Method of recovering molybdenum and cobalt from waste cobalt-molybdenum catalyst
A catalyst and catalyst quality technology, applied in the field of recovering precious metals, can solve the problems of unsuitable popularization and application, high labor intensity, incomplete separation, etc., and achieve the effects of favorable cost control, improved recovery rate and low price
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
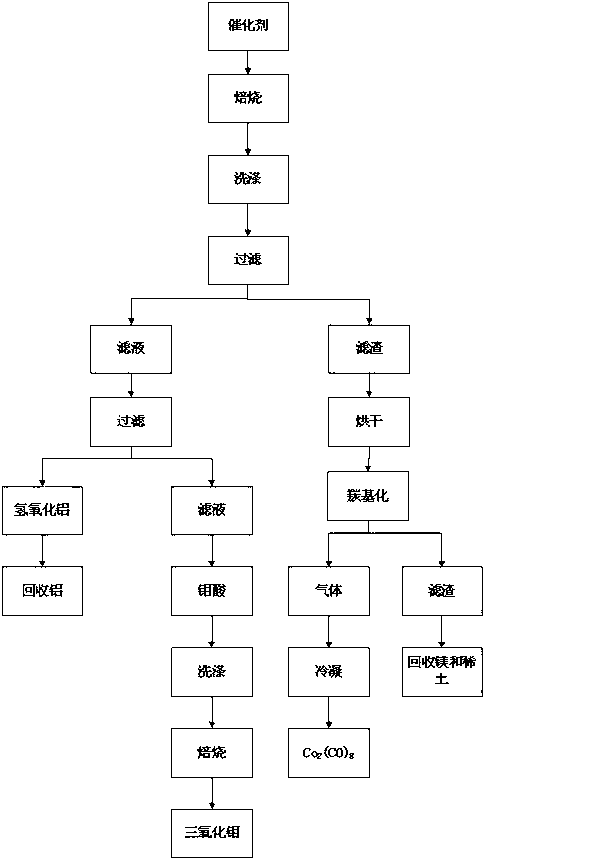
[0031] The method for reclaiming molybdenum and cobalt by the waste cobalt-molybdenum series catalyst described in the application of the present invention comprises the following steps
[0032] 1. Add sodium hydroxide to the spent cobalt-molybdenum-based catalyst at a temperature of 800 °C and roast for 1 hour. The mass ratio of the spent cobalt-molybdenum-based catalyst to the added alkali is 1:5;
[0033] 2. Then wash the roasted product with hot water at 99 ℃, the washing solid-liquid mass ratio is 1:6, the washing time is 1 hour, and then filter;
[0034] 3. Add sulfuric acid to the filtrate to adjust and maintain pH = 6. The reaction temperature is 99 ℃, react for 1 hour, and then filter the solution after the reaction. The filter residue is aluminum hydroxide, and the filtrate is a molybdenum-containing solution. The molybdenum-containing filtrate is adjusted with acid and maintained. pH=2, react at a temperature of 99 °C for 1 hour to obtain molybdic acid precipitation...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Another embodiment of the method described in the application of the present invention adopts the following methods and steps:
[0039] 1. Add sodium carbonate to the spent cobalt-molybdenum-based catalyst at a temperature of 300 °C and roast for 3 hours. The mass ratio of the spent cobalt-molybdenum-based catalyst to the added alkali is 1:3;
[0040]2. Then wash the roasted product with hot water at 60 ℃, the washing solid-liquid mass ratio is 1:2, the washing time is 3 hours, and then filter;
[0041] 3. Add nitric acid to the filtrate to adjust and maintain pH = 8. Reaction temperature is 60 ℃, react for 3 hours, and then filter the solution after reaction. The filter residue is aluminum hydroxide, and the filtrate is molybdenum-containing solution. The molybdenum-containing filtrate is adjusted with acid and maintained pH=0.5, react at a temperature of 60°C for 3 hours to obtain molybdic acid precipitation;
[0042] 4. Wash the obtained molybdic acid precipitate wi...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The method for reclaiming molybdenum-cobalt by the waste cobalt-molybdenum series catalyst described in the application of the present invention adopts the following steps:
[0047] 1. Add calcium hydroxide to the waste cobalt-molybdenum catalyst for roasting at a temperature of 500 °C. The roasting time is 2 hours. The mass ratio of the waste cobalt-molybdenum catalyst to the added alkali is 1:4;
[0048] 2. Then wash the roasted product with hot water at 75 ℃, the washing solid-liquid mass ratio is 1:4, the washing time is 2 hours, and then filter;
[0049] 3. Add hydrochloric acid to the filtrate to adjust and maintain pH = 7. The reaction temperature is 80 ℃, react for 2 hours, and then filter the solution after the reaction. The filter residue is aluminum hydroxide, which is used to recover aluminum. The filtrate is a molybdenum-containing solution, and the molybdenum-containing filtrate Use acid to adjust and maintain pH = 1, react at a temperature of 70 ° C for 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com