Organic solar cell
A solar cell and organic technology, applied in the field of solar cells, can solve the problems of sufficient response and low photoelectric conversion efficiency, and achieve the effects of avoiding corrosion, improving photoelectric conversion efficiency, and prolonging service life
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example approach
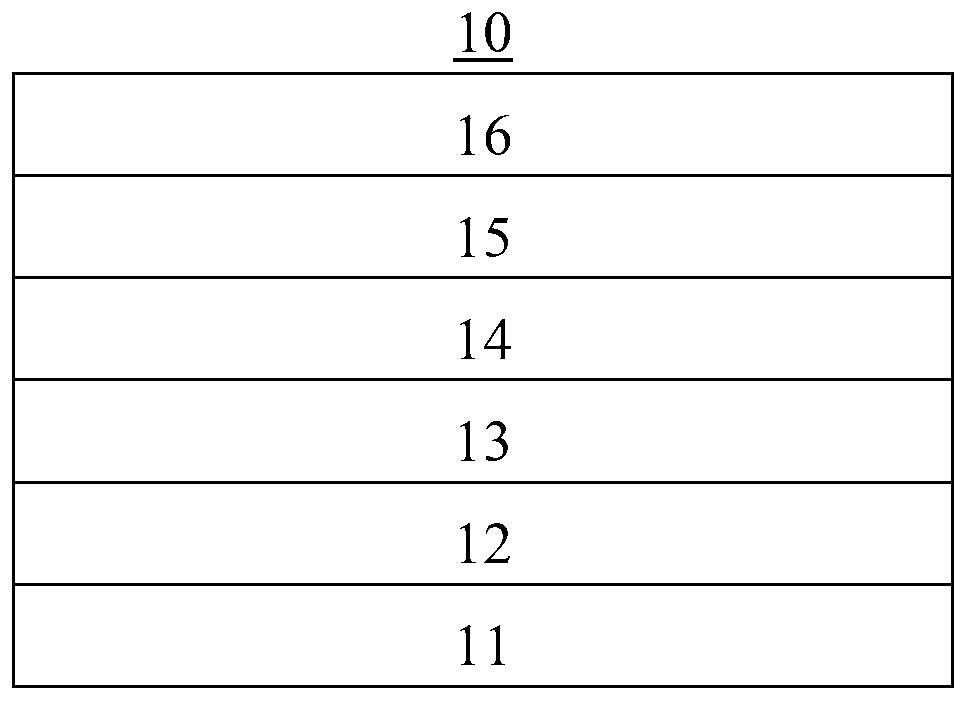
[0052] see figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the structure distribution of the first embodiment of the organic solar cell of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the organic solar cell 10 is an inverted structure, specifically including a substrate 11, and the material of the substrate 11 can be hard, such as glass or quartz, or flexible, such as flexible polymer. Polymer materials that can be used as flexible substrates include (but are not limited to): polyethylene naphthalate (PEN; polyethylene naphthalate), polyethylene terephthalate (PET; polyethylene terephthalate), polyamide (polyamide) , Polymethylmethacrylate, Polycarbonate or Polyurethane. Flexible substrates can be used in continuous processes, such as web-coating or lamination processes. In addition, in addition to insulating materials, the substrate may also be made of conductive materials, such as titanium, aluminum, copper, nickel and other metal materials. The thickness of the s...
no. 2 example approach
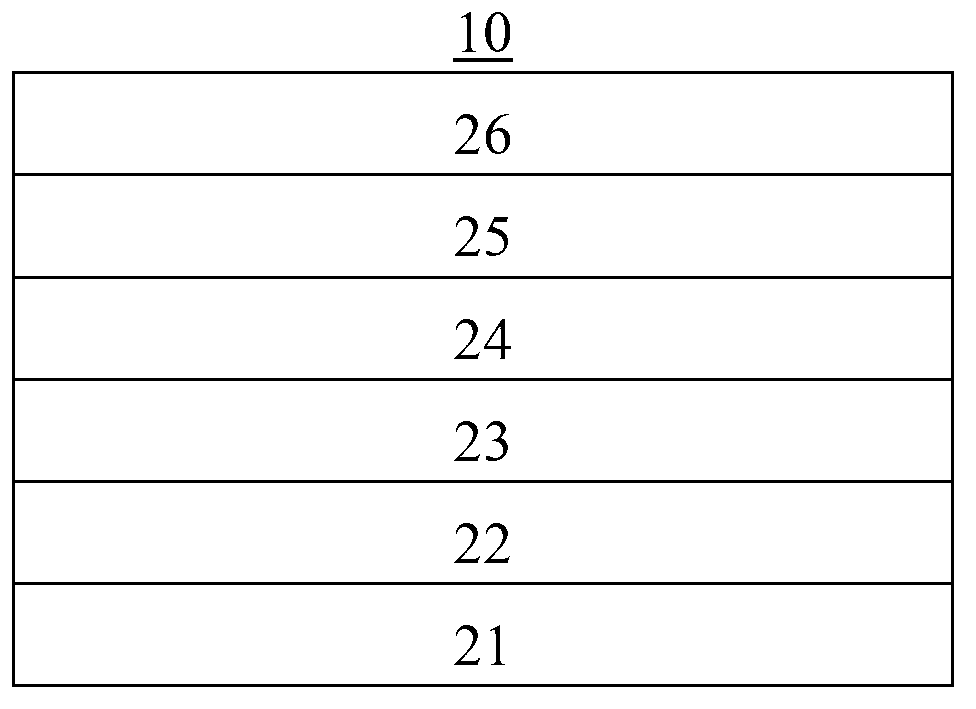
[0074] See also figure 1 Compared with the structure of the organic solar cell shown in the first embodiment, the difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that an organic small molecule layer doped with a light-emitting material is formed on the cathode 12, which is the electron transport layer 13 , wherein the luminescent material is C545T, the small organic molecule in the small organic molecule layer is Alq3, the doping concentration of C545T is 7%, and the rest of the technical solutions are the same as the first embodiment.
no. 3 example approach
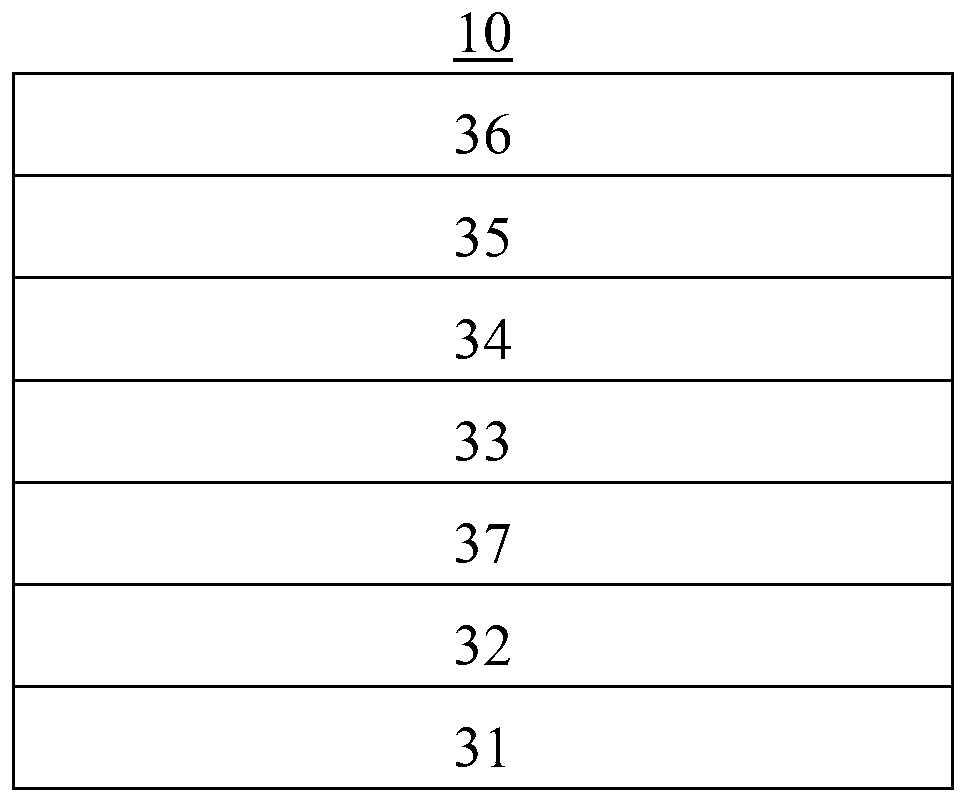
[0076] See also figure 1 Compared with the structure of the organic solar cell shown in the third embodiment, the only difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that an organic small molecule layer doped with a luminescent material is formed on the cathode 12, which is the electron transport layer 13 , wherein the luminescent material is C545T, the small organic molecule in the small organic molecule layer is Alq3, the doping concentration of C545T is 10%, and the rest of the technical solutions are the same as those of the first embodiment.
[0077] The application compares the embodiment of the present invention with the implementation effect of the prior art (with the four core characteristic parameters of the solar cell - the open circuit voltage V OC , Short-circuit current density J SC , fill factor FF photoelectric conversion efficiency n, for specific comparison, see Table 2 below for details:
[0078] Table 2 The implementation effect compa...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com