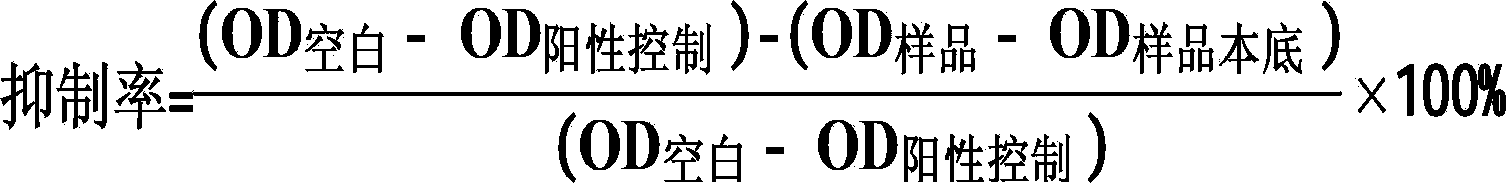Preparation method and application of stemona effective part extract
A technology of effective parts and extracts, which is applied in the field of preparation of extracts of effective parts of basil, can solve problems that have not yet been seen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] Example 1: Preparation of the effective part extract
[0016] (1) The preparation of the total alkaloid extract of Herba Melonifolia
[0017] Take 5kg of herbal medicines, crush them, add 10L of 95% ethanol to reflux and extract twice, each time for two hours, combine the extracts, concentrate to dryness, add 3L of distilled water to dissolve, adjust the pH value to 1-2 with 4M concentrated hydrochloric acid, and statically After 12 to 16 hours, filter with suction. The filtrate was adjusted to pH 9-11 with concentrated ammonia water or aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, and then extracted twice with 5 L of chloroform, and the extracts were combined and concentrated to dryness to obtain the total alkaloid extract (75 g).
[0018] (2) Purification of the total alkaloid extract of Herba Cinnamomi
[0019] After dissolving the above-mentioned total alkaloid extracts of Radix radicis with 100mL ethanol, pass through the macroporous resin column chromatography, use ethanol...
Embodiment 2
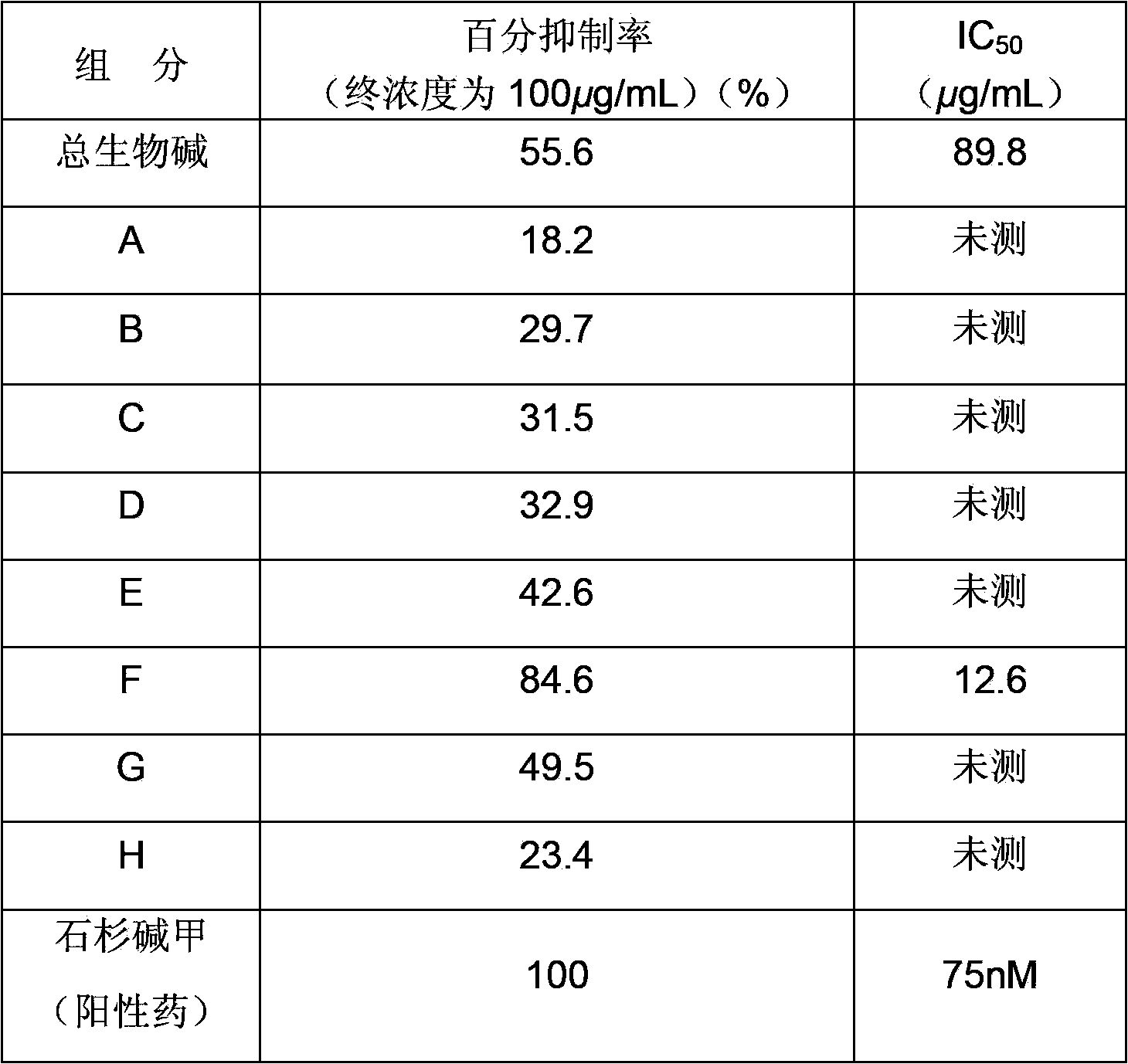
[0020] Embodiment 2: The modified Ellman method measures the acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of each eluted fraction after the macroporous resin column chromatography of the total alkaloids of the plant
[0021] The modified Ellman method was used to determine the inhibition rate of acetylcholinesterase by each elution fraction after macroporous resin column chromatography of the total alkaloids of Phetoperaceae, and Huperzine A was used as the positive control drug. The specific experimental process is as follows:
[0022] Use a 96-well microtiter plate to determine the inhibitory activity of the sample on the enzyme. Add 140 μL of 0.1M phosphate buffer (pH=8.0) to each well of the sample group, and then add 20 μL of the sample. Add 160 μL of phosphate buffer to the blank well without adding For any sample, 20 μL of 0.1 mg / mL physostigmine and 140 μL of phosphate buffer were added to the positive control control group. Add 15 μL of acetylcholinesterase, mix well and...
Embodiment 3
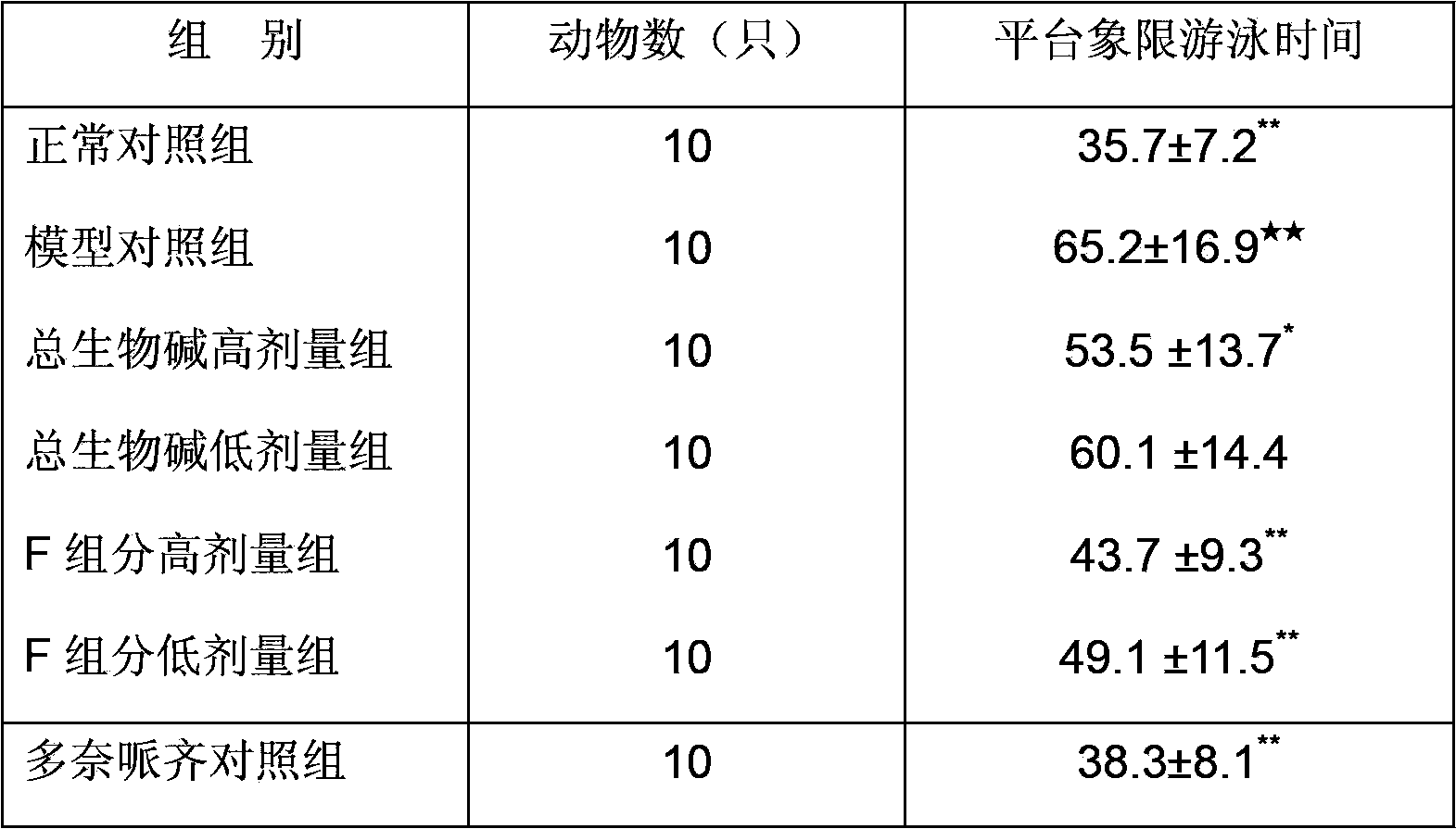
[0027] Embodiment 3: Morris water maze experiment
[0028] 70 healthy Kunming male mice were randomly divided into 7 groups: normal control group, model control group, high-dose total alkaloids group (1 mg / kg), low-dose total alkaloids group (0.5 mg / kg), F component High-dose group (1mg / kg), low-dose group of F component (0.5mg / kg) and donepezil control group (0.1mg / kg). Except the normal control group and the model control group were intraperitoneally injected with the same amount of normal saline, the mice in the other groups were injected intraperitoneally once a day at a fixed time for 5 consecutive days. After 2 days of administration, water maze positioning navigation training was carried out. Except for the normal control group, which was intraperitoneally injected with the same amount of normal saline, the mice in the other groups were intraperitoneally injected with 2 mg / kg of scopolamine before training. One hour after the last administration, positioning navigatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com