Microfluid extraction method for extracting and separating In, Fe and Zn
A microfluidic and extraction technology, applied in the microfluidic field, can solve the problems of difficult separation of impurities, low extraction efficiency, easy emulsification of the solution, etc., and achieve the effect of strong controllability of conditions, high recovery efficiency, and efficient separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
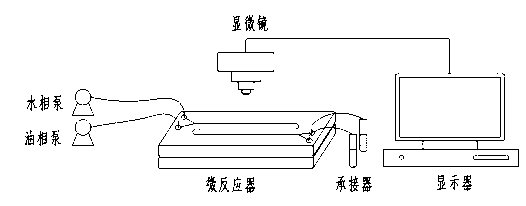
[0036] (1) The sulfuric acid system solution containing 4.52g / L indium, iron, and zinc (leaching solution in the process of hydrometallurgy of zinc) is used as the water phase, and the P204 extraction agent diluted with No. 260 solvent oil (30% volume fraction P204+70 %volume fraction solvent oil) as the organic phase respectively into the two flow pumps, the outlet end of the flow pump is connected to the inlet of the microreactor;
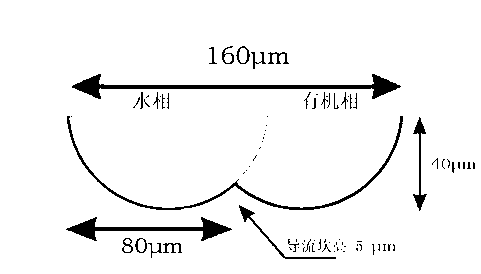
[0037] (2) Turn on the organic phase flow pump first, and after the organic phase enters the microchannel of the microreactor (with a characteristic size of 160 μm and a length of 380 mm), set and turn on the water phase flow pump at 0.65 times the flow rate of the organic phase, and at the same time The two-phase laminar flow interface formed in the microchannel is observed through an optical microscope (observation with a microscope can see that the water phase and the organic phase are moving in parallel from left to right in the microchannel, ...
Embodiment 2
[0040](1) The sulfuric acid system solution containing 3.17g / L of indium, 3.42g / L of iron, and 52.82g / L of zinc (leaching solution in the process of hydrometallurgy of zinc) is used as the water phase, P204 extractant diluted with conventional solvent oil ( 30% volume fraction P204+70% volume fraction solvent oil) as the organic phase respectively passed into two flow pumps, and the outlet end of the flow pump was connected to the inlet of the microreactor;
[0041] (2) Turn on the flow pump of the organic phase first, and after the organic phase enters the microchannel of the microreactor (with a characteristic size of 200 μm and a length of 80 mm), set the flow rate of the organic phase to 0.65 times and turn on the flow pump of the water phase, and at the same time The two-phase laminar flow interface formed in the microchannel is observed through an optical microscope (observation with a microscope can see that the water phase and the organic phase are moving in parallel fr...
Embodiment 3
[0044] (1) The sulfuric acid system solution containing 4.12g / L indium, iron and zinc (leaching solution in the process of hydrometallurgy of zinc) is used as the water phase, and the P204 extractant diluted with conventional solvent oil is used as the organic phase to pass into two flow In the pump, the outlet end of the flow pump is connected to the inlet of the microreactor;
[0045] (2) Turn on the flow pump of the organic phase first, and after the organic phase enters the microchannel of the microreactor (the characteristic size is 800 μm, the length is 90 mm), then set and turn on the flow pump of the water phase at 0.65 times the flow rate of the organic phase, and at the same time The two-phase laminar flow interface formed in the microchannel is observed through an optical microscope (observation with a microscope can see that the water phase and the organic phase are moving in parallel from left to right in the microchannel, and the two-phase laminar flow interface i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com