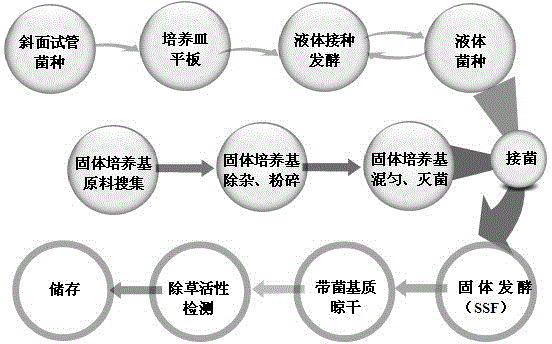
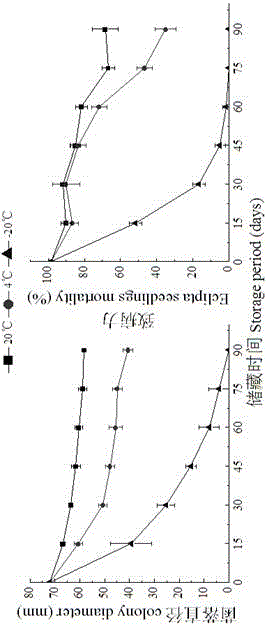
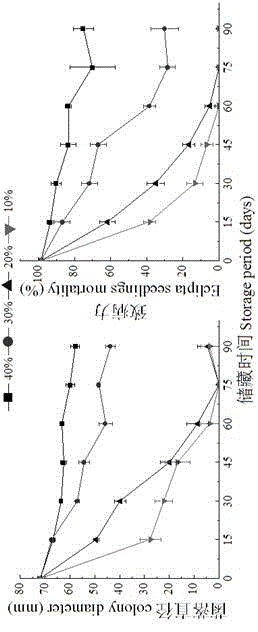
Sclerotium rolfsii solid fermentation culture medium and application thereof
A technology of neat Sclerotinia and solid fermentation, applied in the direction of application, fungi, and microorganism-based methods, can solve the problem of high bran price, and achieve the effects of simple preparation process, cost reduction, and pollution reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2 (composite embodiment of bran and agricultural waste)
[0033] Preparation of solid fermentation medium:
[0034] Different agricultural wastes and bran were mixed as a solid matrix at a weight ratio of 70:30, and after thorough mixing, the preparation was carried out according to the method in Comparative Example 1.
[0035] Biological herbicide preparation:
[0036] The prepared mixed agricultural waste-bran medium was inoculated and cultured according to the method in Comparative Example 1 to obtain various agricultural waste-bran medium herbicides containing mycelium.
[0037] Fermentation effect implementation 2 (example of compounding bran and agricultural waste)
[0038] According to the method in Example 1 of Comparative Fermentation Effect, each herbicide containing mycelium bran-agricultural waste medium prepared in Example 2 was tested. The test results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0039] Table 2 Effects of different agricultural waste-bran ...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3 (bran-rice husk composite embodiment)
[0043] Preparation of solid fermentation medium:
[0044] Different proportions of bran and rice husk were used as the solid matrix, and after thorough mixing, the preparation was carried out according to the method in Comparative Example 1.
[0045] Biological herbicide preparation:
[0046] The bran-rice husk mixed media prepared were inoculated and cultured according to the method in Comparative Example 1 to obtain the bran-rice husk herbicides containing mycelium.
[0047] Fermentation effect implementation 3 (bran-rice husk compound example)
[0048] According to the method in Example 1 of comparative fermentation effect, each bran-rice husk medium containing mycelium prepared in Example 3 was tested. The test results are shown in Table 3 below.
[0049] Table 3 The influence of oxalic acid production and pathogenicity on the fermented oxalic acid production and pathogenicity of whole bran and rice husk mixed...
Embodiment 4
[0052] Embodiment 4 (bran-rice husk composite water content embodiment)
[0053] Preparation of solid fermentation medium:
[0054] The bran is added to the rice husk according to 50% of the weight of the solid matrix, and the humidity of the matrix is adjusted. There are five treatments of 20%, 25%, 30%, 35%, and 40%. Solid fermentation media with different water contents are prepared.
[0055] Biological herbicide preparation:
[0056] The prepared medium with different water contents was inoculated and cultured according to the method in Comparative Example 1 to obtain the herbicide containing mycelium.
[0057] Fermentation effect example 4 (bran-rice husk composite water content example)
[0058] According to the method in Example 1 of Comparative Fermentation Effect, the media with different water contents prepared in Example 4 were tested. The test results are shown in Table 4 below.
[0059] Table 4 Effect of initial moisture content of bran-rice husk medium on o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com