Anti-displacement pulmonary valve stent
A pulmonary artery and valve technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as stent displacement and other problems that are not well solved, and achieve the effects of avoiding blood vessel tearing, avoiding displacement, and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
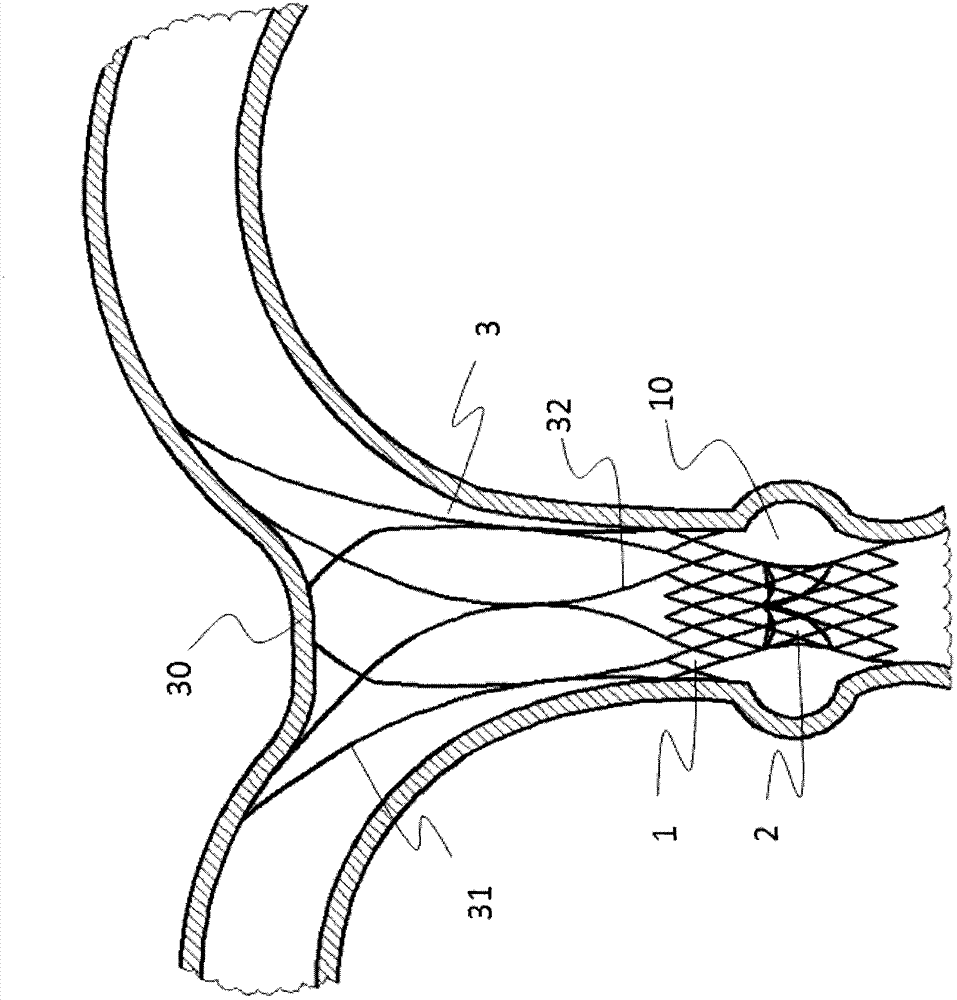
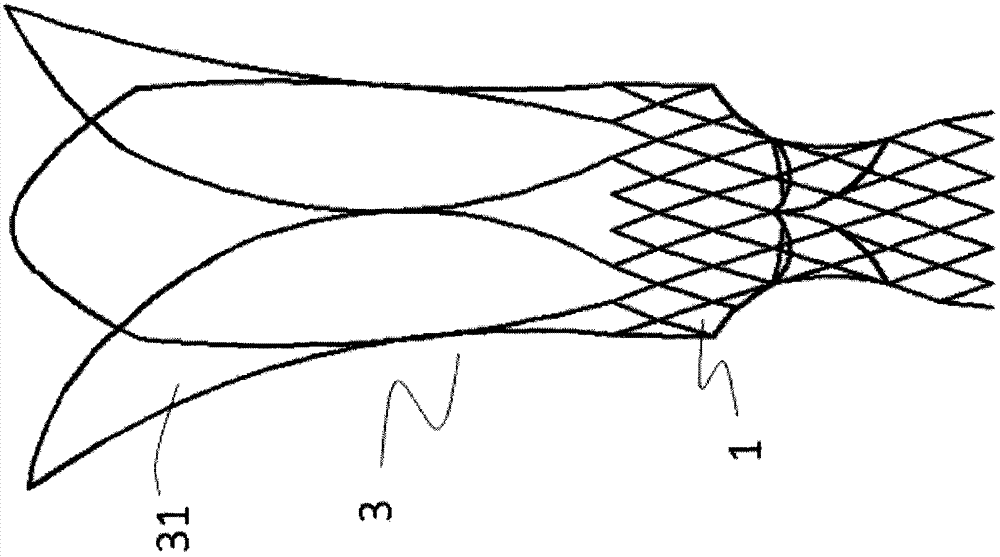
[0047] Such as figure 1As shown, a displacement-preventing pulmonary valve stent includes a valve sewing section 1 and an artificial valve 2, the artificial valve 2 is connected to the valve sewing section 1, and the valve sewing section 1 When released, it is located on the right ventricular outflow tract or the main pulmonary artery 10. The valve stent also includes a limiting mechanism 3, and the bottom part 32 of the limiting mechanism 3 is connected to the distal end of the valve sewing section 1. Connected, the top part 31 of the limiting mechanism 3 is released and interferes with the intersection 30 of the main pulmonary artery and its branches, providing an axial limiting function.
[0048] The top portion 31 of the limiting mechanism is a self-expanding stent made of shape-memory material or elastic material, more preferably nickel-titanium shape-memory alloy. As a preferred embodiment, such as Figure 2a with 2b As shown, the top portion 31 of the limiting mechan...
specific Embodiment 2
[0051] A displacement-preventing pulmonary valve stent, comprising a valve sewing section 1 and an artificial valve 2, the artificial valve 2 is connected to the valve sewing section 1, and the valve sewing section 1 is positioned at On the right ventricular outflow tract or the main pulmonary artery 10, the valve stent also includes a limiting mechanism 3, the bottom part 32 of the limiting mechanism 3 is connected to the distal end of the valve sewing section 1, and the After the top part 31 of the limiting mechanism 3 is released, it interferes with the junction 30 of the main trunk and branches of the pulmonary artery, providing an axial limiting function.
[0052] The top part 31 of the limiting mechanism is a self-expanding stent made of shape-memory material or elastic material, preferably nickel-titanium shape-memory alloy. As a preferred embodiment, such as Figure 8 As shown, the self-expanding stent is a bowl-shaped mesh stent 6, so that it softly touches the inner...
specific Embodiment 3
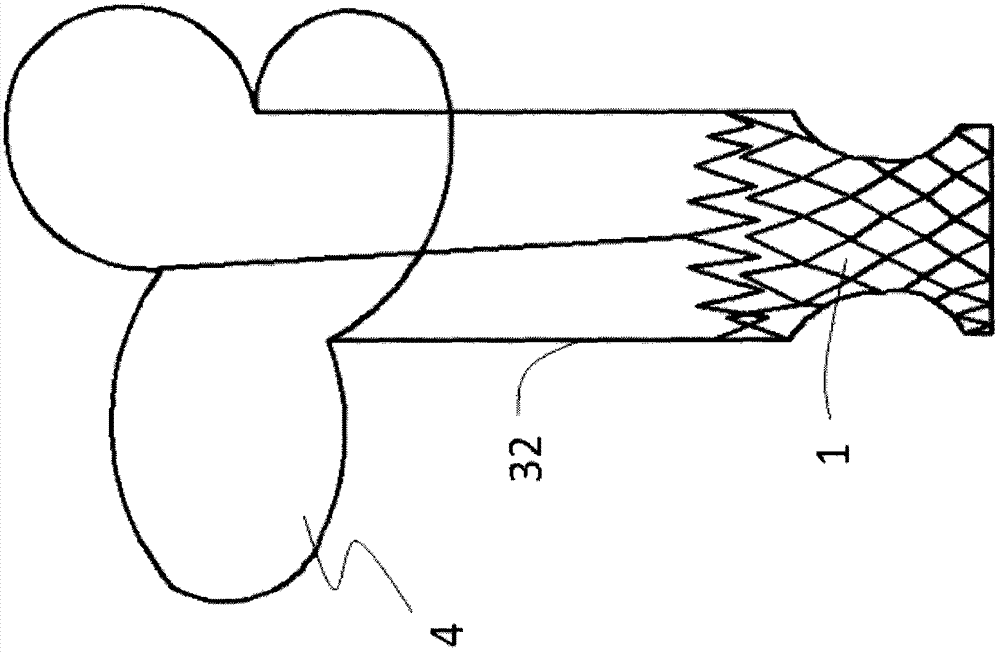
[0060] The difference between this embodiment and the specific embodiment 2 is that the top part 31 of the limiting mechanism is an air-filled or liquid-filled balloon 7, and the balloon is flat to avoid blocking the branch vessels of the pulmonary artery after collision. Such as Figure 9 As shown, the balloon 7 is provided with an inflatable or liquid-filled valve 72, which inflates the balloon 7 to act as a buffer and limiter, preventing the top of the limiter 3 from damaging the vessel wall. In addition, the connecting member 5 is a continuation of the skeleton of the leaflet 41 of the petal-shaped stent 4 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com