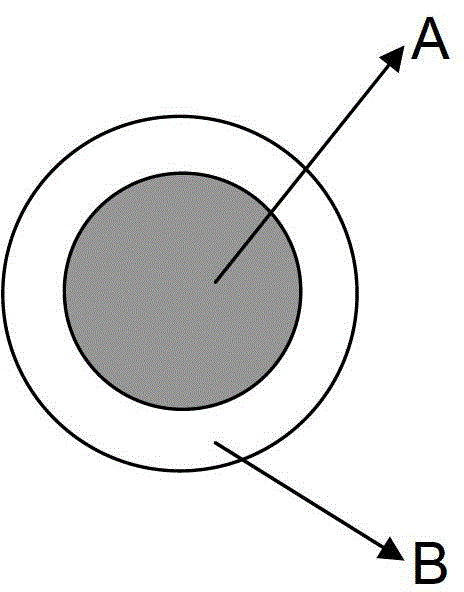
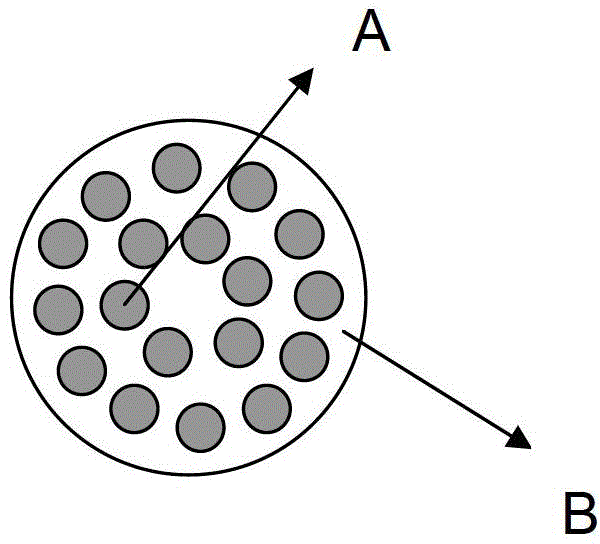
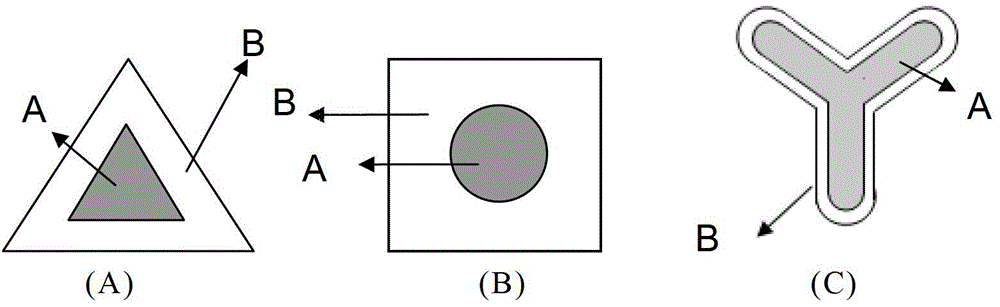
Skin core composite fiber, manufacturing method thereof and fabric
A composite fiber and manufacturing method technology, applied in the fiber field, can solve the problems of high polyester limit viscosity, complicated engineering, damage to fabric touch, etc., and achieve the effect of low modulus and good spinnability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Take polyamide 6 as a skin layer component with a relative viscosity RV of 2.8 and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) as a core layer component with an intrinsic viscosity IV of 0.5dl / g, and carry out in a compound ratio of 50:50 Metering, the polymer is diverted and melted and extruded through an extruder with a core-shaped cross-section spinning nozzle. At this time, the spinning temperature is controlled at 285°C, and then the cooling wind speed is 0.5m / s, and the cooling wind temperature is 18°C. Cooling and solidification, oiling, and spinning and coiling at a spinning speed of 4000m / min, a stretching temperature of 85°C, a setting temperature of 150°C, and a draw ratio of 2.35 to obtain 75d / 36f fibers. The fiber breaking strength was obtained through measurement 1.8g / d, fiber elongation at break 35% and Mod0~5% is 24g / d (see Table 1).
Embodiment 2
[0069] The cationic dyeable polyester (CDP, which is polyethylene terephthalate containing 1.5 % of 5-sodium sulfonate-1,3-isophthalic acid), measured in a composite ratio of 50:50, the polymer is diverted and melted and extruded through an extruder with a core-shaped cross-section spinning nozzle At this time, the spinning temperature is controlled at 275°C, and then cooled and solidified by cooling wind speed of 0.5m / s and cooling wind temperature of 18°C, oiled, and then spinning speed is 4000m / min, stretching temperature is 85°C, and setting temperature is 150°C. ℃ and draw ratio 2.05 for spinning and coiling to obtain 75d / 36f fibers, the fiber breaking strength is 1.6g / d, the fiber breaking elongation is 35% and Mod0~5% is 19g / d (such as Table 1).
Embodiment 3
[0071] Get the polyamide 6 as skin layer component that relative viscosity RV is 2.8 and the polytrimethylene terephthalate (PTT) as core layer component that intrinsic viscosity IV is 0.7dl / g, measure with compound ratio 50:50 mode, The polymer is diverted and melted and extruded through an extruder with a core-shaped cross-section spinning nozzle. At this time, the spinning temperature is controlled at 270°C, and then cooled and solidified by a cooling wind speed of 0.5m / s and a cooling wind temperature of 18°C. , oiled, and then spinning and coiling at a spinning speed of 4000m / min, a stretching temperature of 80°C, a setting temperature of 140°C, and a draw ratio of 1.95 to obtain a fiber of 75d / 36f. It is known through measurement that the fiber breaking strength 2.0g / d, fiber elongation at break 35% and Mod0~5% are 22.6g / d (see Table 1).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com