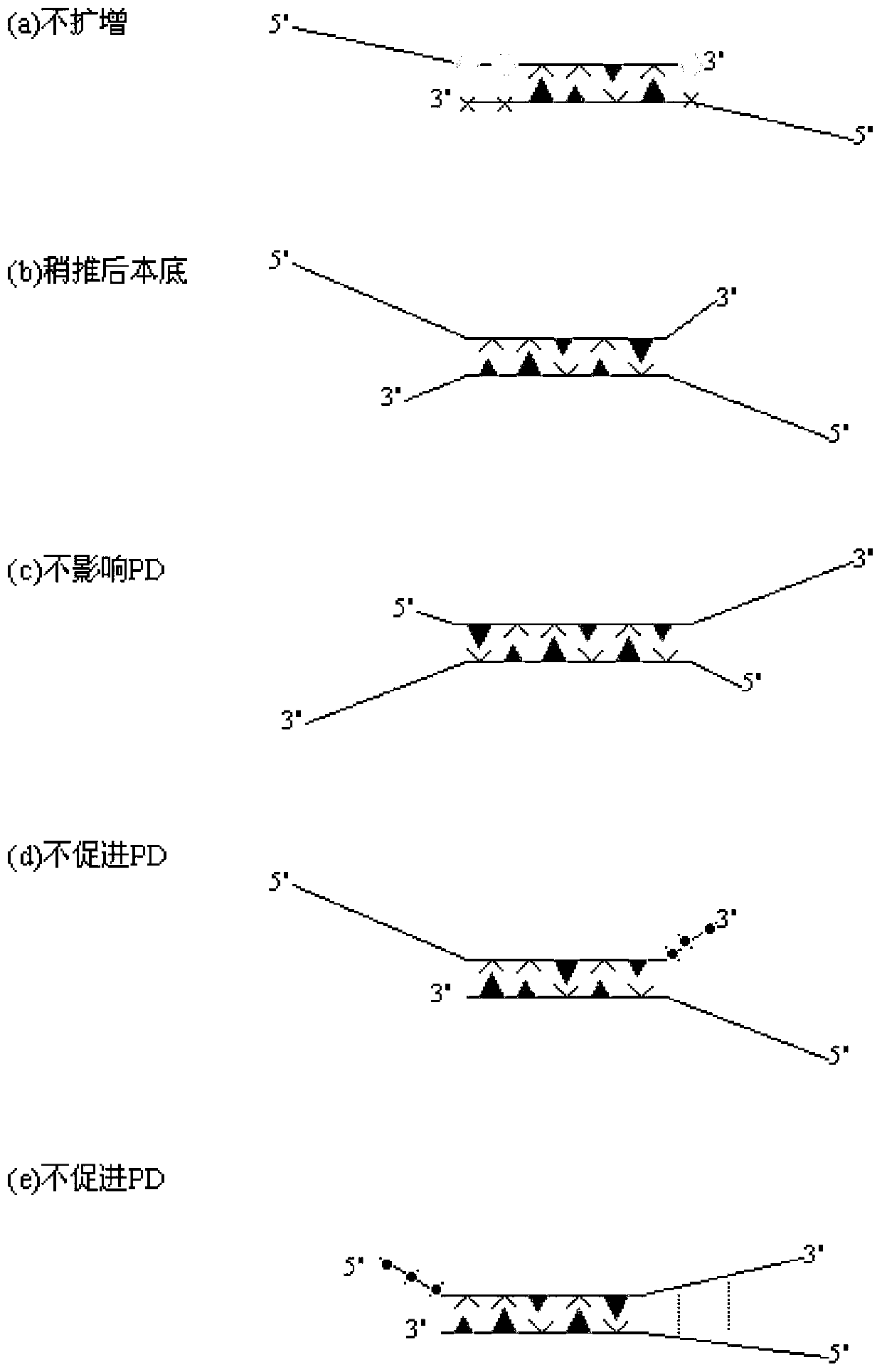
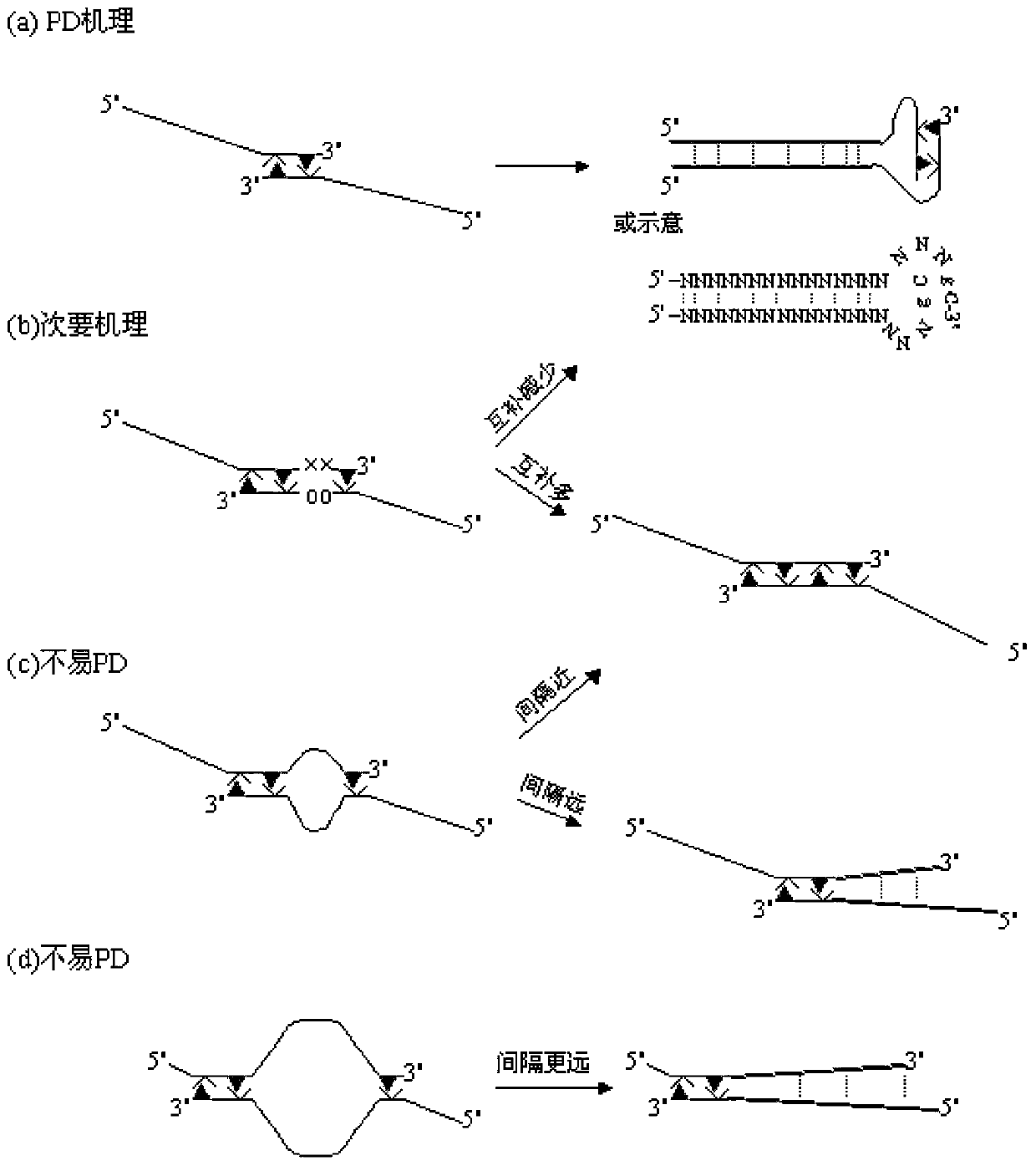
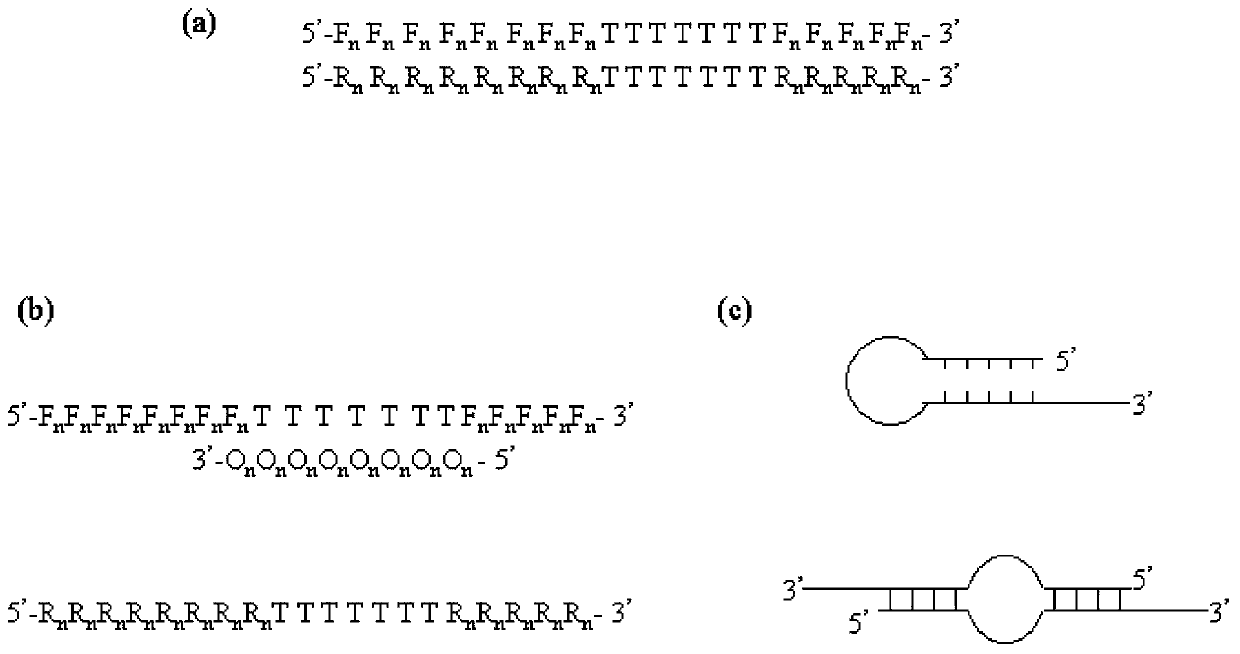
A PCR technique of interfering sequence in the middle of primer
A technology of sequence and comprehensive interference, applied in the field of selective inhibition of PCR non-specific amplification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0177] Example 1: Real-time fluorescent PCR detection of human enterovirus pathogenic strains:
[0178] In recent years, hand, foot and mouth disease has become prevalent among young children in my country, and the case fatality rate is high. The nucleic acid real-time fluorescent PCR detection of its pathogenic enterovirus (EnteroVirus, EV) has become an important technical means to monitor the prevalence of its infection. EV is an RNA virus, which was originally divided into more than 60 different serotypes, including enterovirus 68-71 . Based on its nucleic acid sequence classification, human EVs are classified into five types: A, B, C, D and PolioVirus, among which the main pathogenic strains CoxsackieA16 (CA16) and EnteroVirus 71 (EV71) are classified as human enterovirus A. The EV gene of enteroviruses varies greatly, only the 5'UTR is conserved, and there are three segments common to all strains homologous conserved region (underlined), the published EV universal pri...
Embodiment 2
[0200] Embodiment two: human hepatitis B virus SYBR Green I real-time fluorescent PCR:
[0201] Hepatitis B virus (referred to as hepatitis B) is a worldwide infectious disease caused by hepatitis B virus (Hepatitis B virus, HBV). The infection rate of hepatitis B in our country is very high, which greatly endangers people's health. At present, the detection methods of hepatitis B mainly include enzyme immunoassay, radioimmunoassay, chemiluminescence, immunofluorescence, nucleic acid amplification (PCR) fluorescence quantitative method, etc. Enzyme immunoassay is widely used, but real-time fluorescent PCR analysis can accurately measure the viral gene content of hepatitis B patients, and plays an irreplaceable important role in judging the virus replication level of infected patients, monitoring the infectivity of the disease and the efficacy of antiviral drugs. The HBV real-time fluorescent PCR in this embodiment is further divided into A. hepatitis B HBV load determination ...
Embodiment 3
[0252] Embodiment three: HBV improved TaqMan probe method real-time fluorescent PCR:
[0253] Probe-based real-time fluorescent PCR is mainly represented by TaqMan probes, and also includes MGB probes with increased binding force and locked nucleic acid LNA base probes. The increased signal of the amplified product is detected by a fluorescent probe with a quencher group. Generally, the 5' end of TaqMan probes is labeled with fluorescent groups such as FAM, VIC, NED, and the 3' end is labeled with quenching groups such as TAMRA, DABCYL&BHQ, etc. Free fluorophores generate fluorescence. TaqMan probe design respects the following general principles: 1) T of the probe m Value ratio of primer T m The value should be higher than 10°C; 2) The 5' end of the probe cannot be a G base, and the degraded G still has the effect of quenching reporter fluorescence; 3) The G in the probe cannot be more than C; 4) Avoid Single nucleotides in strings, especially G; 5) AT-rich sequences shou...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com