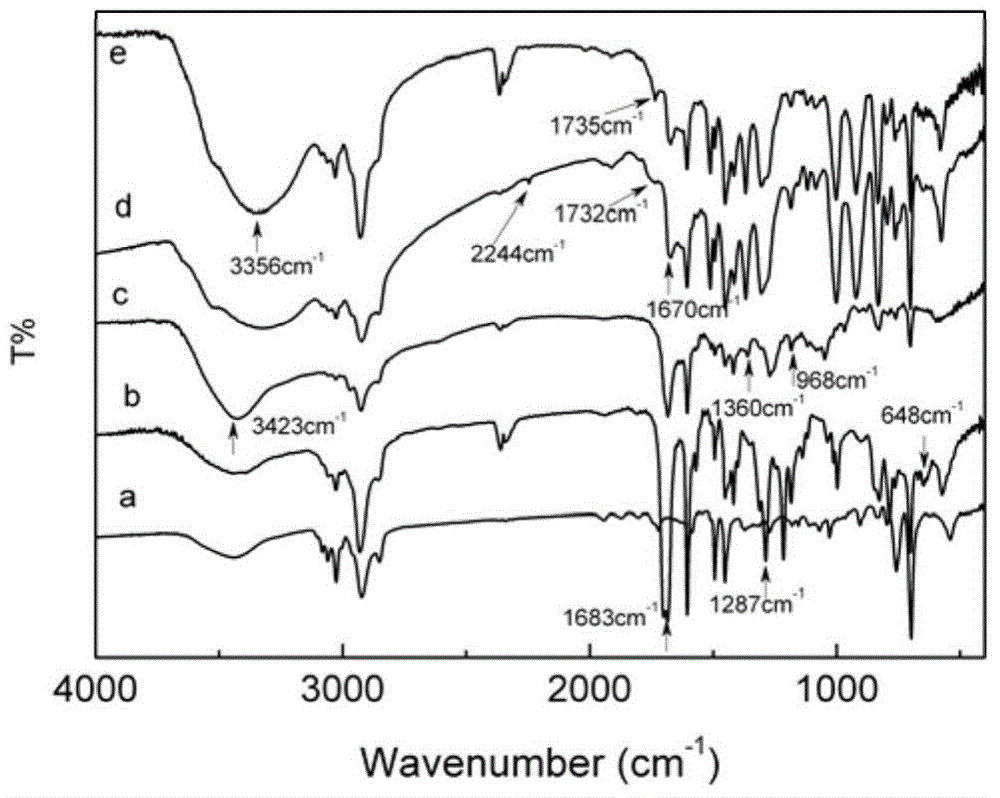
[0047] The chlorine content of the dried chloroacetylated polystyrene was measured by the sodium hydroxide melting method, and the chlorine content of the modified microspheres was 13.95%. Infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis showed that the chloroacetyl group had been successfully coupled to the surface of the microspheres.
[0048] B Chloroacetylated polystyrene ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Chloroacetylation of polystyrene
[0058] Add 0.8g of ordinary polystyrene plate, 20ml of dichloromethane, 1.2g of anhydrous aluminum trichloride to a 50ml flask, stir with a magnet, the solution turns yellow, then add 0.8ml of chloroacetyl chloride dropwise, and react in an oil bath at 30°C 5h. The reaction solution was suction-filtered in anhydrous state, the separated solid matter was quickly poured into glacial hydrochloric acid and stirred, filtered again and washed with deionized water until neutral, finally washed and filtered with absolute ethanol, and dried in a vacuum oven.
[0059] B Chloroacetylated polystyrene amination reaction (PS-NH 2 )
[0060] Swell 0.5 g of the above-obtained chloroacetylated polystyrene with 10 ml of chloroform overnight, add 25 ml of an ethanol solution of 0.6 g of hexamethylenetetramine, add 0.64 g of sodium iodide under stirring, and continue mechanical stirring at room temperature for 20 h. Filter and wash thoroughly with etha...
Embodiment 3
[0068] A bromoacetylation reaction of polystyrene
[0069] Add 0.8g of polystyrene microspheres, 24ml of carbon disulfide, and 1.5g of anhydrous aluminum trichloride into a 50ml flask, stir with a magnet, and the solution turns yellow, then add 0.4ml of bromoacetyl bromide dropwise, and react in an oil bath at 50°C for 3h. The reaction solution was suction-filtered in anhydrous state, the separated solid matter was quickly poured into glacial hydrochloric acid and stirred, filtered again and washed with deionized water until neutral, finally washed and filtered with absolute ethanol, and dried in a vacuum oven. The bromine content of the modified microspheres was 25.54%.
[0070] B Chloroacetylated polystyrene amination reaction (PS-NH 2 )
[0071] Swell 0.5 g of the chloroacetylated polystyrene microspheres obtained above with 10 ml of ethanol overnight, add 25 ml of an ethanol solution of 0.45 g of hexamethylenetetramine, add 0.48 g of sodium iodide under stirring, and con...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com