Processing method of lead-acid battery grid
A technology of lead-acid battery and processing method, which is applied in the direction of sustainable manufacturing/processing, electrode carrier/collector, climate sustainability, etc., and can solve the problem of weakening the support effect of grid ribs on active materials, decreasing deep cycle life, Inappropriate application occasions and other issues, to achieve the effect of expanding the scope of application, reducing material consumption, and improving mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0033] The technical scheme of the present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0034] A method for processing a lead-acid battery grid, comprising the steps of:
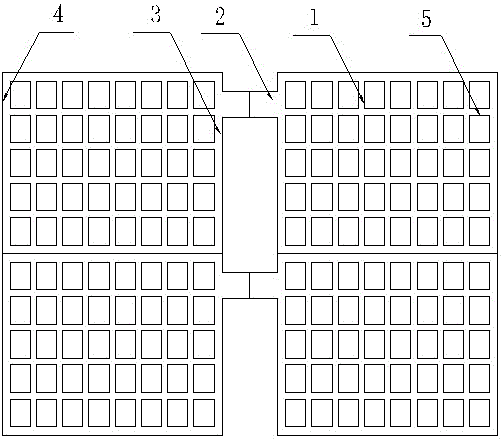
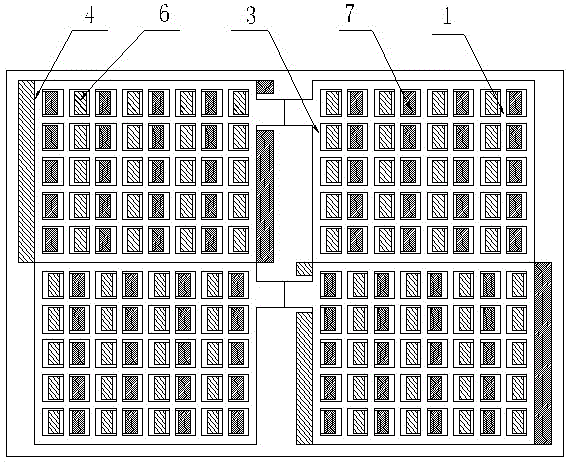
[0035] Such as figure 2 , image 3 As shown, the first step is to extrude the horizontal ribs. The upper and lower molds 6 and 7 are extruded by the horizontal ribs moving up and down and left and right. When the upper and lower molds are closed, the cavity is formed. When the grid 10 reaches the extrusion position:
[0036] (11) The cross bar extrusion lower die 7 rises, and the cross bar extrusion upper die 6 descends;
[0037] (12) The upper and lower molds for cross-bar extrusion move relative to the left and right to extrude the cross-bar 1, and the lead alloy is deformed by force and fills the cavity formed by the upper and lower dies for cross-bar extrusion;
[0038] (13) The upper and lower molds for cross-bar extrusion are separated, the lower die 7 for cros...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com